

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
Design, Synthesis and Hypoglycemic Activity of Cyclopropane-Bearing C-Glucosides as Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors
Received date: 2015-08-05
Revised date: 2015-11-01
Online published: 2015-11-06
Supported by
Project supported by the Scientific Research Projects of Shaanxi Education Department (No. 15JK1203), the National Natural Science Fundation of China (No. 21302141) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2015BM028).
A novel series of cyclopropane-bearing C-glucosides were designed and synthesized as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors starting from the substituted bromobenzoic acids. The reaction condition for the construction of the cyclopropane moiety was studied, and a more economical synthetic route was established. All the synthesized compounds were characterized by 1H NMR and HR-MS. In vivo evaluation of these compounds by rat urinary glucose excretion (UGE) test revealed that all the synthesized seven cyclopropane-bearing C-glucosides 1a~1g exhibited potent hypoglycemic activity, among which (1S)-1-deoxy-1-{4-chloro-3-[1-(4-ethoxyphenyl)cyclopropyl-1-yl]-phenyl}-D-glucopyranose (1e) was the most potent one but still exhibited lower hypoglycemic activity to dapagliflozin, demonstrating that the cyclopropane moiety can not be well tolerated in dapagliflozin molecule and the position of the Cl atom in dapagliflozin is the best among the analogues.
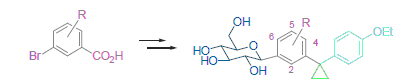
Key words: cyclopropane; C-glucoside; SGLT2 inhibitor; synthesis; hypoglycemic activity
Shi Yongheng , Zhou Chunmei , Zhang Panlong , Liu Jiping , Zhao Guilong , Wang Yuli . Design, Synthesis and Hypoglycemic Activity of Cyclopropane-Bearing C-Glucosides as Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2016 , 36(3) : 604 -612 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201508003
[1] Katsuno, K.; Fujimori, Y.; Takemura, Y.; Sergliflozin, J. Pharmaco. Exp. Ther. 2007, 320(1), 323.
[2] Washburn, W. N. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1785.
[3] Meng, M.; Ellsworth, B. A.; Nirschl, A. A.; McCann, P. J.; Patel, M.; Girotra, R. N.; Wu, G.; Sher, P. M.; Morrison, E. P.; Biller, S. A.; Zahler, R.; Deshpande, P. P.; Pullockaran, A.; Hagan, D. L.; Morgan, N.; Taylor, J. R.; Obermeier, M. T.; Humphreys, W. G.; Khanna, A.; Discenza, L.; Robertson, J. M.; Wang, A.; Han, S.; Wetterau, J. R.; Janovitz, E. B.; Flint, O. P.; Whaley, J. M.; Washburn, W. N. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1145.
[4] Nomura, S.; Sakamaki, S.; Hongu, M. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53(17), 6355.
[5] Himmelsbach, F.; Eckhardt, M.; Eickelmann, P.; Barsoumian, E. L.; Thomas, L. WO 2005092877, 2005 [Chem. Abstr. 2005, 143, 286629].
[6] Mascitti, V.; Maurer. T. S.; Robinson, R. P.; Bian, J. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54(8), 2952.
[7] Shi, Y. H.; Zhao, G. L.; Liu, W.; Shao, H.; Tang, L. D.; Wang, Y. L.; Xu, W. R. Chin. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 21, 57 (in Chinese). (史永恒, 赵桂龙, 刘巍, 邵华, 汤立达, 王玉丽, 徐为人, 中国药物化学杂志, 2011, 21, 57.)
[8] Shi, Y. H.; Zhao, G. L.; Lou, Y. Y.; Wang, Y. L.; Shao, H.; Liu, W.; Xu, W. R.; Tang, L. D. Chin. J. Chem. 2011, 29, 1192.
[9] Zhao, W. J.; Shi, Y. H.; Zhao, G. L.; Wang, Y. L.; Shao, H.; Tang, L. D.; Wang, J. W. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2011, 22, 1215.
[10] Shao, H.; Gao, Y. L.; Lou, Y. Y.; Wang, Y. L.; Liu, W.; Xu, W. R.; Wang, J. W.; Zhao, G. L.; Tang, L. D. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 31, 836 (in Chinese). (邵华, 高云龙, 楼袁媛, 王玉丽, 刘巍, 徐为人, 王建武, 赵桂龙, 汤立达, 有机化学, 2011, 31, 836.)
[11] Cai, W. Q.; Jiang, L. L.; Xie, Y. F.; Liu, Y. Q.; Liu, W.; Zhao, G. L. Med. Chem. 2015, 11(4), 317.
[12] Lorenz, J. C.; Long, J.; Yang, Z.; Xue, S.; Xie, Y.; Shi, Y. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 327.
[13] Hirabayashi, K.; Mori, A.; Hiyama, T. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 461.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |