

Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry >
An Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer (ESIPT) Plus Ag-gregation Induced Emission (AIE) Phenanthro[9, 10-d]imidazole-Based Fluorescence Probe for Detection of Fe3+ in Living Cells
Received date: 2019-04-30
Online published: 2019-06-19
Supported by
the National Natural Science Foundation of China(21506106);the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province(LC2017004);the Fundamental Research Funds in Heilongjiang Provincial Universities(135209209);the Fundamental Research Funds in Heilongjiang Provincial Universities(YSTSXK201853);the Fundamental Research Funds in Heilongjiang Provincial Universities(YSTSXK201859);the Qiqihar University Graduate Innovation Fund Grants(YJSCX2018-ZD18)
Selective detection of Fe3+ has considerable importance due to its active involvement in various biological processes. Based on the mechanism of excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) plus aggregation induced emission (AIE), a fluorescence probe of phenanthro[9, 10-d]imidazole modified by the phenolic hydroxyl (PIP-o-OH) had been designed, synthesized and applied in the detection of Fe3+. The structure of PIP-o-OH was characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, HRMS and X-ray single diffraction. Furthermore, a clear intramolecular hydrogen bond was observed between hydroxyl O-H and imidazole N atom in X-ray single structure, which improved the impossibility of ESIPT activity. ESIPT and AIE activities of PIP-o-OH were adequately determined by absorption, emission spectra and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The aggregated PIP-o-OH in MeOH/H2O (V:V=1:9, Hepes 10 μmol/L, pH=7.4) exhibited a good sensitivity towards Fe3+ with "turn-off" fluorescence response just after 20 s. The limit of detection (LOD) was calculated as low as 0.49 μmol/L. So it could be utilized to detect Fe3+ in biology and environmental samples. In addition, the calculation of the density functional theory (DFT) confirmed the formation of PIP-o-OH-Fe3+ complex. Also, PIP-o-OH was successfully applied to monitor Fe3+ in HeLa cells by the fluorescence change and quantificationally detect Fe3+ in water samples.
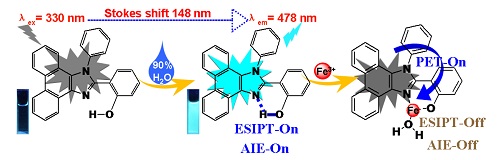
Key words: phenanthro[9, 10-d]imidazole; Fe3+; fluorescence probe; cell imaging; water samples
Yuqian He , Bing Zhao , Wei Kan , Liyan Wang , Bo Song , Guangming Yin , Ye Bi , Shuwen Chen . An Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer (ESIPT) Plus Ag-gregation Induced Emission (AIE) Phenanthro[9, 10-d]imidazole-Based Fluorescence Probe for Detection of Fe3+ in Living Cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2019 , 39(11) : 3250 -3257 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201904078
| [1] | Liu R. J. Zeng J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2017 37 3274. |
| [1] | 刘 瑞姣 曾 竟 有机化学 2017 37 3274. |
| [2] | Yang M. P. Su N. Li Y. X. Wang L. Ma L. F. Zhang Y. Li J. Yang B. Q. Kang L. L. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2018 38 636. |
| [2] | 杨 美盼 苏 娜 李 玉香 王 莉 马 利锋 张 媛 李 靖 杨 秉勤 康 龙丽 有机化学 2018 38 636. |
| [3] | Carter K. P. Young A. M. Palmer A. E. Chem. Rev. 2014 114 4564. |
| [4] | Chung P. K. Liu S. R. Wang H. F. Wu S. P. J. Fluoresc. 2013 23 1139. |
| [5] | Lee M. H. Kim J. S. Sessler J. L. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015 44 4185. |
| [6] | Wang Q. Q. Zhou L. Y. Qiu L. P. Lu D. Q. Wu Y. X. Zhang X. B. Analyst 2015 140 5563. |
| [7] | Barman S. Mukhopadhyay S. K. Gangopadhyay M. Biswas S. Dey S. Singh N. D. P. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015 3 3490. |
| [8] | Maity D. Kumar V. Govindaraju T. Org. Lett. 2012 14 6008. |
| [9] | Yang C. Y. Chen Y. Wu K. Wei T. Wang J. L. Zhang S. S. Han Y. F. Anal. Methods 2015 7 3327. |
| [10] | Wang H. Shi D. L. Li J. Tang H. Y. Guo Y. Sens. Actuators, B 2018 256 600. |
| [11] | Shen Y. M. Zhang X. Y. Zhang C. X. Zhang Y. Y. Jin J. L. Li H. T. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2018 191 427. |
| [12] | Hu J. Cheng K. Wu Q. Ding D. S. Li C. G. Li Z. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018 2 1201. |
| [13] | Tian M. G. Sun J. Tang Y. H. Dong B. L. Lin W. Y. Anal. Chem. 2018 90 998. |
| [14] | Feng L. Liu Z. M. Hou J. Lv X. Ning J. Ge G. B. Cui J. N. Yang L. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015 65 9. |
| [15] | Hu Q. Zeng H. F. Yu C. M. Wu S. Z. Sens. Actuators, B 2015 220 72. |
| [16] | Feng W. P. Wang Y. C. Chen S. Z. Wang C. Wang S. X. Li S. H. Li H. Y. Zhou G. Q. Zhang J. C. Dyes Pigm. 2016 131 145. |
| [17] | Shvadchak V. V. Klymchenko A. S. De Rocquigny H. Mely Y. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 37 e25. |
| [18] | Luo J. D. Xie Z. L. Lam J. W. Y. Chen L. Chen H. Y. Qiu C. F. Kwok H. S. Zhan X. W. Liu Y. Q. Zhu D. B. Tang B. Z. Chem. Commun. 2001 1740 1740. |
| [19] | Kwok R. T. K. Leung C. W. T. Tang B. Z. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015 44 4228. |
| [20] | Xia Q. Chen Z. K. Zhang Z. D. Liu R.Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2018 38 2700. |
| [20] | 夏 琦 陈 子康 张 志德 刘 瑞源 有机化学 2018 38 2700. |
| [21] | Zhan G. J. Han K. L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012 3 404. |
| [22] | Zhan N. Lam J. W. Y. Sung H. H. Y. Su H. M. Williams I. D. Wong K. S. Tang B. Z. Chem.-Eur. J. 2014 1 133. |
| [23] | Cui G. L. Lan Z. G. Thiel W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012 3 1662. |
| [24] | Xiao H. D. Chen K. Cui D. D. Jiang N. N. Yin G. Wang J. Wang R. Y. New J. Chem. 2014 38 2386. |
| [25] | Hu R. R. Leung N. L. C. Tang B. Z. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014 43 4494. |
| [26] | Hu R. R. MaldonadoJose J. L. Rodriguez M. Deng C. M. Lam J. W. Y. Yuen M. M. F. Ramos-Ortiz G. Tang B. Z. J. Mater. Chem. 2012 22 232. |
| [27] | Chen Y. Xu W. C. Kou J. F. Yu B. L. Wei X. H. Chao H. Ji L. N. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2010 10 1140. |
| [28] | Alam P. Das P. Climent C. Karanam M. Casanova D. Choudhury A. P. Alemany P. Jana N. R. Laskar I. R. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014 2 5615. |
| [29] | Chen Q. Jia C. M. Zhang Y. F. Du W. Wang Y. L. Huang Y. Yang Q. Y. Zhang Q. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017 5 7736. |
| [30] | Liu Y. Nie J. Niu J. Wang W. S. Lin W. Y. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6 1973 6 1973. |
| [31] | Liu H. W. Li K. Hu X. X. Zhu L. M. Rong Q. M. Liu Y. C. Zhang X. B. Hasserodt J. Qu F. L. Tan W. H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017 56 11788. |
| [32] | Datta B. K. Thiyagajan D. Samanta S. Ramesh A. Das G. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014 12 4975. |
| [33] | Job P. Ann. Chim. 1928 9 113. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |