

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
Structural Properties of Ethyl 5-Phenyl-2-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate and Chromo Genic Responses of Its Rhodamine B Derivatives to Hg2+ Ions
Received date: 2017-09-01
Revised date: 2017-11-11
Online published: 2017-12-08
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21562019), the Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province (No. 20162027), the Hainan Province Natural Science Foundation of Innovative Research Team Project (No. 2016CXTD007) and the Program of Hainan Association for Science and Technology Plans to Youth R & D Innovation (No. HAST201621).
Ethyl 5-phenyl-2-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate (EPFC), a newly synthesized compound, is used to study its structural properties and explore as a fluorescent probe for metal ions. EPFC was investigated in terms of structural, fluorescence spectroscopic, UV-Vis spectroscopic and theoretical analysis by using HF/6-31G(d), CIS/6-31G(d) and B3LYP/6-31G(d) methods, respectively. The corresponding product was characterized by NMR and HRESIMS methods. The interactions of the compound with 15 kinds of metal ions (Pb2+, Mn2+, K+, Na+, Ag+, Ca2+, Cd2+, Co2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Hg2+, Li+ and Mg2+) were investigated by UV absorption spectroscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy. The quantum chemical values suggested that it is easy for EPFC to lose electron with weak electron accepting ability by frontier molecular orbital analysis. The calculated spectra were complimented with experimental measurements in great degree. In addition, a novel rhodamine B derivative containing 1,2,3-triazole unit, and REPFC was successfully designed and synthesized by the reaction between rhodamine B and EPFC. REPFC displayed more selectivity response to Hg2+ ion than other metal ions in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF)-H2O (V/V=1/1, pH 7.4) within a REPFC concentration range of 2.67×10-5~4.67×10-5 mol·L-1 with an fluorescent enhancement and a rapid chemical reaction. The triazole appended colorless chemosensor turns to pink upon complex formation only with Hg2+ions even in the presence of other common metal ions and enables naked-eye detection. The coordination mechanism and turn on/off fluorescence for Hg2+ ions were well proposed by explaining Hg2+ inducing the ring-opened rhodamine B moiety. This study was an advancement for the application of 1,2,3-triazole compound and provides guidance for using simple and high-selectivity Hg2+ probes in aqueous solutions under physiological conditions.
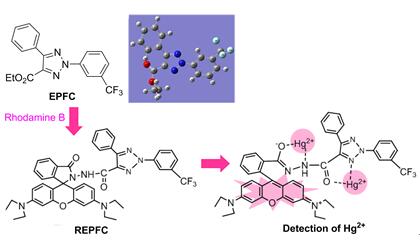
Li Jianling , Ding Guohua , Niu Yanyan , Wu Luyong , Duan Hongye , Feng Huajie , He Wenying . Structural Properties of Ethyl 5-Phenyl-2-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate and Chromo Genic Responses of Its Rhodamine B Derivatives to Hg2+ Ions[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2018 , 38(4) : 931 -939 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201709001
[1] Tornøe, C. W.; Christensen, C.; Meldal, M. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 3057.
[2] Totobenazara, J.; Burke, A. J. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 2853.
[3] El-Sayed, N. N. E.; Abdelaziz, M. A.; Wardakhan, W. W.; Mohareb, R. M. Steroids 2016, 107, 98.
[4] Zhao, B. T.; Tao, J. J.; Chen, X. J.; Zhu, W. M. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 37, 1964(in Chinese). (赵邦屯, 陶晶晶, 陈小纪, 朱卫民, 有机化学, 2017, 37, 1964.)
[5] Aromi, G.; Barrios, L. A.; Roubeau, O.; Gamez, P. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 485.
[6] Maisonial, A.; Serafin, P.; Traikia, M.; Debiton, E.; Thery, V.; Aitken, D. J.; Lemoine, P.; Viossat, B.; Gautier, A. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 2, 298.
[7] Gutknecht, J. J. Membr. Biol. 1981, 61, 61.
[8] Han, Z. X.; Zhu, B. S.; Wu, T. L.; Yang, Q. Q.; Xue, Y. L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X. Y. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 73.
[9] Li, X. M.; Zhao, R. R.; Wei, Y. L.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Z. J.; Zhang, J. F.; Zhou, Y. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 813.
[10] Xiao, H. F.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Han, Z. X.; Yang, L. Q.; Wu, X. Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 2413(in Chinese). (肖慧丰, 张敏, 刘杰, 韩志湘, 仰榴青, 吴向阳, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 2413.)
[11] Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Han, Y. F. Sensor Actuators, B 2016, 237, 1.
[12] Jeong, Y. S.; Yoon, J. Y. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 381, 2.
[13] Wechakorna, K.; Suksenc, K.; Piyachaturawat, P.; Kongsaeree, P. Sensor Actuators, B 2016, 228, 27.
[14] Erdemir, S.; Malkondu, S. J. Lumin. 2015, 158, 401.
[15] Erdemir, S.; Kocyigit, O.; Malkondu, S. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 2015, 309, 15.
[16] Shen, B. X.; Qian. Y. Sens. Actuators, B 2017, 239, 226.
[17] Lv, Y. L.; Zhu, L. L.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y. S.; Chen, Z. L.; Fu, H. B.; Tian, Z. Y. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 839, 74.
[18] Wang, H.; Chen, B. B.; Zhu, S. Q. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 796.
[19] Amiri, N.; Rofouei, M. K.; Ghasemi, J. B. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 1111.
[20] Lee, S.; Rao, B. A.; Son, Y. A. Sens. Actuators, B 2015, 210, 519.
[21] Jadhav, S.; Bakker, E. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 80.
[22] Wu, L. Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, X. H.; Guo, Z. F.; Yao, G. G.; Lin, Q.; Wu, M. S. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 2145.
[23] Anusuya, N.; Sounthari, P.; Saranya, J.; Paramswar, K.; Chitra, S. Orient. J. Chem. 2015, 31, 1741.
[24] Zhan, D. L.; Gao, N.; Han, W. W.; Feng, Y. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2014, (1), 146(in Chinese). (詹冬玲, 高楠, 韩葳葳, 冯雁, 高等学校化学学报, 2014, (1), 146.)
[25] Li, X. H.; Cui, H. L.; Zhang, R. Z.; Zhang, X. Z. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2015,137, 321
[26] Kurtz, H. A.; Stewart, J. J. P.; Dieter, K. M. J. Comput. Chem. 1990, 11, 82.
[27] Zhu, M. H.; Hu, P. Instrumental Analysis, 4th ed., Higher Education Press, Beijing, 2008, pp. 335~345(in Chinese). (朱明华, 胡坪, 仪器分析, 第四版,高等教育出版社, 北京, 2008, pp. 335~345.)
[28] Xu, J. G.; Wang, Z. B. Fluorescence Analysis, 3rd ed., Science Press, Beijing, 2006, pp. 53~56(in Chinese). (许金钩, 王尊本, 荧光分析法, 第三版, 科学出版社, 北京, 2006, pp. 53~56.)
[29] Chen, W. Q.; Jin, G. Y. Chin. J. Appl. Chem. 2000, 17, 479(in Chinese). (陈卫强, 金桂玉, 应用化学, 2000, 17, 479.)
[30] SaSaki, H.; Hanaoka, K.; Urano, Y.; Teral, T.; Nagano, T. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 1072.
[31] Jiang, C. C.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y. X.; Tang, X. N.; Zhang, Y. M.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Wang, J. Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 2560.
[32] Zhang, X. B.; Gong, Y. J.; Su, L.; Mao, G. J. J. Nanjing Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2015, (2), 1(in Chinese). (张晓兵, 龚毅君, 苏莉, 毛国江, 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 2015, (2), 1.)
[33] Ge, F.; Ye, H.; Luo, J. Z.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y. J.; Zhao, B. X.; Miao, J. Y. Sens. Actuat. B 2013, 181, 215.
[34] Wang, X. X.; Li, X. L.; Shi, W.; Wei, S.; Giesy, J. P.; Yu, H. X.; Wang, Y. L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 89, 143.
[35] SYBYL Software, Version 6.9, St. Louis, Tripos Associates Inc, 2002.
[36] Chou, Y. C. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2015, 1069, 112.
[37] Gupta, R. C.; Razi, S. S.; Ali, R.; Dwivedi, S. K.; Srivastava, P.; Singh, P.; Koch, B.; Mishra, H.; Misra, A. Sensor Actuators, B 2017, 251, 729.
[38] Bhatta, S. R.; Bheemireddy, V.; jaykumar, G. V.; Arunabha Thakur, A. Sens. Actuators, B 2017, 240, 640.
[39] Wu, J. D.; Lu, J. R.; Liu, J. G.; Zheng, C. H.; Gao, Y. X.; Hu, J.; Ju, Y. Sens. Actuators, B 2017, 241, 931.
[40] Wang, L. Y.; Fang, G. P.; Ye, D. C.; Derong Cao, D. R. Sens. Actuators, B 2017, 195, 572.
[41] Wang, N. J.; Sun, C. M.; Chung, W. S. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 8131.
[42] Mandal, D.; Thakur, A.; Ghosh, S. Polyhedron 2013, 52, 1109.
[43] Cao, Q. Y.; Han, Y. M.; Wang, H. M.; Xie, Y. Dyes Pigm. 2013, 99, 798.
[44] Sulak, M.; Kursunlu, A. N.; Girgin, B.; Özlem Özen Karaku?, Ö. Ö.; Güler, E. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 2017, 349, 129.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |