

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
One Pot Solvent-Free Synthesis of Benzodiazepinones Catalyzed by CuI
Received date: 2016-11-18
Revised date: 2016-12-14
Online published: 2017-01-04
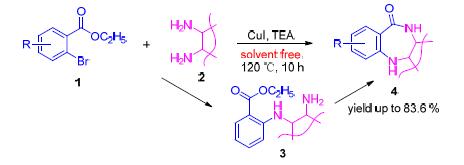
Benzodiazepinones are the important class of organic heterocyclic compounds with physiological activities. Herein, one pot procedure for the synthesis of benzodiazepinones has been developed under solvent-free condition. The substituted ethyl 2-bromobenzoates were cross-coupled with adjacent diamine compounds using CuI as a catalyst to give the intermediates, which spontaneously underwent an intramolecular N-acylation producing corresponding benzodiazepinones. This method has the advantages of enviroment frendly, mild reaction conditions, simple one pot operation and high yields. Under the optimized conditions, the effect of various substituted group on the reaction was investigated and the tolerance of this system was evaluated. This protocol could tolerate a variety of functional groups, and provide efficient access to a wide variety of substituted benzodiazepinones in good yields, including biological active molecules.
Key words: solvent-free; one pot; CuI; benzodiazepinones; catalyzed-coupling reaction
Zhang Qingyang , Wang Xiaojian , Xiao Qiong , Yin Dali . One Pot Solvent-Free Synthesis of Benzodiazepinones Catalyzed by CuI[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2017 , 37(4) : 954 -958 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201611020
[1] (a) Shen, S.-C.; Sun, X.-W.; Lin, G.-Q. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 896.
(b) DeSimone, J. M. Science 2002, 297, 799.
(c) Jeon, S. J.; Li, H.; Walsh, P. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 16416.
[2] (a) Poliakoff, M.; Anastas, P. Nature 2001, 413, 257.
(b) Gross, R. A.; Kalra, B. Science 2002, 297, 803.
(c) Wang, D.; Li, L.; Li, N.; Gao, T. T.; Hou, S. H.; Chen, B. H. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 45.
[3] (a) Singh, M. S.; Nagaraju, A.; Verma, G. K.; Shukla, G.; Verma, R. K.; Srivastava, A.; Raghuvanshi, K. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 954.
(b) Horváth, I. T. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 1024.
[4] (a) Sanchez, Y.; Wong, C.; Thoma, R. S.; Richman, R.; Wu, Z.; Piwnica-Worms, H.; Elledge, S. J. Science 1997, 277, 1497.
(b) Xiao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Gunasekera, A. H.; Sowin, T. J.; Rosenberg, S. H.; Fesik, S.; Zhang, H. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21767.
[5] Hussenether, T.; Hübner, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Troschütz, R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 2625.
[6] Misiti, D.; Gatta, F.; Landi-Vittory, R. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1971, 8, 231.
[7] (a) Cortés, E. C.; Islas, P. M.; Romero, M. O. Z. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1996, 33, 1723.
(b) Bunce, R. A.; Schammerhorn, J. E. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2006, 37, 1031.
[8] Wang, L.; Sullivan, G. M.; Hexamer, L. A.; Hasvold, L. A.; Thalji, R.; Przytulinska, M.; Tao, Z. F.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Gu, W. Z.; Xue, J.; Bui, M. H.; Merta, P.; Kovar, P.; Bouska, J. J.; Zhang, H.; Park, C.; Stewart, K. D.; Sham, H. L.; Sowin, T. J.; Rosenberg, S. H.; Lin, N. H. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 4162.
[9] (a) Liu, Y.-Y.; Wan, J.-P. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 6873.
(b) Liu, Y.-Y.; Wan, J.-P. Chem. Asian J. 2012, 7, 1488.
[10] Klapars, A.; Parris, S.; Anderson, K. W.; Buchwald, S. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 3529.
[11] Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Ma, D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16050.
[12] Zhang, Q. Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Tian, Y.-L.; Qi, J.-G.; Li, C.; Yin, D.-L. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2013, 24, 825.
[13] Binaschi, M.; Boldetti, A.; Gianni, M.; Maggi, C. A.; Gensini, M.; Bigioni, M.; Parlani, M.; Giolitti, A.; Fratelli, M.; Valli, C.; Mineko, T.; Garattini, E. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 411.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |