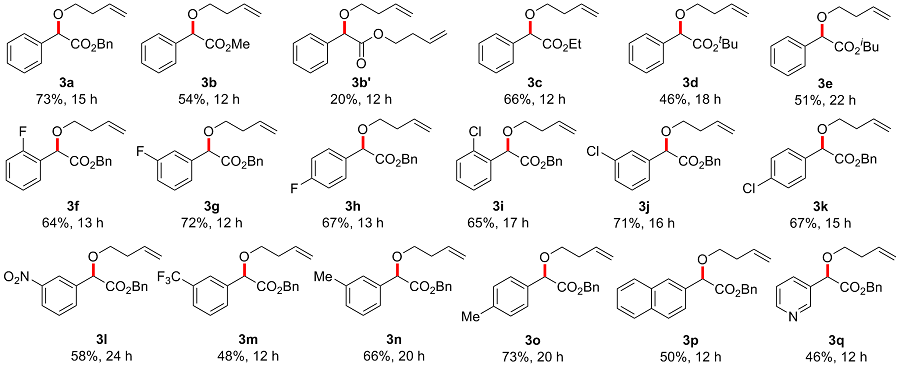
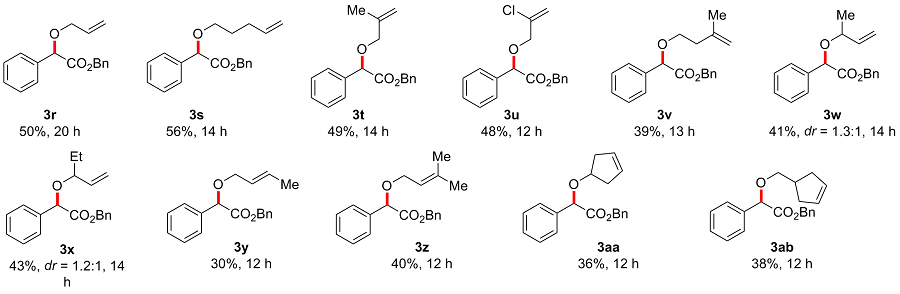
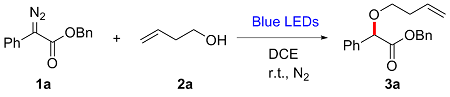
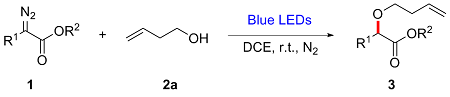
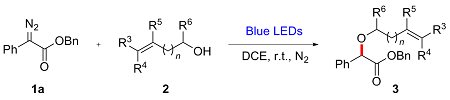
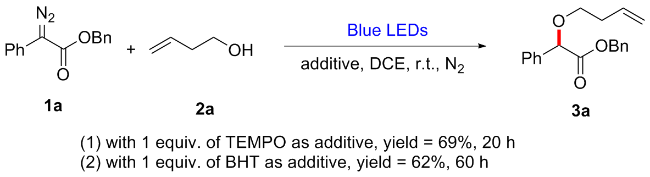
In a reaction vial (10 mL), aryldiazoacetate 1 (0.2 mmol) and alkenyl alcohol 2 (2 mmol) were dissolved in DCE (0.5 mL). The vial was capped under nitrogen and closed tightly. The mixture was stirred at room temperature under irradiation with blue LEDs (470 nm, 5 W) for a given time. Then the reaction mixture was concentrated and directly purified by flash column chromatography (eluted with EtOAc/petroleum ether, V∶V=1∶10) to give product 3.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3a): Colorless oil, 73% yield (43 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.44~7.41 (m, 2H), 7.34~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.29~7.25 (m, 3H), 7.21~7.18 (m, 2H), 5.84~5.74 (m, 1H), 5.16~5.08 (m, 2H), 5.08~5.03 (m, 1H), 5.02~4.98 (m, 1H), 4.90 (s, 1H), 3.60~3.54 (m, 1H), 3.50~3.44 (m, 1H), 2.42~2.36 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 170.8, 136.5, 135.6, 134.8, 128.7, 128.7, 128.6, 128.3, 128.0, 127.3, 116.8, 81.1, 69.3, 66.8, 34.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H21O3 [M+H]+ 297.1485, found 297.1478.
Methyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3b): Colorless oil, 54% yield (24 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.46~7.43 (m, 2H), 7.39~7.30 (m, 3H), 5.88~5.77 (m, 1H), 5.12~5.07 (m, 1H), 5.05~5.02 (m, 1H), 4.89 (s, 1H), 3.71 (s, 3H), 3.62~3.57 (m, 1H), 3.52~3.46 (m, 1H), 2.45~2.40 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.4, 136.6, 134.7, 128.7, 128.7, 127.2, 116.7, 81.1, 69.3, 52.3, 34.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H17O3 [M+H]+ 221.1172, found 221.1168.
But-3-en-1-yl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3b'): Colorless oil, 20% yield (10.2 mg), Rf=0.7. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.46~7.44 (m, 2H), 7.37~7.32 (m, 3H), 5.87~5.80 (m, 1H), 5.70~5.63 (m, 1H), 5.12~4.97 (m, 4H), 4.87 (s, 1H), 4.17 (t, J=6.6 Hz, 2H), 3.63~3.58 (m, 1H), 3.52~3.46 (m, 1H), 2.45~2.39 (m, 2H), 2.36~2.30 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.0, 136.7, 134.8, 133.7, 128.7, 128.6, 127.3, 117.5, 116.8, 81.1, 69.3, 64.2, 34.2, 33.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C16H21O3 [M+H]+ 261.1485, found 261.1483.
Ethyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3c): Colorless oil, 66% yield (31 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.47~7.44 (m, 2H), 7.38~7.32 (m, 3H), 5.87~5.78 (m, 1H), 5.13~5.07 (m, 1H), 5.05~5.02 (m, 1H), 4.87 (s, 1H), 4.22~4.12 (m, 2H), 3.63~3.57 (m, 1H), 3.52~3.47 (m, 1H), 2.45~2.40 (m, 2H), 1.21 (t, J=7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 171.1, 136.7, 134.9, 128.7, 127.2, 116.8, 81.2, 69.3, 61.3, 34.2, 14.2; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C14H19O3 [M+H]+ 235.1329, found 235.1325.
tert-Butyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3d): Colorless oil, 46% yield (24 mg), Rf=0.4. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.45~7.42 (m, 2H), 7.37~7.30 (m, 3H), 5.88~5.81 (m, 1H), 5.13~5.07 (m, 1H), 5.05~5.01 (m, 1H), 4.75 (s, 1H), 3.63~3.58 (m, 1H), 3.51~3.45 (m, 1H), 2.45~2.39 (m, 2H), 1.39 (s, 9H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 170.2, 137.2, 135.0, 128.5, 128.4, 127.2, 116.6, 81.8, 81.5, 69.1, 34.2, 28.0; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C16H23O3 [M+H]+ 263.1642, found 263.1638.
Isobutyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3e): Colorless oil, 51% yield (27 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.47~7.45 (m, 2H), 7.38~7.31 (m, 3H), 5.87~5.80 (m, 1H), 5.12~5.07 (m, 1H), 5.05~5.02 (m, 1H), 4.88 (s, 1H), 3.94~3.85 (m, 2H), 3.64~3.58 (m, 1H), 3.53~3.47 (m, 1H), 2.46~2.40 (m, 2H), 1.91~1.84 (m, 1H), 0.82 (dd, J=6.7, 1.2 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.1, 136.9, 134.9, 128.7, 128.6, 127.3, 116.8, 81.2, 71.2, 69.3, 34.2, 27.8, 19.0; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C16H23O3 [M+H]+ 263.1642, found 263.1641.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(2-fluorophenyl)acetate (3f): Colorless oil, 64% yield (40 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.44~7.39 (m, 2H), 7.34~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.26~7.20 (m, 4H), 5.80~5.73 (m, 1H), 5.31 (s, 1H), 5.16 (s, 2H), 5.09~5.04 (m, 1H), 5.00~4.97 (m, 1H), 3.66~3.60 (m, 1H), 3.52~3.47 (m, 1H), 2.31~2.26 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 169.6, 161.0, 158.5, 135.7, 135.0, 130.8, 130.7, 129.2, 129.1, 128.4, 128.1, 127.6, 124.7, 124.6, 124.1, 124.0, 116.6, 115.6, 115.4, 74.0, 74.0, 68.8, 66.1, 33.5; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H20FO3 [M+H]+ 315.1391, found 315.1390.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(3-fluorophenyl)acetate (3g): Colorless oil, 72% yield (45 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.45~7.42 (m, 1H), 7.34~7.30 (m, 3H), 7.26~7.22 (m, 3H), 7.21~7.17 (m, 2H), 5.83~5.76 (m, 1H), 5.17 (s, 1H), 5.15 (s, 2H), 5.11~5.06 (m, 1H), 5.03~4.99 (m, 1H), 3.59~3.55 (m, 1H), 3.50~3.46 (m, 1H), 2.34~2.29 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.0, 160.9, 139.5, 139.4, 135.7, 135.2, 130.7, 130.6, 128.5, 128.2, 127.8, 123.2, 123.2, 116.7, 115.5, 115.3, 114.0, 113.8, 79.1, 68.6, 66.2, 33.5; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H20FO3 [M+H]+ 315.1391, found 315.1398.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)acetate (3h): Colorless oil, 67% yield (42 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.45~7.42 (m, 2H), 7.33~7.30 (m, 3H), 7.25~7.18 (m, 4H), 5.81~5.74 (m, 1H), 5.14~5.13 (m, 3H), 5.10~5.05 (m, 1H), 5.02~4.98 (m, 1H), 3.57~3.53 (m, 1H), 3.47~3.43 (m, 1H), 2.32~2.27 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.2, 163.3, 160.8, 135.7, 135.1, 133.0, 133.0, 129.3, 129.2, 128.4, 128.1, 127.7, 116.6, 115.5, 115.2, 79.1, 68.3, 66.0, 33.5; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H20FO3 [M+H]+ 315.1391, found 315.1394.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)acetate (3i): Colorless oil, 65% yield (43 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.50~7.48 (m, 1H), 7.45~7.43 (m, 1H), 7.40~7.36 (m, 2H), 7.35~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.26~7.23 (m, 2H), 5.81~5.74 (m, 1H), 5.37 (s, 1H), 5.17 (s, 2H), 5.09~5.05 (m, 1H), 5.01~4.98 (m, 1H), 3.66~3.62 (m, 1H), 3.53~3.49 (m, 1H), 2.32~2.27 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 169.5, 135.7, 135.1, 134.5, 132.7, 130.4, 129.6, 129.1, 128.4, 128.1, 127.7, 127.6, 116.7, 77.1, 69.1, 66.2, 33.6; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H19ClNaO3 [M+Na]+ 353.0915, found 353.0914.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(3-chlorophenyl)acetate (3j): Colorless oil, 71% yield (47 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.42~7.41 (m, 3H), 7.37~7.31 (m, 4H), 7.25~7.22 (m, 2H), 5.85~5.72 (m, 1H), 5.15 (s, 3H), 5.08 (dd, J1=23.2 Hz, J2=2.6 Hz, 1H), 5.00 (d, J=10.4 Hz, 1H), 3.62~3.55 (m, 1H), 3.51~3.43 (m, 1H), 2.31 (q, J1=13.4 Hz, J2=6.7 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 169.9, 139.1, 135.6, 135.1, 133.1, 130.5, 128.5, 128.4, 128.1, 127.8, 126.9, 125.7, 116.6, 79.0, 68.5, 66.2, 33.5; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H19ClNaO3 [M+Na]+ 353.0915, found 353.0912.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)acetate (3k), Colorless oil, 67% yield (44 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.46~7.40 (m, 4H), 7.33~7.30 (m, 3H), 7.25~7.23 (m, 2H), 5.81~5.73 (m, 1H), 5.14~5.13 (m, 3H), 5.10~5.05 (m, 1H), 5.01~4.98 (m, 1H), 3.59~3.54 (m, 1H), 3.48~3.42 (m, 1H), 2.32~2.27 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.1, 135.8, 135.7, 135.2, 133.2, 129.0, 128.6, 128.5, 128.2, 127.8, 116.7, 79.1, 68.5, 66.2, 33.6; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H19ClNaO3 [M+Na]+ 353.0915, found 353.0918.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(3-nitrophenyl)acetate (3l): yellow oil, 58% yield (40 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 8.24~8.20 (m, 2H), 7.86~7.84 (m, 1H), 7.69 (t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.33~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.26~7.23 (m, 2H), 5.83~5.76 (m, 1H), 5.38 (s, 1H), 5.16 (s, 2H), 5.11~5.06 (m, 1H), 5.03~4.99 (m, 1H), 3.65~3.62 (m, 1H), 3.54~3.50 (m, 1H), 2.35~2.30 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 169.7, 147.8, 138.9, 135.6, 135.1, 133.6, 130.3, 128.4, 128.2, 127.9, 123.5, 121.7, 116.8, 78.6, 68.8, 66.5, 33.5; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H19NNaO5 [M+Na]+ 364.1155, found 364.1151.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(3-(trifluoromethyl)- phenyl)acetate (3m): yellow oil, 48% yield (35 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.73 (s, 1H), 7.64 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.59 (d, J=7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.33~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.23~7.21 (m, 2H), 5.85~5.77 (m, 1H), 5.16 (s, 2H), 5.13~5.07 (m, 1H), 5.06~5.03 (m, 1H), 4.97 (s, 1H), 3.69~3.63 (m, 1H), 3.53~3.48 (m, 1H), 2.46~2.40 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 170.2, 137.6, 135.3, 134.6, 130.5, 129.2, 128.7, 128.6, 128.2, 125.6, 125.5, 124.1, 117.0, 80.5, 69.7, 67.2, 34.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C20H19F3NaO3 [M+Na]+ 387.1178, found 387.1176.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(m-tolyl)acetate (3n): Colorless oil, 66% yield (41 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.34~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.25~7.22 (m, 3H), 7.19~7.14 (m, 3H), 5.83~5.73 (m, 2H), 5.14 (s, 2H), 5.10~5.05 (m, 1H), 5.04 (s, 1H), 5.02~4.98 (m, 1H), 3.58~3.52 (m, 1H), 3.47~3.41 (m, 1H), 2.33~2.28 (m, 2H), 2.28 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.4, 137.7, 136.7, 135.8, 135.2, 129.2, 128.4, 128.1, 127.8, 127.7, 124.4, 116.6, 80.0, 68.4, 65.9, 33.6, 21.0; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C20H22NaO3 [M+Na]+ 333.1461, found 333.1463.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(p-tolyl)acetate (3o): Colorless oil, 73% yield (45 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.34~7.28 (m, 5H), 7.25~7.23 (m, 2H), 7.18~7.16 (m, 2H), 5.83~5.73 (m, 1H), 5.16~5.05 (m, 3H), 5.04 (s, 1H), 5.01~4.98 (m, 1H), 3.57~3.51 (m, 1H), 3.46~3.40 (m, 1H), 2.32~2.27 (m, 5H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.5, 137.9, 135.8, 135.2, 133.8, 129.1, 128.4, 128.1, 127.8, 127.2, 116.6, 79.8, 68.2, 65.9, 33.6, 20.8; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C20H22NaO3 [M+Na]+ 333.1461, found 333.1460.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)acetate (3p): Colorless oil, 50% yield (35 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.91 (s, 1H), 7.84~7.81 (m, 3H), 7.58~7.55 (m, 1H), 7.51~7.46 (m, 2H), 7.29~7.20 (m, 5H), 5.88~5.78 (m, 1H), 5.21~5.01 (m, 5H), 3.67~3.61 (m, 1H), 3.57~3.51 (m, 1H), 2.47~2.42 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 170.8, 135.6, 134.8, 133.9, 133.5, 133.2, 128.6, 128.6, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 127.8, 126.8, 126.5, 126.4, 124.8, 116.8, 81.3, 69.4, 66.9, 34.2; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C23H22NaO3 [M+Na]+ 369.1461, found 369.1458.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)acetate (3q): yellow oil, 46% yield (27 mg), Rf=0.4. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 8.68~8.57 (m, 2H), 7.78 (d, J=7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.35~7.28 (m, 4H), 7.27~7.23 (m, 2H), 5.86~5.76 (m, 1H), 5.20~5.02 (m, 4H), 4.95 (s, 1H), 3.69~3.64 (m, 1H), 3.53~3.48 (m, 1H), 2.41 (q, J=6.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 170.2, 150.1, 148.9, 135.2, 134.7, 134.6, 132.4, 128.7, 128.6, 128.3, 123.7, 117.0, 79.0, 69.8, 67.3, 34.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C18H20NO3 [M+H]+ 298.1438, found 298.1435.
Benzyl 2-(allyloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3r): Colorless oil, 50% yield (28 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.44~7.35 (m, 5H), 7.33~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.25~7.22 (m, 2H), 5.96~5.86 (m, 1H), 5.29~5.24 (m, 1H), 5.18~5.09 (m, 4H), 4.11~4.05 (m, 1H), 4.02~3.96 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.3, 136.6, 135.8, 134.4, 128.6, 128.6, 128.4, 128.1, 127.7, 127.2, 117.3, 79.4, 69.9, 66.0; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C18H18NaO3 [M+Na]+ 305.1148, found 305.1149.
Benzyl 2-(pent-4-en-1-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3s): Colorless oil, 56% yield (35 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.42~7.35 (m, 5H), 7.33~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.24~7.21 (m, 2H), 5.82~5.75 (m, 1H), 5.13~5.13 (m, 2H), 5.06 (s, 1H), 5.00~4.95 (m, 1H), 4.94~4.91 (m, 1H), 3.53~3.48 (m, 1H), 3.43~3.39 (m, 1H), 2.09~2.03 (m, 2H), 1.65~1.58 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.4, 138.1, 136.8, 135.7, 128.5, 128.5, 128.4, 128.0, 127.7, 127.1, 115.0, 80.0, 68.5, 65.9, 29.7, 28.3; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C20H23O3 [M+H]+ 311.1642, found 311.1639.
Benzyl 2-((2-methylallyl)oxy)-2-phenylacetate (3t): Colorless oil, 49% yield (29 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.42~7.34 (m, 5H), 7.33~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.25~7.22 (m, 2H), 5.18~5.11 (m, 2H), 5.06 (s, 1H), 4.94 (s, 1H), 4.88 (s, 1H), 3.92 (q, J=12.5 Hz, 2H), 1.67 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.3, 141.5, 136.6, 135.8, 128.6, 128.6, 128.4, 128.1, 127.8, 127.2, 112.5, 79.2, 72.7, 66.0, 19.3; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H21O3 [M+H]+ 297.1485, found 297.1487.
Benzyl 2-((2-chloroallyl)oxy)-2-phenylacetate (3u): Colorless oil, 48% yield (30 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.43~7.41 (m, 2H), 7.35~7.31 (m, 3H), 7.29~7.25 (m, 3H), 7.21~7.17 (m, 2H), 5.44 (q, J=1.4 Hz, 1H), 5.35 (s, 1H), 5.18~5.08 (m, 2H), 5.00 (s, 1H), 4.14~4.04 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 170.2, 137.2, 135.7, 135.4, 129.1, 128.8, 128.6, 128.4, 128.1, 127.5, 114.5, 79.9, 71.6, 67.0; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C18H18ClO3 [M+H]+ 317.0939, found 317.0935.
Benzyl 2-((3-methylbut-3-en-1-yl)oxy)-2-phenylacetate (3v): Colorless oil, 39% yield (24 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.40~7.35 (m, 5H), 7.33~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.24~7.22 (m, 2H), 5.14 (s, 2H), 5.10 (s, 1H), 4.73~4.70 (m, 2H), 3.66~3.60 (m, 1H), 3.54~3.48 (m, 1H), 2.26 (t, J=6.7 Hz, 2H), 1.67 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.4, 142.4, 136.7, 135.7, 128.5, 128.5, 128.4, 128.0, 127.7, 127.1, 111.6, 79.9, 67.5, 65.9, 37.1, 22.4; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C20H22NaO3 [M+Na]+ 333.1461, found 333.1463.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-2-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3w, one isomer): Colorless oil, 18% yield (11 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.39~7.30 (m, 8H), 7.25~7.23 (m, 2H), 5.77~5.68 (m, 1H), 5.18~5.11 (m, 4H), 5.03 (s, 1H), 4.02~3.98 (m, 1H), 1.23 (d, J=6.3 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.8, 139.3, 136.8, 135.8, 128.5, 128.4, 128.1, 127.8, 127.2, 117.0, 77.4, 75.7, 66.1, 21.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H20NaO3 [M+Na]+ 319.1304, found 319.1305.
Benzyl 2-(but-3-en-2-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3w', another isomer): Colorless oil, 23% yield (14 mg), Rf=0.4. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.42~7.34 (m, 5H), 7.33~7.29 (m, 3H), 7.22~7.20 (m, 2H), 5.79~5.70 (m, 1H), 5.21~5.16 (m, 1H), 5.13~5.04 (m, 3H), 5.04 (s, 1H), 3.91~3.87 (m, 1H), 1.18 (d, J=6.4 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.5, 139.5, 137.0, 135.8, 128.6, 128.6, 128.4, 128.1, 127.8, 127.2, 116.8, 77.7, 75.6, 65.9, 20.9; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H20NaO3 [M+Na]+ 319.1304, found 319.1306.
Benzyl 2-(pent-1-en-3-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3x, one isomer): Colorless oil, 20% yield (12 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.42~7.40 (m, 2H), 7.32~7.24 (m, 6H), 7.22~7.18 (m, 2H), 5.65~5.56 (m, 1H), 5.19~5.16 (m, 1H), 5.12~5.07 (m, 3H), 5.01 (s, 1H), 3.74~3.68 (m, 1H), 1.76~1.68 (m, 1H), 1.57~1.50 (m, 1H), 0.91 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.6, 138.0, 137.0, 135.8, 128.6, 128.6, 128.4, 128.1, 127.3, 118.6, 82.3, 77.8, 66.7, 28.5, 9.8; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C20H22NaO3 [M+Na]+ 333.1461, found 333.1455.
Benzyl 2-(pent-1-en-3-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3x', another isomer): Colorless oil, 23% yield (14 mg), Rf=0.4. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 7.40~7.30 (m, 8H), 7.26~7.23 (m, 2H), 5.70~5.61 (m, 1H), 5.24~5.13 (m, 4H), 5.01 (s, 1H), 3.80~3.75 (m, 1H), 1.67~1.57 (m, 1H), 1.55~1.45 (m, 1H), 0.89~0.85 (m, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 170.7, 137.8, 136.9, 135.8, 128.5, 128.4, 128.1, 127.8, 127.1, 118.3, 81.2, 77.2, 66.0, 27.8, 9.5; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C20H22NaO3 [M+Na]+ 333.1461, found 333.1458.
Benzyl (E)-2-(but-2-en-1-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3y): Colorless oil, 30% yield (18 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.43~7.41 (m, 2H), 7.34~7.25 (m, 6H), 7.22~7.18 (m, 2H), 5.69~5.62 (m, 1H), 5.60~5.53 (m, 1H), 5.17~5.06 (m, 2H), 4.95 (s, 1H), 3.96 (d, J=6.3 Hz, 2H), 1.68~1.65 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 170.9, 136.5, 135.6, 131.0, 128.7, 128.7, 128.6, 128.3, 128.1, 128.1, 127.5, 127.5, 126.7, 79.5, 70.3, 66.8, 17.9; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H21O3 [M+H]+ 297.1485, found 297.1477.
Benzyl 2-((3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)oxy)-2-phenylacetate (3z): Colorless oil, 40% yield (25 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.47~7.44 (m, 2H), 7.37~7.28 (m, 6H), 7.24~7.21 (m, 2H), 5.39~5.36 (m, 1H), 5.21~5.09 (m, 2H), 4.96 (s, 1H), 4.09~4.01 (m, 2H), 1.73 (s, 3H), 1.58 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.1, 138.5, 136.7, 135.7, 128.7, 128.7, 128.6, 128.3, 128.2, 127.5, 120.3, 79.7, 66.8, 66.0, 26.0, 18.2; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C20H22NaO3 [M+Na]+ 333.1461, found 333.1457.
Benzyl 2-(cyclopent-3-en-1-yloxy)-2-phenylacetate (3aa): Colorless oil, 36% yield (22 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.43~7.41 (m, 2H), 7.32~7.25 (m, 6H), 7.21~7.18 (m, 2H), 5.64~5.59 (m, 2H), 5.15~5.07 (m, 2H), 4.98 (s, 1H), 4.29~4.24 (m, 1H), 2.60~2.38 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.2, 136.8, 135.7, 128.7, 128.6, 128.4, 128.3, 128.3, 128.1, 127.4, 79.4, 78.6, 66.8, 39.3, 39.3; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C20H20NaO3 [M+Na]+ 331.1304, found 331.1304.
Benzyl 2-(cyclopent-3-en-1-ylmethoxy)-2-phenylacetate (3ab): Colorless oil, 38% yield (25 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.47~7.45 (m, 2H), 7.38~7.29 (m, 6H), 7.24~7.21 (m, 2H), 5.63 (s, 2H), 5.19~5.11 (m, 2H), 4.92 (s, 1H), 3.48~3.44 (m, 1H), 3.39~3.35 (m, 1H), 2.70~2.61 (m, 1H), 2.52~2.45 (m, 2H), 2.20~2.06 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.0, 136.8, 135.7, 129.7, 129.5, 128.7, 128.7, 128.6, 128.3, 128.1, 127.3, 81.3, 74.3, 66.8, 36.8, 36.1, 36.0; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C21H22NaO3 [M+Na]+ 345.1461, found 345.1462.
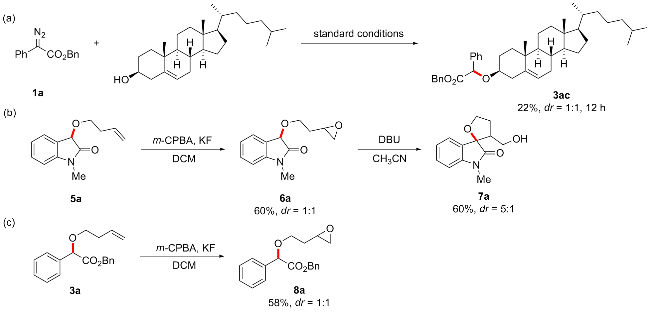
Benzyl-2-(((3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl- 17-((R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl)-2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl)oxy)-2-phenylacetate (3ac): Colorless oil, 22% yield (27 mg), Rf=0.5. m.p. 99~102 ℃; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.49~7.47 (m, 4H), 7.37~7.30 (m, 12H), 7.24~7.22 (m, 4H), 5.33~5.29 (m, 2H), 5.19~5.14 (m, 4H), 5.11 (s, 2H), 3.30~3.27 (m, 2H), 2.42~2.33 (m, 4H), 2.03~1.95 (m, 5H), 1.89~1.81 (m, 5H), 1.64~1.25 (m, 30H), 1.18~1.06 (m, 13H), 1.00 (s, 14H), 0.97~0.92 (m, 8H), 0.89~0.87 (m, 13H), 0.68 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.5, 171.4, 140.7, 140.7, 137.2, 137.2, 135.7, 128.7, 128.6, 128.6, 128.3, 128.1, 128.1, 127.3, 122.0, 78.6, 78.6, 78.5, 78.4, 66.8, 66.8, 56.9, 56.2, 50.2, 42.4, 39.9, 39.6, 39.1, 37.3, 36.9, 36.3, 35.9, 32.1, 32.0, 32.0, 28.4, 28.4, 28.1, 24.4, 23.9, 23.0, 22.7, 21.2, 19.5, 18.8, 12.0; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C42H58NaO3 [M+Na]+ 633.4278, found 633.4274.
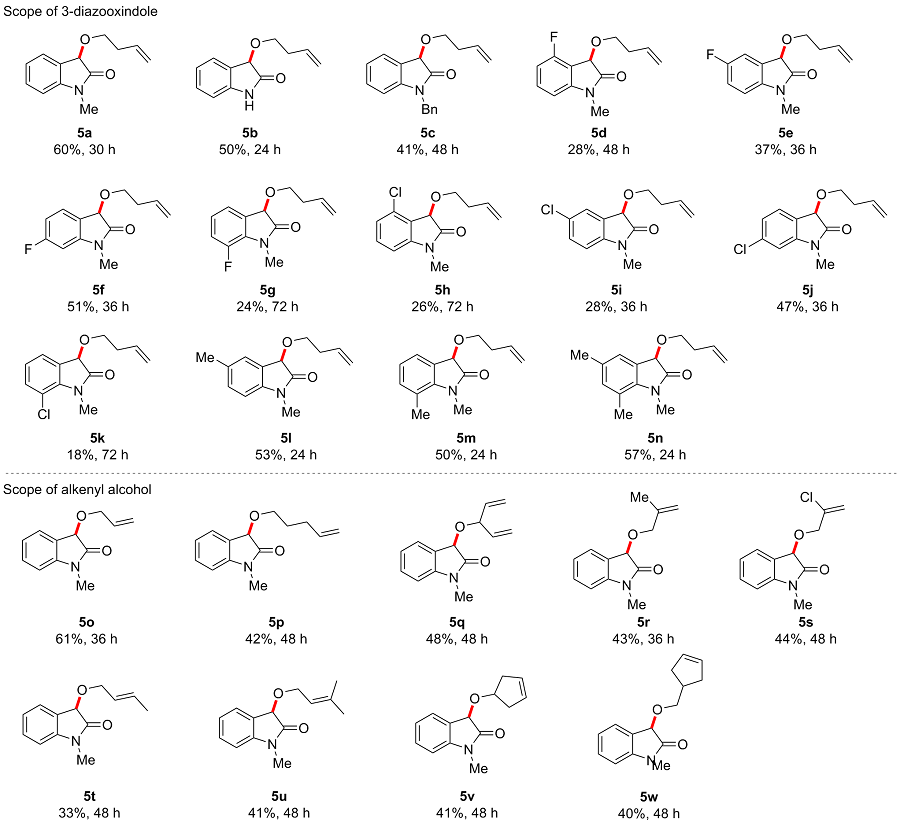
In a reaction vial (10 mL), 3-diazooxindole 4 (0.2 mmol) and alkenyl alcohol 2 (2 mmol) were dissolved in DCE (2 mL). The vial was capped under nitrogen and closed tightly. The mixture was stirred at room temperature under irradiation with blue LEDs (470 nm, 5 W) for a given time. Then the reaction mixture was concentrated and directly purified by flash column chromatography (eluted with EtOAc/petroleum ether, V∶V=1∶3) to give product 5.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-1-methylindolin-2-one (5a): Yellow oil, 60% yield (26 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.38 (d, J=7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (t, J=7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.08 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 1H), 6.80 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.88~5.78 (m, 1H), 5.14-5.09 (m, 1H), 5.07-5.03 (m, 1H), 4.91 (s, 1H), 3.86~3.81 (m, 1H), 3.68~3.62 (m, 1H), 3.17 (s, 3H), 2.44~2.38 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.7, 144.3, 134.9, 130.0, 125.4, 125.2, 123.0, 116.8, 108.5, 76.0, 68.1, 34.4, 26.2; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H16NO2 [M+H]+ 218.1176, found 218.1173.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)indolin-2-one (5b): Yellow oil, 50% yield (20 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 8.73 (s, 1H), 7.37 (d, J=7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.29~7.25 (m, 1H), 7.08~7.04 (m, 1H), 6.88 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.89~5.79 (m, 1H), 5.15~5.10 (m, 1H), 5.07~5.04 (m, 1H), 4.97 (s, 1H), 3.83~3.78 (m, 1H), 3.70~3.64 (m, 1H), 2.45~2.40 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 177.2, 141.4, 134.9, 130.1, 125.8, 125.6, 123.1, 116.9, 110.5, 76.4, 68.0, 34.4; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C12H14NO2 [M+H]+ 204.1019, found 204.1015.
1-Benzyl-3-(but-3-en-1-yloxy)indolin-2-one (5c): Red oil, 41% yield (24 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.38 (d, J=7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.32~7.23 (m, 5H), 7.19 (t, J=7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.03 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 1H), 6.68 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.88~5.81 (m, 1H), 5.15~5.09 (m, 1H), 5.08~5.04 (m, 1H), 5.00 (s, 1H), 4.86 (d, J=2.8 Hz, 2H), 3.90~3.85 (m, 1H), 3.72~3.67 (m, 1H), 2.45~2.40 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.8, 143.4, 135.6, 134.9, 129.9, 128.9, 127.8, 127.4, 125.5, 125.2, 123.1, 116.8, 109.5, 76.0, 68.2, 43.8, 34.4; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C19H20NO2 [M+H]+ 294.1489, found 294.1488.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-4-fluoro-1-methylindolin-2-one (5d): Colorless oil, 28% yield (13 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.34~7.28 (m, 1H), 6.77 (t, J=8.6 Hz, 1H), 6.61 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.90~5.80 (m, 1H), 5.12 (dd, J1=17.2 Hz, J2=1.9 Hz, 1H), 5.02 (d, J=10.7 Hz, 1H), 5.01 (s, 1H), 3.93~3.88 (m, 1H), 3.78~3.72 (m, 1H), 3.17 (s, 3H), 2.43 (q, J=6.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 173.9, 161.1, 158.6, 146.6, 134.8, 132.2, 132.1, 116.8, 111.1, 111.0, 110.8, 104.6, 104.6, 74.5, 69.4, 34.3, 26.6; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H15FNO2 [M+H]+ 236.1082, found 236.1080.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-5-fluoro-1-methylindolin-2-one (5e): Colorless oil, 37% yield (17 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.14 (dd, J1=7.5, J2=1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.03 (td, J1=8.9, J2=2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.72 (dd, J1=8.5, J2=4.0 Hz, 1H), 5.88~5.78 (m, 1H), 5.15~5.10 (m, 1H), 5.08~5.05 (m, 1H), 4.89 (s, 1H), 3.89~3.84 (m, 1H), 3.69~3.64 (m, 1H), 3.16 (s, 3H), 2.41 (q, J=6.7 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.4, 160.7, 158.3, 140.2, 140.2, 134.8, 126.8, 126.7, 117.0, 116.4, 116.1, 113.7, 113.4, 109.0, 109.0, 76.0, 76.0, 68.5, 34.4, 26.3; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H15FNO2 [M+H]+ 236.1082, found 236.1079.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-6-fluoro-1-methylindolin-2-one (5f): Colorless oil, 51% yield (24 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.33~7.30 (m, 1H), 6.77~6.72 (m, 1H), 6.54 (dd, J1=8.8, J2=2.3 Hz, 1H), 5.86~5.77 (m, 1H), 5.14~5.09 (m, 1H), 5.07~5.03 (m, 1H), 4.85 (s, 1H), 3.89~3.83 (m, 1H), 3.68~3.62 (m, 1H), 3.15 (s, 3H), 2.43~2.37 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 175.0, 165.5, 163.0, 146.1, 146.0, 134.8, 126.7, 126.6, 120.6, 120.6, 116.9, 109.2, 109.0, 97.5, 97.3, 75.4, 68.3, 34.3, 26.3; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H15FNO2 [M+H]+ 236.1082, found 236.1079.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-7-fluoro-1-methylindolin-2-one (5g): Colorless oil, 24% yield (11 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.17 (d, J=7.0 Hz, 1H), 7.08~6.98 (m, 2H), 5.88~5.78 (m, 1H), 5.12 (dd, J1=17.2, J2=1.8 Hz, 1H), 5.06 (d, J=10.2 Hz, 1H), 4.89 (s, 1H), 3.88~3.83 (m, 1H), 3.69~3.63 (m, 1H), 3.38 (d, J=2.7 Hz, 3H), 2.41 (q, J=6.8 Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.3, 149.1, 146.6, 134.8, 130.8, 128.0, 128.0, 123.7, 123.6, 121.3, 121.2, 118.1, 117.9, 116.9, 75.9, 75.8, 68.3, 34.4, 28.8, 28.7; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H15FNO2 [M+H]+ 236.1082, found 236.1077.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-4-chloro-1-methylindolin-2-one (5h): Colorless oil, 26% yield (13 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.29~7.25 (m, 1H), 7.03 (d, J=8.2 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.92~5.82 (m, 1H), 5.15~5.10 (m, 1H), 5.06~5.03 (m, 1H), 4.92 (s, 1H), 3.95~3.89 (m, 1H), 3.72~3.66 (m, 1H), 3.16 (s, 3H), 2.44 (q, J=6.6 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.0, 146.0, 135.0, 132.7, 131.4, 123.8, 122.7, 116.7, 106.8, 75.8, 69.2, 34.4, 26.4; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H15ClNO2 [M+H]+ 252.0786, found 252.0784.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-5-chloro-1-methylindolin-2-one (5i): Colorless oil, 28% yield (14 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.36~7.35 (m, 1H), 7.32~7.29 (m, 1H), 6.73 (d, J=8.3 Hz, 1H), 5.88~5.78 (m, 1H), 5.16~5.10 (m, 1H), 5.09~5.05 (m, 1H), 4.88 (s, 1H), 3.91~3.85 (m, 1H), 3.69~3.64 (m, 1H), 3.16 (s, 3H), 2.44~2.38 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.3, 142.8, 134.7, 129.9, 128.5, 126.9, 125.9, 117.0, 109.4, 75.8, 68.6, 34.3, 26.3; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H15ClNO2 [M+H]+ 252.0786, found 252.0784.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-6-chloro-1-methylindolin-2-one (5j): Colorless oil, 47% yield (24 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.29 (d, J=7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.06~7.04 (m, 1H), 6.80 (d, J=1.8 Hz, 1H), 5.87~5.77 (m, 1H), 5.14~5.09 (m, 1H), 5.07~5.04 (m, 1H), 4.86 (s, 1H), 3.88~3.82 (m, 1H), 3.68~3.62 (m, 1H), 3.15 (s, 3H), 2.43~2.37 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.7, 145.6, 135.9, 134.8, 126.3, 123.6, 122.9, 116.9, 109.3, 75.5, 68.4, 34.3, 26.3; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H15ClNO2 [M+H]+ 252.0786, found 252.0783.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-7-chloro-1-methylindolin-2-one (5k): Colorless oil, 18% yield (9 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.28~7.24 (m, 2H), 7.01~6.97 (m, 1H), 5.88~5.78 (m, 1H), 5.12 (dd, J1=17.2, J2=1.7 Hz, 1H), 5.06 (d, J =10.2 Hz, 1H), 4.86 (s, 1H), 3.88~3.83 (m, 1H), 3.68~3.63 (m, 1H), 3.54 (s, 3H), 2.40 (q, J=6.7 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.9, 140.1, 134.8, 132.3, 128.0, 123.9, 123.9, 116.9, 115.9, 75.4, 68.3, 34.4, 29.6; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H15ClNO2 [M+H]+ 252.0786, found 252.0778.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-1,5-dimethylindolin-2-one (5l): Colorless oil, 53% yield (25 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.20 (s, 1H), 7.12 (d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.68 (d, J=7.9 Hz, 1H), 5.89~5.79 (m, 1H), 5.15~5.09 (m, 1H), 5.07~5.03 (m, 1H), 4.87 (s, 1H), 3.88~3.83 (m, 1H), 3.68~3.62 (m, 1H), 3.15 (s, 3H), 2.44~2.38 (m, 2H), 2.34 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.6, 141.9, 134.9, 132.6, 130.2, 126.2, 125.2, 116.8, 108.2, 76.1, 68.2, 34.4, 26.2, 21.2; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C14H18NO2 [M+H]+ 232.1332, found 232.1332.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-1,7-dimethylindolin-2-one (5m): Colorless oil, 50% yield (23 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.21 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.05 (d, J=7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.96 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 1H), 5.88~5.78 (m, 1H), 5.14~5.08 (m, 1H), 5.06~5.03 (m, 1H), 4.84 (s, 1H), 3.84~3.79 (m, 1H), 3.65~3.60 (m, 1H), 3.44 (s, 3H), 2.54 (s, 3H), 2.43~2.37 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 175.4, 141.9, 135.0, 133.7, 125.8, 123.3, 123.0, 120.1, 116.7, 75.5, 67.9, 34.4, 29.5, 19.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C14H18NO2 [M+H]+ 232.1332, found 232.1331.
3-(But-3-en-1-yloxy)-1,5,7-trimethylindolin-2-one (5n): Colorless oil, 57% yield (28 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.02 (s, 1H), 6.85 (s, 1H), 5.88~5.78 (m, 1H), 5.14~5.09 (m, 1H), 5.06~5.03 (m, 1H), 4.80 (s, 1H), 3.86~3.81 (m, 1H), 3.65~3.59 (m, 1H), 3.41 (s, 3H), 2.49 (s, 3H), 2.43~2.37 (m, 2H), 2.27 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 175.3, 139.5, 135.0, 134.1, 132.5, 125.9, 124.0, 119.8, 116.7, 75.6, 67.9, 34.4, 29.5, 20.8, 18.9; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C15H20NO2 [M+H]+ 246.1489, found 246.1488.
3-(Allyloxy)-1-methylindolin-2-one (5o): Colorless oil, 61% yield (25 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.39 (d, J=7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.35~7.30 (m, 1H), 7.10~7.06 (m, 1H), 6.80 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.03~5.93 (m, 1H), 5.37~5.31 (m, 1H), 5.24~5.21 (m, 1H), 4.92 (s, 9H), 4.39~4.34 (m, 1H), 4.29~4.24 (m, 1H), 3.16 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.8, 144.3, 134.2, 130.1, 125.4, 125.3, 123.0, 118.2, 108.5, 74.9, 70.0, 26.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C12H14NO2 [M+H]+ 204.1019, found 204.1016.
1-Methyl-3-(pent-4-en-1-yloxy)indolin-2-one (5p): Colorless oil, 42% yield (19 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.38 (d, J=7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.08 (t, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.80 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.86~5.75 (m, 1H), 5.05~4.99 (m, 1H), 4.97~4.93 (m, 1H), 4.88 (s, 1H), 3.83~3.77 (m, 1H), 3.63~3.58 (m, 1H), 3.17 (s, 3H), 2.19~2.12 (m, 2H), 1.77~1.72 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.8, 144.3, 138.2, 130.0, 126.0, 125.3, 123.0, 115.0, 108.5, 76.0, 68.4, 30.3, 29.2, 26.2; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C14H18NO2 [M+H]+ 232.1332, found 232.1329.
1-Methyl-3-(penta-1,4-dien-3-yloxy)indolin-2-one (5q): Colorless oil, 48% yield (22 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.35~7.29 (m, 2H), 7.08~7.04 (m, 1H), 6.78 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.98~5.83 (m, 1H), 5.41~5.30 (m, 3H), 5.22~5.18 (m, 1H), 5.11 (t, J=6.8 Hz, 1H), 4.95 (s, 1H), 3.14 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 175.5, 144.3, 137.3, 136.7, 129.9, 126.0, 125.3, 122.9, 119.3, 117.1, 108.4, 81.1, 72.4, 26.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C14H16NO2 [M+H]+ 230.1176, found 230.1174.
1-Methyl-3-((2-methylallyl)oxy)indolin-2-one (5r): Colorless oil, 43% yield (19 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.37 (d, J=7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.07 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 1H), 6.79 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.06 (s, 1H), 4.94 (s, 1H), 4.89 (s, 1H), 4.22 (s, 2H), 3.16 (s, 3H), 1.81 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.8, 144.3, 141.6, 130.0, 125.4, 125.3, 122.9, 113.4, 108.4, 74.7, 72.9, 26.1, 19.7; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H16NO2 [M+H]+ 218.1176, found 278.1174.
1-Methyl-3-((3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)oxy)indolin-2-one (5s): Colorless oil, 44% yield (21 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.42 (d, J=7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.09 (td, J1=7.5, J2=1.0 Hz, 1H), 6.80 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.62 (d, J=1.3 Hz, 1H), 5.44 (s, 1H), 4.91 (s, 1H), 4.53~4.38 (m, 2H), 3.16 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.5, 144.3, 137.6, 130.3, 125.6, 124.8, 123.2, 115.2, 108.5, 74.5, 71.5, 26.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C12H12ClNNaO2 [M+Na]+ 260.0449, found 260.0452.
(E)-3-(But-2-en-1-yloxy)-1-methylindolin-2-one (5t): Colorless oil, 33% yield (14 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.38 (d, J=7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (t, J=7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.07 (td, J1=7.5, J2=1.0 Hz, 1H), 6.79 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.82~5.73 (m, 1H), 5.69~5.61 (m, 1H), 4.91 (s, 1H), 4.32~4.27 (m, 1H), 4.21~4.16 (m, 1H), 3.17 (s, 3H), 1.72~1.70 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 175.0, 144.3, 131.3, 130.0, 127.0, 125.5, 125.4, 123.0, 108.4, 74.7, 69.8, 26.1, 18.0; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C13H15NNaO2 [M+Na]+ 240.0995, found 240.0992.
1-Methyl-3-((3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)oxy)indolin-2-one (5u): Colorless oil, 41% yield (19 mg), Rf=0.6. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.39 (d, J=7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (t, J=7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.08 (t, J=7.6 Hz, 1H), 6.80 (d, J=7.7 Hz, 1H), 5.44~5.40 (m, 1H), 4.91 (s, 1H), 4.34~4.23 (m, 2H), 3.17 (s, 3H), 1.75 (s, 3H), 1.67 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 175.1, 144.4, 139.2, 129.9, 125.6, 125.4, 123.0, 120.4, 108.4, 74.7, 65.3, 26.1, 26.0, 18.2; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C14H17NNaO2 [M+Na]+ 254.1151, found 254.1144.
3-(Cyclopent-3-en-1-yloxy)-1-methylindolin-2-one (5v): Colorless oil, 41% yield (19 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.35~7.29 (m, 2H), 7.06 (td, J1=7.5, J2=1.0 Hz, 1H), 6.78 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.70 (s, 2H), 4.90~4.85 (m, 2H), 3.16 (s, 3H), 2.73~2.52 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 175.3, 144.1, 129.9, 128.8, 128.0, 126.0, 125.3, 123.0, 108.4, 79.6, 74.5, 40.4, 39.7, 26.2; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C14H15NNaO2 [M+Na]+ 252.0995, found 252.0991.
3-(Cyclopent-3-en-1-ylmethoxy)-1-methylindolin-2-one (5w): Colorless oil, 40% yield (19 mg), Rf=0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.38 (d, J=7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (t, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.09 (t, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.80 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.64 (s, 2H), 4.92 (s, 1H), 3.66 (t, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 3.48 (t, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 3.18 (s, 3H), 2.68~2.58 (m, 1H), 2.53~2.45 (m, 2H), 2.18~2.10 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 174.7, 144.3, 130.0, 129.7, 129.6, 125.3, 125.3, 123.0, 108.4, 76.1, 73.0, 67.4, 39.4, 37.0, 36.1, 36.1, 35.7, 26.2; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C15H17NNaO2 [M+ Na]+ 266.1151, found 266.1147.