

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
Antitumor and DNA Topoisomerase Ⅱα Inhibitory Activity of 6-Substituted-aryl-2-methoxyquinolines
Received date: 2018-06-12
Revised date: 2018-08-05
Online published: 2018-09-05
Supported by
Project supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2010CB833802), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81373304, 81502921, 90913024) and the Distinguished Young Scholars Grant (No. 30325044).
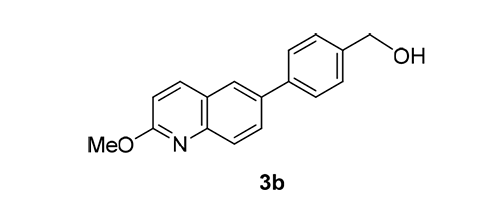
Human DNA Topoisomerase Ⅱα (Topo Ⅱα) is one of the important therapeutic targets for the treatment of cancers. Our previous study showed that p-terphenyls have inhibitory effects on Topo Ⅱα and inhibit the proliferation of human breast ductal carcinoma cells. In this study, nineteen 6-substituted aryl-2-methoxyquinolines (3a~3s) were designed, synthesized and evaluated for their cytotoxicity against the growth of human triple negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cell line and inhibitory activity against Topo Ⅱα. Among these compounds, 6-(4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl)-2-methoxyquinoline (3b) showed the most potent activity (IC50=9.9 μmol·L-1). These results have important significance for the further study of aryl quinoline TopoⅡα inhibitors.
Key words: Topoisomerase Ⅱα; Synthesis; Structure optimization; Antitumor activity
Li Zhiying , Ding Yanjiao , Bu Huagang , Shen Yuemao . Antitumor and DNA Topoisomerase Ⅱα Inhibitory Activity of 6-Substituted-aryl-2-methoxyquinolines[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2018 , 38(12) : 3204 -3210 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201806015
[1] Wang, J. C. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 635.
[2] Azarova, A. M.; Lyu, Y. L.; Lin, C. P.; Tsai, Y. C.; Lau, J. Y.; Wang, J. C.; Liu, L. F. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 11014.
[3] Deweese, J. E.; Osheroff, N. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 738.
[4] Haffner, M. C.; Aryee, M. J.; Toubaji, A.; Esopi, D. M.; Albadine, R.; Gurel, B.; Isaacs, W. B.; Bova, G. S.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.; Meeker, A. K.; Netto, G.; De Marzo, A. M.; Nelson, W. G.; Yegnasubramanian, S. Nat. Genetics 2010, 42, 668.
[5] Liu, S. S.; Zhao, B. B.; Lu, C. H.; Huang, J. J.; Shen, Y. M. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 1057.
[6] Qiu, J.; Zhao, B.; Shen, Y.; Chen, W.; Ma, Y.; Shen, Y. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 68, 192.
[7] Ibrahim, M. K.; Taghour, M. S.; Metwaly, A. M.; Belal, A.; Mehany, A. B. M.; Elhendawy, M. A.; Yassin, M. M.; Yassin, A. M.; El-Deeb, N. M.; Hafez, E. E.; Elsohly, M. A.; Eissa, I. H. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 115, 117.
[8] Kaur, G.; Cholia, R. P.; Joshi, G.; Amrutkar, S. M.; Kalra, S.; Mantha, A. K.; Banerjee, U. C.; Kumar, R.. Pham. Chem. Life Sci. 2018, 351, e1800023.
[9] Ruchelman, A. L.; Singh, S. K.; Wu, X.; Ray, A.; Yang, J. M.; Li, T. K.; Liu, A.; Liu, L. F.; LaVoie, E. J. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 3333.
[10] Lu, C. M.; Chen, Y. L.; Chen, H. L; Chen, C. A.; Lu, P. J.; Yang, C. N.; Tzeng, C. C. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1948.
[11] Carmichael, J.; DeGraff, W. G.; Gazdar, A. F.; Minna, J. D.; Mitchell, J. B. Cancer Res 1987, 47, 936.
[12] Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Zheng, Z.; Su, W. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 31, 163.
[13] Chen, W.; Shen, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 86, 782.
[14] Shen, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, B.; Hao, H.; Li, Z.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 453, 302.
[15] Shen, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Shen, Y. Med. Chem. 2014, 10, 533.
[16] Barrett, J.; Sutcliffe, J.; Gootz, T. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 1.
[17] Marini, J. C.; Levene, S. D.; Crothers, D. M.; Englund, P. T. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1982, 79, 7664.
[18] Xiao, X.; Cushman, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9960.
[19] Trott, O.; Olson, A. J. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455.
[20] Sanner, M. F. J. Mol.-Graphies Modell. 1999, 17, 57.
[21] Morris, G. M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M. F.; Belew, R. K.; Goodsell, D. S.; Olson, A. J. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |