

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
Functionalized Graphene Oxide as a Nanocarrier for Loading and Delivering of Eriocalyxin B
Received date: 2013-06-07
Revised date: 2013-06-18
Online published: 2013-06-25
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31100549, 21204098), the Shanghai Scientific and Technological Innovation Project (No. 10431903000) and the National Special Fund for State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering (No. 2060204).
Graphene oxide (GO) was firstly prepared by modified Hummers method. In order to improve its water solubility and biocompatibility, 6-arm PEG was grafted to GO via a facile amidation reaction. The size of obtained GO-PEG was less than 250 nm. Stability test indicated the good dispersibility of GO-PEG in water and PBS buffer. Furthermore, eriocalyxin B, a widely used cancer chemotherapy drug, is adsorbed onto GO-PEG via physical blending with a drug loading ratio of 18.8% obtained by UV spectrum. Lung cancer cell A549 and breast cancer cell MCF-7 were selected to study the cytotoxicity of GO-PEG/eriocalyxin B, GO-PEG, and free eriocalyxin B. The results demonstrated that GO-PEG nano-carrier possessed low toxicity (relative cell viability>85%), even cultivated for 48 h at a relatively high concentration of 100 mg/L. Compared to pure drug, GO-PEG/eriocalyxin B nanocarrier shows higher cytotoxicity in A549 and MCF-7 cells.
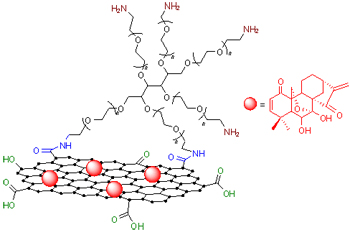
Key words: graphene oxide; eriocalyxin B; drug delivery; cell viability
Xu Zhiyuan , Li Yongjun , Shi Ping , Wang Bochan , Huang Xiaoyu . Functionalized Graphene Oxide as a Nanocarrier for Loading and Delivering of Eriocalyxin B[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2013 , 33(10) : 2162 -2168 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201306011
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |