

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
Synthesis and Anti-HIV-1 Activity of Stapled HIV-1 Fusion Inhibitors
Received date: 2017-10-25
Revised date: 2018-01-08
Online published: 2018-01-18
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21602121), the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (No. 2016BS0201) and the Doctoral Science Foundation of Baotou Medical College (No. BSJJ201620).
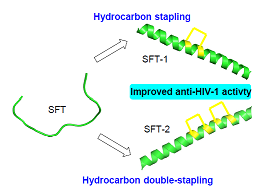
Sifuvirtide (SFT) is a potent anti-HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus-1) fusion inhibitor and it shows higher potency and pharmacokinetic stability than the approved fusion inhibitor T20. At present, sifuvirtide has completed the phase Ⅱb clinical trial in China. In this study, SFT-1 and SFT-2 were synthesized via all-hydrocarbon cross-linking system with replacing the original salt bridge in SFT by hydrocarbon covalent bond, using sifuvirtide as template. The anti-HIV-1 activity was evaluated for all synthetic peptides. The results indicated that SFT stapled peptides displayed high inhibitory activity against seven HIV-1 pseudovirus strains, and SFT-1 showed the highest inhibitory activity against B' and B'C subtype virus strains, SFT-2 showed the highest inhibitory activity against B, CRF01_AE and CRF08_BC subtype virus strains.
Guo Ye , Fu Lili , Fan Xiaowen , Shi Xuanling . Synthesis and Anti-HIV-1 Activity of Stapled HIV-1 Fusion Inhibitors[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2018 , 38(5) : 1267 -1270 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201710033
[1] Dai, S. J.; Dou, G. F.; Qiang, X. H.; Song, H. F.; Tang, Z. M.; Liu, D. S.; Liu, X. W.; Yang, L. M.; Zheng, Y. T.; Liang, Q. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 1274.
[2] He, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Song, H.; Liang, Q.; Ju, D.; Chen, X.; Lu, H.; Jing, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 11126.
[3] Tan, J. J.; Ma, X. T.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X. Y.; Wang, C. X. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1810.
[4] Tennyson, R. L.; Walker, S. N.; Ikeda, T.; Harris, R. S.; Kennan, A. J.; McNaughton, B. R. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 1945.
[5] Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, S. Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 159.
[6] Yu, F.; Lu, L.; Du, L. Y.; Zhu, X. J.; Debnath, A. K.; Jiang, S. B. Viruses 2013, 5, 127.
[7] Yao, X.; Chong, H.; Zhang, C.; Waltersperger, S.; Wang, M.; Cui, S.; He, Y. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6788.
[8] Schafmeister, C. E.; Po, J.; Verdine, G. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 5891.
[9] Wachter, F.; Morgan, A. M.; Godes, M.; Mourtada, R.; Bird, G. H.; Walensky, L. D. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2184.
[10] Bird, G. H.; Mazzola, E.; Opoku-Nsiah, K.; Lammert, M. A.; Godes, M.; Neuberg, D. S.; Walensky, L. D. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 845.
[11] Gao, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, H. Y.; Fang, G. M. Prog. Chem. 2014, 26, 100(in Chinese). (高帅, 郭叶, 李海燕, 方葛敏, 化学进展, 2014, 26, 100.)
[12] Hu, X.; He, Y.; Wu, L.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, W. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 5446.
[13] Cui, H. K.; Qing, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y. J.; Cui, L. J.; He, T. H.; Zhang, L. Q.; Liu, L. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3547.
[14] Cui, H. K.; Zhao, B.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Hu, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. G. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 581.
[15] Lau, Y. H.; de Andrade, P.; Wu, Y.; Spring, D. R. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 91.
[16] Keeling, K. L.; Cho, O.; Scanlon, D. B.; Booker, G. W.; Abell, A. D.; Wegener, K. L. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 9731
[17] Wang, D. Y.; Chen, K.; Kulp Ⅲ, J. L.; Arora, P. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9248.
[18] Fang, G. M.; Wang, J.-X.; Liu, L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10347.
[19] Fang, G. M.; Li, Y. M.; Shen, F.; Huang, Y. C.; Li, J. B.; Lin, Y.; Cui, H. K.; Liu, L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7645.
[20] Zheng, J. S.; Tang, S.; Qi, Y. K.; Wang, Z. P.; Liu, L. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2483.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |