

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
A Method for the Synthesis of the Isorhapontigenin and the Stilbene Compounds in Similar Structures
Received date: 2015-08-27
Revised date: 2015-10-31
Online published: 2015-11-16
Supported by
Project supported by the Award for Innovative Talents in Chengdu High-tech Zone.
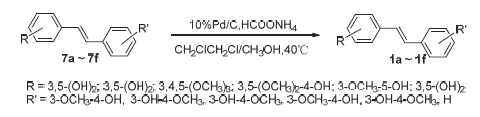
A method for the synthesis of the isorhapontigenin and the stilbene compounds in similar structures was developed. Using 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid as starting material, benzyl protecting the phenolic hydroxyl, via the Wittig-Horner reaction to construct the trans stilbene structure, and then debenzylation under the palladium on carbon/ammonium formate system condition, the isorhapontigenin could be obtained in the yield of up to 48%. The catalytic system was successfully applied in the synthesis of a series of hydroxyl stilbene compounds, which could achieve good results. All the reactions worked under mild conditions and obtained in good yield. Furthermore the materials were of cheap and less toxicity. It provided us a simple way to synthesize hydroxyl stilbene compounds in large scale.
Zhao Jianyang , Zheng Zihua , Huang Qingfei , Deng Jingen , Zhu Jin , Wang Qiwei . A Method for the Synthesis of the Isorhapontigenin and the Stilbene Compounds in Similar Structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2016 , 36(3) : 648 -652 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201508027
[1] Wang, Q. L.; Lin, M.; Liu, G. T. Chin. Pharm. J. 2001, 36, 810 (in Chinese). (王庆利, 林茂, 刘耕陶, 中国药学杂志, 2001, 36, 810.)
[2] Iliya, I.; Ali, Z.; Tanaka, T.; Iinuma, M.; Furusawa, M.; Nakaya, K.-I.; Murata, J.; Darnaedi, D.; Matsuura, N.; Ubukata, M. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 601.
[3] Matsuda, H.; Tewtrakul, S.; Morikawa, T.; Yoshikawa, M. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 4871.
[4] Li, H.-L.; Wang, A.-B.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.-P.; Wei, C.; Williams, G. M. Free Radical Biology Med. 2005, 38, 243.
[5] Liu, A.-L.; Yang, F.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, D.; Lin, M.; Lee, S. M.-Y. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1874.
[6] Fang,Y.; Hou, Q.; Pang, H.-M. Chin. Pharm. J. 2014, 49, 653 (in Chinese). (方勇, 侯琦, 潘宏铭, 中国药学杂志, 2014, 49, 653.)
[7] He, P.; Liu, Z.-M.; Liao, Z.-Y. Anat. Res. 2005, 27, 279 (in Chinese). (何平, 刘振明, 廖振裕, 解剖学研究, 2005, 27, 279.)
[8] Li, W.-L.; He, K.-K.; Li, Y.; Hou, Z.-J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2005, 63, 1607 (in Chinese). (李文玲, 何侃侃, 李瀛, 侯自杰, 化学学报, 2005, 63, 1607.)
[9] Bieg, T.; Szeja, W. Synth. Commun. 1985, 15, 76.
[10] Thakkar, K.; Geahlen, R. L.; Cushman, M. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 2950.
[11] Ranu, B. C.; Sarkar, A. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35(46), 8649.
[12] Negi, A. S.; Darokar, M.-P.; Chattapodhyay, S.-K.; Grag, A.; Bhattacharya, A.-K.; Srivastava, V.; Khanuja, S. P. S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 1243.
[13] Negi, A. S.; Chattapodhyay, S.-K.; Srivastava, S.; Bhattacharya, A.-K. Synth. Commun. 2005, 35, 15.
[14] Koolaji, N.; Abdallah, A. M.; Tran, V. H.; Duke, R. K.; Duke, C. C. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 415.
[15] Kim, D.-H.; Park, E.-K.; Bae, E.-A.; Han, M.-J. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23(7), 830.
[16] Lee, H.-S.; Lee, B.-W.; Kim, M.-R.; Jun, J.-G. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31(4), 971.
[17] Zhou, Y.; Huang, Q.; Huang, T.-K.; Ni, Q.-C.; Zhang, E.-S.; Xu, T.-L.; Yuan, M.; Li, J. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 6967.
[18] Lonsky, L.; Lonsky, W.; Kratzl, K. Monatsh. Chem. 1976, 107, 685.
[19] Cheng, J.-C.; Fang, J.-G.; Chen, W.-F.; Zhou, B.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.-L. Bioorg. Chem. 2006, 34, 142.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |