化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (4): 319-327.DOI: 10.6023/A22120494 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
蒋江民a,b, 郑欣冉a, 孟雅婷a, 贺文杰d, 陈亚鑫a, 庄全超a, 袁加仁c,*( ), 鞠治成a,*(
), 鞠治成a,*( ), 张校刚b,*(
), 张校刚b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2022-12-12
发布日期:2023-03-28
基金资助:
Jiangmin Jianga,b, Xinran Zhenga, Yating Menga, Wenjie Hed, Yaxin Chena, Quanchao Zhuanga, Jiaren Yuanc,*( ), Zhicheng Jua,*(
), Zhicheng Jua,*( ), Xiaogang Zhangb,*(
), Xiaogang Zhangb,*( )
)
Received:2022-12-12
Published:2023-03-28
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

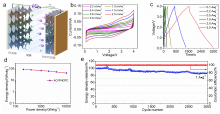
钾离子电容器是一种新型的电化学储能器件, 碳基材料被认为是最有前途的储钾候选材料之一. 然而, K+半径较大使得迁移速率缓慢, 脱嵌过程中材料的结构易破坏, 导致性能显著下降. 因此, 开发出低成本的碳材料来适应K+扩散的热力学与动力学需求, 已成为当前发展的瓶颈. 煤沥青是煤焦油经蒸馏提取液体馏分后得到的残余物, 它的组成主要为稠环芳烃, 具有高的含碳量、可塑性好、资源集中、价格低廉等显著优点, 是一种优质的碳基材料前驱体. 鉴于此, 本工作采用煤沥青作为碳源、聚四氟乙烯为氟源, 氯化钠为模板剂, 通过直接高温碳化的策略制备了氟氮共掺杂的多孔碳纳米片(FNCPC). 研究表明, 纳米片层的结构设计有效缩短了离子的传输路径, F、N共掺杂拓宽了碳的层间距, 缓解了体积膨胀问题, 并且形成更多的表面缺陷, 可为K+的存储提供更多的反应活性位点. 此外, 电化学动力学分析和密度泛函理论(DFT)表明, FNCPC具备显著的赝电容特性和强的对K吸附能. 得益于结构和化学性质的协同优化, FNCPC负极展现出优异的储钾能力(2 A•g-1电流密度下具有212.8 mAh•g-1的比容量)和循环稳定性. 进一步将商业化活性炭(AC)为正极, FNCPC为负极构筑了钾离子电容器(AC//FNCPC), 该器件能实现最大的能量密度为87.5 Wh•kg-1, 并且在循环3000次后具有86.1%的容量保持率, 展现出广阔的应用前景.
蒋江民, 郑欣冉, 孟雅婷, 贺文杰, 陈亚鑫, 庄全超, 袁加仁, 鞠治成, 张校刚. 氟氮共掺杂多孔碳纳米片的制备及其储钾性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(4): 319-327.
Jiangmin Jiang, Xinran Zheng, Yating Meng, Wenjie He, Yaxin Chen, Quanchao Zhuang, Jiaren Yuan, Zhicheng Ju, Xiaogang Zhang. Research on the Preparation and Potassium Storage Performance of F, N Co-doped Porous Carbon Nanosheets[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(4): 319-327.
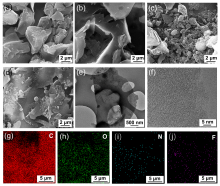

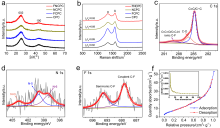

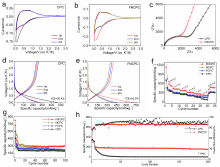

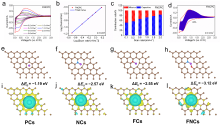


| [1] |
Wang, C.; Liu, T.; Yang, X.; Ge, S.; Stanley, N. V.; Rountree, E. S.; Leng, Y.; McCarthy, B. Nature 2022, 611, 485.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05281-0 |
| [2] |
Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Kintner-Meyer, M. C. W.; Lu, X.; Choi, D.; Lemmon, J. P.; Liu, J. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3577.
doi: 10.1021/cr100290v |
| [3] |
Bi, S.; Banda, H.; Chen, M.; Niu, L.; Chen, M.; Wu, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Feng, J.; Chen, T.; Dinca, M.; Kornyshev, A. A.; Feng, G. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 552.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0598-7 |
| [4] |
Chang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Yang, H.; Deng, H.; Zhu, X.; He, P.; Zhou, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 139. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20090442 |
|
(常智, 乔羽, 杨慧军, 邓瀚, 朱星宇, 何平, 周豪慎, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 139.)
doi: 10.6023/A20090442 |
|
| [5] |
Amatucci, G. G.; Badway, F.; Du Pasquier, A.; Zheng, T. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A930.
doi: 10.1149/1.1383553 |
| [6] |
Ding, J.; Hu, W.; Paek, E.; Mitlin, D. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6457.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00116 pmid: 29953230 |
| [7] |
Li, B.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Jin, L.; Yang, D.; Lv, H.; Shen, C.; Shellikeri, A.; Zheng, Y.; Gong, R.; Zheng, J. P.; Zhang, C. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705670.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.17 |
| [8] |
Aravindan, V.; Gnanaraj, J.; Lee, Y.; Madhavi, S. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11619.
doi: 10.1021/cr5000915 |
| [9] |
Naoi, K.; Ishimoto, S.; Miyamoto, J.; Naoi, W. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9363.
doi: 10.1039/c2ee21675b |
| [10] |
Shao, M.; Li, C.; Li, T.; Zhao, H.; Yu, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2006561.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v30.51 |
| [11] |
Gu, X.; Hong, Y.; Ai, G.; Wang, C.; Mao, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 644. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18020081 |
|
(顾晓瑜, 洪晔, 艾果, 王朝阳, 毛文峰, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 644.)
doi: 10.6023/A18020081 |
|
| [12] |
Wu, L.; Gu, M.; Feng, Y.; Chen, S.; Fan, L.; Yu, X.; Guo, K.; Zhou, J.; Lu, B. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2109893.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v32.8 |
| [13] |
Hu, Y.; Fan, L.; Rao, A. M.; Yu, W.; Zhuoma, C.; Feng, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lu, B. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac134.
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwac134 |
| [14] |
Fan, L.; Hu, Y.; Rao, A. M.; Zhou, J.; Hou, Z.; Wang, C.; Lu, B. Small Methods 2021, 5, 202101131.
|
| [15] |
Liu, S.; Kang, L.; Henzie, J.; Zhang, J.; Ha, J.; Amin, M. A.; Hossain, M. S. A.; Jun, S. C.; Yamauchi, Y. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18931.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c08428 |
| [16] |
Dong, S.; Lv, N.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Dong, X. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100455.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.21 |
| [17] |
Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y. A.; Wang, W. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131093.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131093 |
| [18] |
Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Deng, J.; Gou, Y.; Fang, J.; Cui, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shang, K. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 1974.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v14.9 |
| [19] |
Sajjad, M.; Cheng, F.; Lu, W. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25450.
doi: 10.1039/D1RA02445K |
| [20] |
Liu, M.; Chang, L.; Le, Z.; Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, C.; Xu, T.; Nie, P.; Wang, L. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 5837.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v13.22 |
| [21] |
Dong, Q.; Wu, F.; Bai, Y.; Wu, C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1461. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21060284 |
|
(董瑞琪, 吴锋, 白莹, 吴川, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1461.)
doi: 10.6023/A21060284 |
|
| [22] |
Vaalma, C.; Buchholz, D.; Passerini, S. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 9, 41.
|
| [23] |
Pramudita, J. C.; Sehrawat, D.; Goonetilleke, D.; Sharma, N. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602911.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v7.24 |
| [24] |
Eftekhari, A.; Jian, Z.; Ji, X. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 4404.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b07989 |
| [25] |
Fan, L.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, X.; Lu, B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10500.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.31 |
| [26] |
Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zang, X.; Zhai, D.; Kang, F. Batteries & Supercaps 2021, 4, 554.
|
| [27] |
Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Xing, Z.; Lam, C. W. K.; Pang, S.; Zhang, W.; Ju, Z. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900343.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v9.21 |
| [28] |
Ye, J.; Simon, P.; Zhu, Y. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 191.
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz140 |
| [29] |
Kumar, R.; Sahoo, S.; Joanni, E.; Singh, R. K.; Kar, K. K. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 20306.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c15934 |
| [30] |
Ding, H.; Zhou, J.; Rao, A. M.; Lu, B. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa276.
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa276 |
| [31] |
Li, S.; Deng, H.; Chu, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lu, B. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 50005.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c15524 |
| [32] |
Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, W.; Zheng, Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Shi, J.; Shi, Z.; Mitlin, D. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1652.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c09290 |
| [33] |
Deng, H.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, S.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Lu, B. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2107246.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.51 |
| [34] |
Yuan, F.; Sun, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 611, 513.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.12.121 |
| [35] |
Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Shi, K.; Li, J.; Jian, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Wu, M.; Dang, H.; Liu, Q. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 14401.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.2c02965 |
| [36] |
Liu, M.; Chang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Pang, G.; Wang, H.; Nie, P.; Zhao, C.; Xu, T.; Wang, L. J. Power Sources 2020, 469, 228415.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228415 |
| [37] |
Li, Z.; Lin, J.; Li, B.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Li, Q. J. Energy Storage 2021, 44, 103437.
doi: 10.1016/j.est.2021.103437 |
| [38] |
Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, T.; Miao, Y.; Qi, J.; Sui, Y.; Meng, Q.; Wei, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, P. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 6339.
doi: 10.1039/D2NR01110G |
| [39] |
Gao, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Yu, L.; Peng, B.; El-Harairy, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6255.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c00140 |
| [40] |
Ghosh, S.; Barg, S.; Jeong, S. M.; Ostrikov, K. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001239.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v10.32 |
| [41] |
Huang, L.; Luo, Z.; Luo, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Shi, K.; Zhu, S. J. Energy Storage 2021, 38, 102509.
doi: 10.1016/j.est.2021.102509 |
| [42] |
Wang, P.; Gong, Z.; Wang, D.; Hu, R.; Ye, K.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, K.; Yan, J.; Wang, G.; Cao, D. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 389, 138799.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138799 |
| [43] |
Zhang, T.; Mao, Z.; Shi, X.; Jin, J.; He, B.; Wang, R.; Gong, Y.; Wang, H. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 158.
doi: 10.1039/D1EE03214C |
| [44] |
Guo, W.; Geng, C.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, J.; Ju, Z. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 623, 1075.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.05.073 |
| [45] |
Chen, Y.; Xi, B.; Huang, M.; Shi, L.; Huang, S.; Guo, N.; Li, D.; Ju, Z.; Xiong, S. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108621.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v34.7 |
| [46] |
Huang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Peng, Z.; Qi, R.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706294.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v28.10 |
| [47] |
Jiang, J.; Yuan, J; Nie, P.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, C.; He, W.; Zhang, T.; Dou, H.; Zhang, X. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 3956.
doi: 10.1039/C9TA08676E |
| [48] |
Wei, F.; He, X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, N.; Qiu, J. Nano Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 1.
|
| [49] |
Li, S.; Liu, P.; Zheng, X.; Wu, M. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 428, 140921.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2022.140921 |
| [50] |
Ghosh, S.; Bhattacharjee, U.; Patchaiyappan, S.; Nanda, J.; Dudney, N. J.; Martha, S. K. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100135.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v11.17 |
| [51] |
Na, W.; Jun, J.; Park, J. W.; Lee, G.; Jang, J. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17379.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA04406B |
| [52] |
Jiang, J.; Nie, P.; Ding, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Wu, L.; Dou, H.; Zhang, X. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 23283.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA05972H |
| [53] |
Sim, Y.; Kim, S. J.; Janani, G.; Chae, Y.; Surendran, S.; Kim, H.; Yoo, S.; Seok, D. C.; Jung, Y. H.; Jeon, C.; Moon, J.; Sim, U. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 507, 145157.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.145157 |
| [54] |
Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Cheng, X.; Huang, H.; Shi, P.; Yao, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Q.; Feng, Y.; Rui, X.; Yu, Y. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 10217.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c02275 |
| [55] |
Lu, X.; Pan, X.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Shao, G.; Fu, D.; Teng, J.; Yang, W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 41619.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c10655 |
| [56] |
Zhuang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y. Prog. Chem. 2020, 32, 761.
|
| [57] |
Shen, L.; Lv, H.; Chen, S.; Kopold, P.; van Aken, P. A.; Wu, X.; Maier, J.; Yu, Y. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700142.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.27 |
| [58] |
Le, Z.; Liu, F.; Nie, P.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Bian, Z.; Chen, G.; Wu, H. B.; Lu, Y. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2952.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b08332 |
| [59] |
Valencia, F.; Romero, A. H.; Ancilotto, F.; Silvestrelli, P. L. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 14832.
doi: 10.1021/jp062126+ |
| [60] |
Jin, L.; Shen, C.; Shellikeri, A.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, J.; Andrei, P.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, J. P. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 2341.
doi: 10.1039/D0EE00807A |
| [61] |
Li, J.; Hu, X.; Zhong, G.; Liu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Chen, J.; Wen, Z. Nano Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 1.
|
| [1] | 李燕丽, 于丹丹, 林森, 孙东飞, 雷自强. α-MnO2纳米棒/多孔碳正极材料的制备及水系锌离子电池性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 200-207. |
| [2] | 赵婧, 龚俊伟, 李一举, 程魁, 叶克, 朱凯, 闫俊, 曹殿学, 王贵领. 自掺杂氮多孔交联碳纳米片在超级电容器中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(2): 107-112. |
| [3] | 唐典勇, 胡建平, 吕申壮, 孙国峰, 张元勤. CO 在M55 (M=Cu, Ag, Au)团簇上吸附的密度泛函研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(08): 943-948. |
| [4] | 赵新新, 陶向明, 宓一鸣, 吴建宝, 汪丽莉, 谭明秋. 钡原子对Ru(0001)表面氮分子吸附和解离过程的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(19): 2201-2206. |
| [5] | 徐信, 李志强, 张荻, 陈志新. 以苯为模块自组装合成碳纳米片[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(12): 1205-1209. |
| [6] | 王三跃, 阳庆元, 仲崇立. 柔性金属-有机骨架材料中甲醇吸附和扩散的分子模拟[J]. 化学学报, 2006, 64(17): 1775-1779. |
| [7] | 王文宁,范康年,邓景发. 分子态氧在Ag(110)面上的吸附构型、吸附态和吸附能的CM和DAM从头算研究[J]. 化学学报, 1995, 53(10): 1000-1004. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||