

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation of Aminoguanidine Derivatives Containing a Biphenyl Moiety
Received date: 2018-11-06
Revised date: 2018-12-18
Online published: 2019-01-10
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81560561), and the Doctoral Foundation of Jinggangshan University (No. JZB1317).
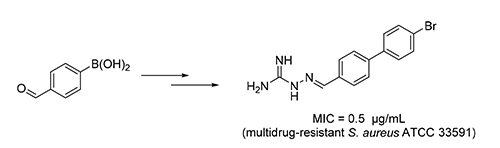
A series of aminoguanidine derivatives containing a biphenyl moiety were designed, synthesized, and characterized by spectra methods using chalcone-aminoguanidine derivative as the lead compound. The antibacterial activity of the target compounds was evaluated. The results indicated that most of the target compounds showed potent inhibitory activity with the minimum inhibitory concentration values (MICs) in range of 0.5~8 μg/mL. Among of which, 2-((4'-bromo-[1,1'- biphenyl]-4-yl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carboximidamide (3j) exhibited broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, effective to all the chosen strains including two multidrug-resistant gram-positive strains, showed the most potent inhibitory against S. aureus CMCC(B) 26003, E. faecalis CMCC 29212 and multidrug-resistant S. aureus ATCC 33591 with a MIC value of 0.5 μg/mL. Moreover, low cytotoxicity of compound 3j (HEK 293T, IC50=60.90 µmol/L) was found. These results suggested that the Compound 3j, with high safety, was potential and valuable in the research of novel antibacterial drugs.
Key words: aminoguanidine; biphenyl; antimicrobial activity
Yu Haihong , Zhou Shengchao , Guo Tingting , Liang Zhuo , Chen Huabin , Dai Weikai , Song Mingxia . Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation of Aminoguanidine Derivatives Containing a Biphenyl Moiety[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2019 , 39(5) : 1497 -1502 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201811012
[1] Bi, Y.; Liu, X. X.; Zhang, H. Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z. Y.; Lu, J.; Lewis, P. J.; Wang, C. Z.; Xu, J. Y.; Meng, Q. G.; Ma, C.; Yuan, C. S. Molecules 2017, 22, 590.
[2] Carrel, M.; Perencevich, E. N.; David, M. Z. Emerging Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1973.
[3] Hvistendahl, M. Science 2012, 336, 795.
[4] Yezli, S.; Li, H. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 389.
[5] Azeredo da Silveira, S.; Perez, A. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 531.
[6] Kang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J. Chin. J. Antibiot. 2017, 42, 169(in Chinese). (康悦, 赵明, 张菁, 中国抗生素杂志, 2017, 42, 169.)
[7] Ward, R. S. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1999, 16, 75.
[8] Whiting, D. A. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 583.
[9] Chang, J. B.; Reiner, J.; Xie, J. X. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 4581.
[10] Chen, D. F.; Zhang S. X.; Lan, X. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1997, 5, 715.
[11] Raffa, D.; Plescia, F.; Maggio, B.; Raimondi, M. V.; D'Anneo, A.; Lauricella, M.; Daidone, G. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 132, 262.
[12] Chen, Y.; Du, Y. J.; Suo, F. X. J. Henan Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2001, 29, 43(in Chinese). (陈勇, 杜燕军, 索福喜, 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 29, 43.)
[13] Wei, Z. Y.; Chi, K. Q.; Yu, Z. K.; Liu, H. Y.; Sun, L. P.; Zheng, C. J.; Piao, H. R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5920.
[14] Sidoryk, K.; Switalska, M.; Rózga, P.; Wietrzyk, J.; Bujak, I.; Zerek, B.; Kaczmarek, L.; Cybulski, M. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 3354.
[15] Gao, Z. M.; Wang, T. T.; Li, S. Z.; Wan, H. Q.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y. B.; Deng, X. Q.; Song, M. X. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 2484(in Chinese). (高智敏, 王田田, 李深圳, 万慧琪, 王刚, 吴银彬, 邓先清, 宋明霞, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 2484.)
[16] Li, Y. R.; Li, C.; Liu, J. C.; Guo, M.; Zhang, T. Y.; Sun, L. P.; Zheng, C. J.; Piao, H. R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5052.
[17] Xu, H.; Wang, Y. Y. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 7274
[18] Mourer, M.; Dibama, H. M.; Fontanay, S.; Grare, M.; Duval, R. E.; Finance, C.; Vains, J. B. R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5496.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |