

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
Investigation on Coupling Reaction Mechanism from N-(2-Bromophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide and Terminal Alkyne to Indol Catalyzed by CuI
Received date: 2013-03-08
Revised date: 2013-05-03
Online published: 2013-06-21
Supported by
Project supported by the Department of Education of Sichuan Province (No. 13ZA0150).
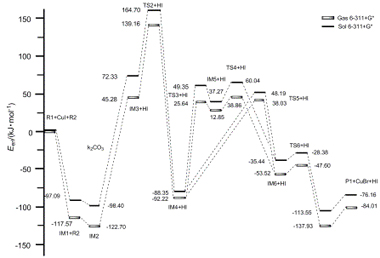
The reaction mechanism of N-(2-bromophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide and terminal alkyne catalyzed by CuI has been investigated by using density functional theory. The geometries of the reactants, transition states, intermediates and products have been optimized completely at B3LY P/6-31+G* level with the validation of the vibration analysis and the energy calculation. Atoms in molecules (AIM) theories and nature bond orbital (NBO) have been applied to discuss the orbits interaction and the bond natures. Catalytic mechanism is also interpreted by frontier orbital theory. Two possible reaction paths IA and IB were obtained. The results indicated that IA is the really main possible path of the reaction. Meanwhile, the single point energy of the reaction process in gas and solvent at 6-311+G* level has been individually investigated with higher precision. The results indicate that the reaction mechanism and the change trend of correspondence energy at two different levels are consistent. The final result of the our theory study agrees with the experimental data, and it illustrate that CuI is an effective catalyst in this reaction.
Zhang Ming , Wang Lingling , Li Laicai , Tian Anmin . Investigation on Coupling Reaction Mechanism from N-(2-Bromophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide and Terminal Alkyne to Indol Catalyzed by CuI[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2013 , 33(10) : 2169 -2177 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201303011
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |