

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
A New Flavone Glycoside from Liparis bootanensis
Received date: 2016-04-26
Revised date: 2016-06-24
Online published: 2016-07-13
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81274193),the Small Molecular Natural Medicine Innovation Team of Sichuan Province (No.15TD0048),the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (No.2682015YXZT03),the Project of Science and Technology Bureau of Chengdu City (No.2015-HM01-00041-SF) and the Southwest Jiaotong University Graduate Students Creative Experiment (No.YC201510104).
A new flavonoid glycoside, kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside-7-O-[6-(4-hydroxy-3-prenybenzoic ester)-β-D-glucopyranosy]-(1→2)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (1) was isolated from the aerial parts of Liparis bootanensis, together with a known compound kaempferol-3,7-di-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (2) by silica gel column and Pre-HPLC. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analysis, including HR-ESIMS, 1D and 2D NMR experiments.
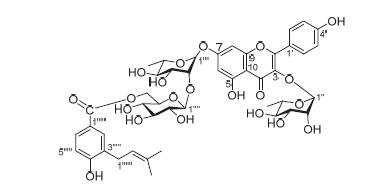
Key words: Liparis L. C. Rich; Liparis bootanensis; flavone glycoside
Wu Run , Huang Shuai , Shan Lianhai , Li Suiyan , Wei Yi , Zhou Xianli . A New Flavone Glycoside from Liparis bootanensis[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2016 , 36(11) : 2735 -2738 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201604054
[1] Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae 1999, 18, 53 (in Chinese). (中国科学院植物所, 中国医学科学院药物所, 中国植物志, 1999, 18, 53.)
[2] Zhen, Y.-Z.; Zhang, Z.-K.; Ma, H.-W.; Bo, Y.-H. China Med. Her. 2016, 13, 44 (in Chinese). (郑叶子, 张智宽, 马宏文, 卜亚恒, 中国医药导报, 2016, 13, 44.)
[3] The State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of the Chinese Herbal Medicine Editorial Board Chin. Mater. Med. 1999, 24, 734 (in Chinese). (国家中医药管理局编委会, 中华本草, 1999, 24, 734.)
[4] Fang, Z.-X.; Liao, C.-L. Flora of Enshi in Hubei Medicinal (Part ii), Hubei Science and Technology Press, Wuhan, 2006, 12, p. 721 (in Chinese). (方志先, 廖朝林, 湖北恩施药用植物志(下册), 湖北科学技术出版社, 武汉, 2006, 12, p. 721.)
[5] Li, H.-F.; Guan, X.-Y.; Yang, W.-Z.; Liu, K.-D.; Ye, M.; Sun, C.; Lu, S.; Gao, D.-A. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 44.
[6] Zhen, Y.; Li, X.-W.; Gui, M.-Y.; Jin, Y.-R. China Pharm J. 2006, 43(3), 176 (in Chinese). (郑莹, 李绪文, 桂明玉, 金永日, 中国药学杂志, 2006, 43(3), 176.)
[7] Huang, S.; Zhou, X. L.; Wang, C.-J.; Wang, Y.-S.; Xiao, F.; Shan, L. H.; Guo, Z.-Y.; Weng, J. Phytochemistry 2013, 93, 154.
[8] Pang, Y.-W.; Wang, J.-D.; Xiang, S.-W.; Liu, C.-F.; Wang, X.-J. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2012, 24, 1331 (in Chinese). (庞艳伟, 王继栋, 向文胜, 刘乾峰, 王相晶, 天然产物研究与开发. 2012, 24, 1331.)
[9] Marzouk, M. M.; Kawashty, S. A.; Saleh, N. A. M.; Al-Nowaihi, A. S. M. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2009, 45, 483.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |