

Recent Advances in the Synthesis, Structural Characterization, and Reactivity of Zero-Valent Main Group Compounds★
★ For the VSI “Rising Stars in Chemistry”.
Received date: 2025-08-06
Online published: 2025-10-11
Supported by
National Key R&D Program of China(2023YFF0723900)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22071124)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22371130)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(223B2109)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22188101)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22221002)
Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter at Nankai University(C029215001)
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(63206007)
Nankai University.
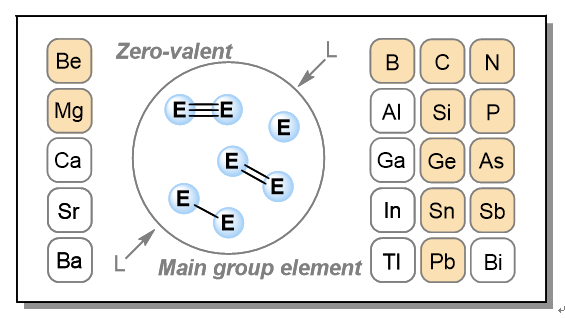
Zero-valent main group elements give rise to a diverse array of allotropes through various bonding modes, such as covalent network bonding, molecular aggregation and polymeric chain formation. This structural diversity not only reflects the intrinsic bonding flexibility of these elements but also showcases their significant application potential in synthetic chemistry and the development of advanced new materials. In recent years, with the rapid advancement of main group element chemistry, ligand-stabilized low-valent main group element compounds have garnered increasing attention. Compounds containing zero-valent main group elements feature electron-rich main group element centers and exhibit extremely high reactivity, making their stable existence difficult to achieve for a long time. With the design and development of novel ligands for low-valent main group elements, a series of groundbreaking zero-valent main group element compounds have been successfully synthesized and characterized. Among these, ligand-stabilized mono- and dinuclear zero-valent main group element compounds exhibit unique electronic structures, and their isolation and characterization enhance our understanding of the bonding mechanisms associated with zero-valent main group elements. Since the differences in the electronic properties of ligands significantly affect the bonding modes between zero-valent element atoms and ligands, such compounds usually exhibit unique electronic structural characteristics and a rich variety of chemical reactivities. Furthermore, their excellent solub ility in common organic solvents greatly broadens their applications in homogeneous synthetic chemistry. Additionally, due to the unusual oxidation states of the central elements, zero-valent main group element compounds show promise in small molecule activation. This review mainly summarizes the synthesis of zero-valent compounds of elements from Group 13 to 15 in the p-block of the periodic table as well as a few alkaline earth metal elements in the s-block. The article elaborates on their isolation, electronic structures and bonding modes, and unique chemical reaction properties while addressing the challenges they face in this field and outlining future development directions.
Ming Chen , Zhenbo Mo . Recent Advances in the Synthesis, Structural Characterization, and Reactivity of Zero-Valent Main Group Compounds★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025 , 83(12) : 1576 -1591 . DOI: 10.6023/A25080274
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |