

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
Novel Coumarin-Based Fluorescent Probes for Detecting Zn2+ in Living Cells
Received date: 2015-11-10
Revised date: 2015-12-08
Online published: 2015-12-21
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21472148, 21072158), the Special Foundation of the Education Committee of Shaanxi Province (No. 12JK0580), and the Academic Back-bone of Northwest University Outstanding Youth Support Program.
Zinc ion (Zn2+) is one of the most important transition-metal ions in the human body which is involved in many important life activities and many diseases can be displayed by its situation. Thus, monitoring of Zn2+ is very meaningful to diagnosis of diseases. Compared to the traditional detection methods, fluorescence probe is safer and more practical. Because coumarin derivatives possess several advantages in optics, we choose them as key structures to prepare new fluorescent probes. Based on the mechaism of photoinduced electron transfer (PET), the water-soluble fluorescent probes 1 and 2that are coumarin-based derivatives were designed, which demonstrated sensitivity for Zn2+ and exhibited high selectivity to Zn2+ over other metal ions. The receptor unit serves as an electron donor in the absence of Zn2+, quenching the fluorophore excited state that makes the probe have no fluorescence. However, when Zn2+ binds to the receptor, photoinduced electron transfer is prevented and the quenching is blocked, resulting the fluorescence intensity significantly enhanced. There is a good correlation between fluorescence intensity and Zn2+ concentration. With the increase of Zn2+ concentration, fluorescence intensity becomes stronger. Furthermore, the two probes were successfully labelled on the MCF-7 cell and B. subtilis. The single crystals of the coumarin-based compounds 1~4 and zinc complex [Zn(2)] were also obtained. The X-ray crystal structure of the zinc complex [Zn(2)] reveals that the hydroxyl group and the 2,2-dipicolylaminomethyl group participate in coordination. Zn2+ is five-coordinated with three nitrogen atoms from the pyridine rings, the substituted amino group and two oxygen atoms from the 7-site hydroxyl group, also coordinated with water molecule forming a pentacoordinated bipyramid geometry.
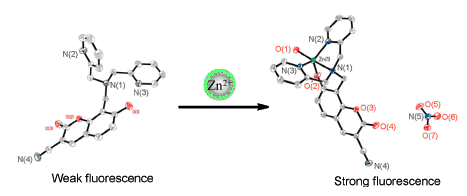
Key words: coumarin; Zn2+ fluorescent probe; cell imaging
Li Changwei , Yang Dong , Yin Bing , Guo Yuan . Novel Coumarin-Based Fluorescent Probes for Detecting Zn2+ in Living Cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2016 , 36(4) : 787 -794 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201511016
[1] Xu, Z. C.; Yoon, J.; Spring, D. R. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1996.
[2] Prasad, A. S., Biochemistry of Zinc, Plenum Press, New York, 1993.
[3] Geiser, J.; Venken, K. J. T.; De Lisle, R. C.; Andrews, G. K. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002766.
[4] Thambiayya, K.; Wasserloos, K.; Kagan, V. E.; Stoyanovsky, D.; Pitt, B. R. Am. J. Physiol. 2012, 302, 1351.
[5] Maret, W.; Jacob, C.; Vallee, B. L.; Fischer, E. H. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1999, 96, 1936.
[6] (a)Nikseresht, S.; Etebary, S.; Karimian, M.; Nabavizadeh, F.; Zarrindast, M. R.; Sadeghipour, H. R. Arch. Iran. Med. 2012, 15, 306.
(b) Morris, D. R.; Levenson, C. W. J. Toxicol. 2012, 785647.
[7] Fraustoda Silva, J. J. R.; Williams, R. J. P. The Biological Chemistry of the Elements,Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1991, p. 561.
[8] Fischer Walker, C. L.; Lamberti, L.; Roth, D.; Black, R. E. Biomed. Health Res. 2011, 76, 234.
[9] Grabrucker, A. M.; Rowan, M.; Garner, C. C. Drug Delivery Lett. 2011, 1, 13.
[10] Gower-Winter, S. D.; Levenson, C. W. BioFactors 2012, 38, 186.
[11] Bicer, M.; Gunay, M.; Baltaci, A. K.; Uney, K.; Mogulkoc, R.; Akil, M. Br. Med. J. 2012, 113, 199.
[12] Chen, X.; Yu, H. N.; Shen, S. R.; Yin, J. J. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2007, 21, 125.
[13] (a) Srichaikul, B. Adv. Nat. Sci. 2012, 5, 1.
(b) Lee, J. Y.; Cho, E.; Seo, J. W.; Hwang, J. J.; Koh, J. Y. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neur. 2012, 71, 211.
[14] (a) Jayabharathi, J.; Thanikachalam, V.; Jayamoorthy, K. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2012, 95, 143.
(b) Liu, Z. P.; Zhang, C. L.; Chen, Y. C.; He, W. J.; Guo, Z. J. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8365.
(c) Mandal, A. K.; He, T. C.; Maji, S. K.; Sun, H. D.; Zhao, Y. L. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14378.
(d) Tang, L. J.; Zheng, Z. X.; Bian, Y. J. Chem. Online 2015, 78, 388 (in Chinese). (汤立军, 郑竹轩, 边延江, 化学通报, 2015, 78, 388.)
[15] (a) Tsien, R. W.; Tsien, R. Y. Rev. Cell Biol. 1990, 6, 715.
(b) Jitendra, B.; Umesh, F.; Banashree, B.; Simanpreet, K.; Narin- der, S.; Anupam, B.; Rajesh, D.; Ratnamala, B.; Anil, K. J. Mol. Recognit. 2015, 28, 369.
(c) Liu, M.; Tan, H. L.; Liu, Z. G.; Wang, W.; Zeng, W. B. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 33, 1655 (in Chinese). (刘敏, 谭慧龙, 刘治国, 王维, 曾文彬, 有机化学, 2013, 33, 1655.)
[16] (a) Priya, C.; Sivaramapanicker, S.; Ayyappanpillai, A. Chem. Asian J. 2007, 2, 338.
(b) Nolan, E. M.; Lippard, S. J. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 193.
(c) Wong, B. A.; Friedle, S.; Lippard, S. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7142.
(d) Walkup, G. K.; Burdette, S. C.; Lippard, S. J.; Tsien, R. Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 5644.
(e) Mizukami, S.; Okada, S.; Kimura, S.; Kikuchi, K. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 7630.
(f) Song, Z. K.; Dong, B.; Lei, G. J.; Peng, M. J.; Guo, Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 4945.
[17] (a) Domaille, D. W.; Zeng, L.; Chang, C. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1194.
(b) Yang, Z.; She, M. Y.; Yin, B.; Hao, L. K.; Obst, M.; Liu, P.; Li, J. L. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 868, 53.
(c) Fan, J. L.; Xu, Q. L.; Zhu, H.; Peng, X. J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 34, 1623 (in Chinese). (樊江莉, 徐群利, 朱浩, 彭孝军, 有机化学, 2014, 34, 1623.)
[18] (a) Yuan, L.; Lin, W. Y.; Yang, Y. T.; Song, J. Z.; Wang, J. L. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 3730.
(b) Jung, H. S.; Han, J. H.; Kim, Z. H.; Kang, C. H.; Kim, J. S. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5056.
(c) Perry, C. C.; Tang, V. J.; Konigsfeld, K. M.; Aguilera, J. A.; Milligan, J. R. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 9889.
(d) Huo, F. J.; Sun, Y. Q.; Su, J.; Chao, J. B.; Zhi, H. J.; Yin, C. X. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4918.
(e) Peng, M. J.; Yang, X. F; Yin, B; Guo, Y.; Suzenet, F.; En, D.; Li, J.; Li, C. W.; Duan, Y. W. Chem. Asian J. 2014, 9, 1817.
[19] (a) Ciesienski, K. L.; Hyman, L. M.; Derisavifard, S.; Franz, K. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 6808.
(b) Park, J. E.; Choi, M. G.; Chang, S. K. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 2880.
(c) Ezeh, V. C.; Harrop, T. C. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 1213.
(d) En, D.; Guo, Y.; Chen, B. T.; Dong, B.; Peng, M. J. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 248.
(e) Hong, T.; Song, H. L.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. B.; Xie, Y. S. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 6133.
[20] (a) Wu, J. S.; Sheng, R. L.; Liu, W. M.; Wang, P. F.; Ma, J. J.; Zhang, H. Y.; Zhuang, X. Q. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 6543.
(b) Yuan, L.; Lin, W. Y.; Xie, Y. N.; Chen, B.; Zhu, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1305.
(c) Zhou, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, J. Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, T. C.; Yao, C. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1290.
(d) Choi, M. G.; Hwang, J. Y.; Moon, J. O.; Sung, J. Y.; Chang, S. K. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5260.
(e) Reddie, K. G.; Humphries, W. H.; Bain, C. P.; Payne, C. K.; Kemp, M. L.; Murthy, N. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 680.
[21] (a) Runge, E.; Gross, E. K. U. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 52, 997.
(b) Dreuw, A.; Head-Gordon, M. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 4009.
(c) Becke, A. D. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648.
(d) Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R. G. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |