化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (10): 1448-1462.DOI: 10.6023/A22060276 上一篇
综述
朱凤巧a, 王文贵a, 瞿旭东b,*( ), 王守锋a,*(
), 王守锋a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2022-06-27
发布日期:2022-08-09
通讯作者:
瞿旭东, 王守锋
作者简介: |
朱凤巧, 女, 济南大学化学化工学院在读硕士研究生, 主要从事硫肽类抗生素化学半合成修饰研究. |
 |
王文贵, 男, 济南大学化学化工学院讲师, 硕士生导师, 毕业于中国科学院上海有机化学研究所. 承担山东省自然基金面上项目、山东省重点研发项目以及企业委托研发等项目. 主要从事有机氟化学研究, 包括单电子转移、金属催化、可见光催化的含氟化合物的合成、氟利昂的转化及天然产物的修饰等. |
 |
瞿旭东, 男, 上海交通大学生命科学技术学院教授, 博士生导师, 毕业于中国科学院上海有机化学研究所, 美国麻省理工学院化学系博士后. 国家自然科学基金“优秀青年科学基金”获得者、教育部“新世纪优秀人才支持计划”、武汉大学“珞珈学者特聘教授”. 承担国家自然基金面上项目、国家重点研发计划. 主要研究天然产物碳骨架的生物合成与编辑: 研究聚酮、含氮杂环和甾体三大类药用分子碳骨架的形成机制, 发展高效的生物合成方法用于碳骨架合成和结构修饰, 开发创新药物和实现药物的高效生产, 解决新药研发和工业生产过程中的瓶颈问题. |
 |
王守锋, 男, 济南大学化学化工学院教授, 济南大学化学化工学院化学系系主任, 博士生导师, 毕业于中国科学院上海有机化学研究所, 英国曼彻斯特大学访问学者. 承担国家自然基金面上项目、国家自然基金青年基金、“973”项目子课题、山东省自然基金面上项目、山东省重点研发项目以及企业委托研发等项目. 主要研究天然产物修饰: 抗生素的半合成, 药物化学生物学: 抗生素的传输, 以及含氟精细化学品的合成. 在含氟化合物的合成、复杂天然产物的生物合成及其类似物的突变生物合成研究中取得一系列成果. |
基金资助:
Fengqiao Zhua, Wengui Wanga, Xudong Qub( ), Shoufeng Wanga(
), Shoufeng Wanga( )
)
Received:2022-06-27
Published:2022-08-09
Contact:
Xudong Qu, Shoufeng Wang
Supported by:文章分享
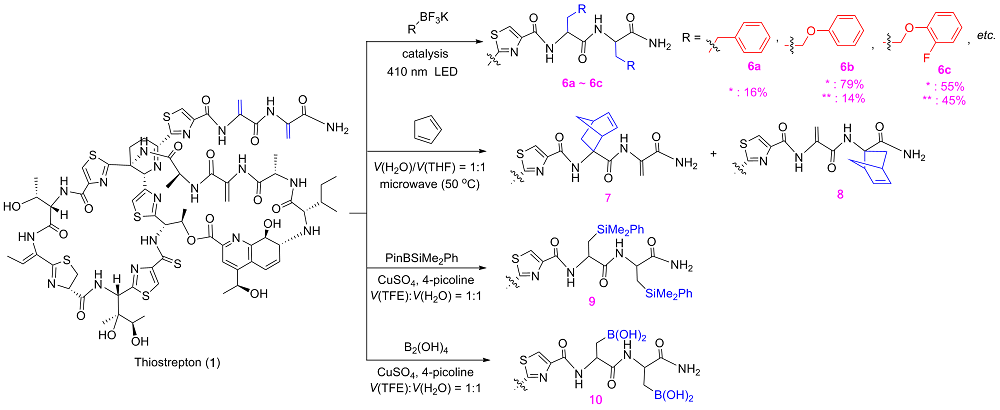
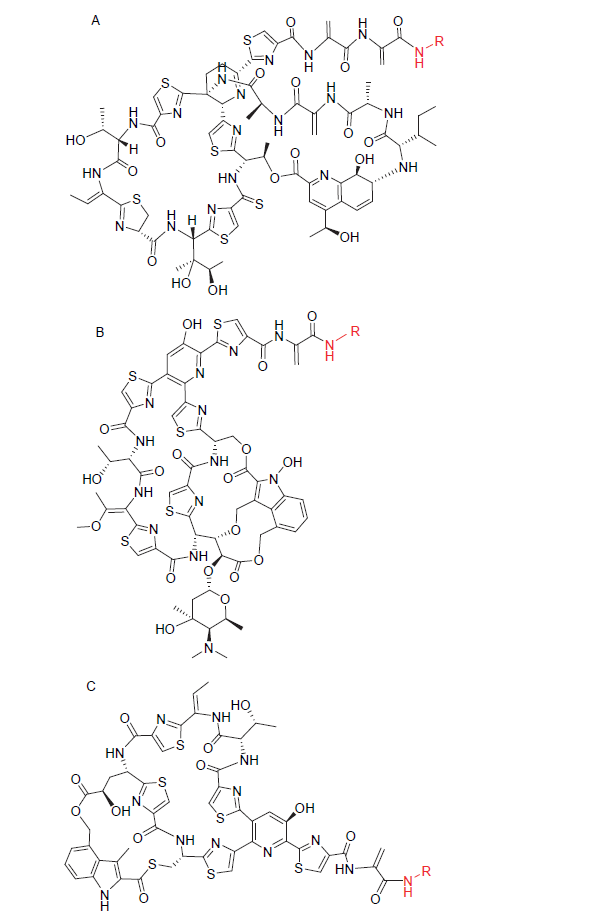
硫肽类抗生素是一类由微生物次级代谢产生、富含硫元素并且氨基酸残基被高度修饰的核糖体肽类天然产物. 硫肽类抗生素具有包括抗感染、抗肿瘤和免疫抑制在内的一系列十分重要的生物活性, 并且其以核糖体为靶点的作用机制与目前临床上普遍使用的抗生素均不同, 这使得硫肽类抗生素发展潜力巨大, 但是其水溶性差、生物利用度低等问题限制了它们在临床上的应用. 为了提高硫肽类抗生素的理化性质, 研究者尝试用化学半合成、组合生物合成以及前体导向突变生物合成等方法对硫肽类抗生素的结构进行修饰. 硫肽类抗生素本身具有的复杂结构为其化学半合成修饰提供了众多的可修饰位点. 近年来, 对于硫肽类抗生素的化学半合成修饰研究发展迅速. 综述了近十年通过化学半合成修饰方法获得的硫肽类抗生素类似物的研究进展.
朱凤巧, 王文贵, 瞿旭东, 王守锋. 硫肽类抗生素化学半合成修饰研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1448-1462.
Fengqiao Zhu, Wengui Wang, Xudong Qu, Shoufeng Wang. Research Progress in Chemical Semi-synthetic Modification of Thiopeptide Antibiotics[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(10): 1448-1462.
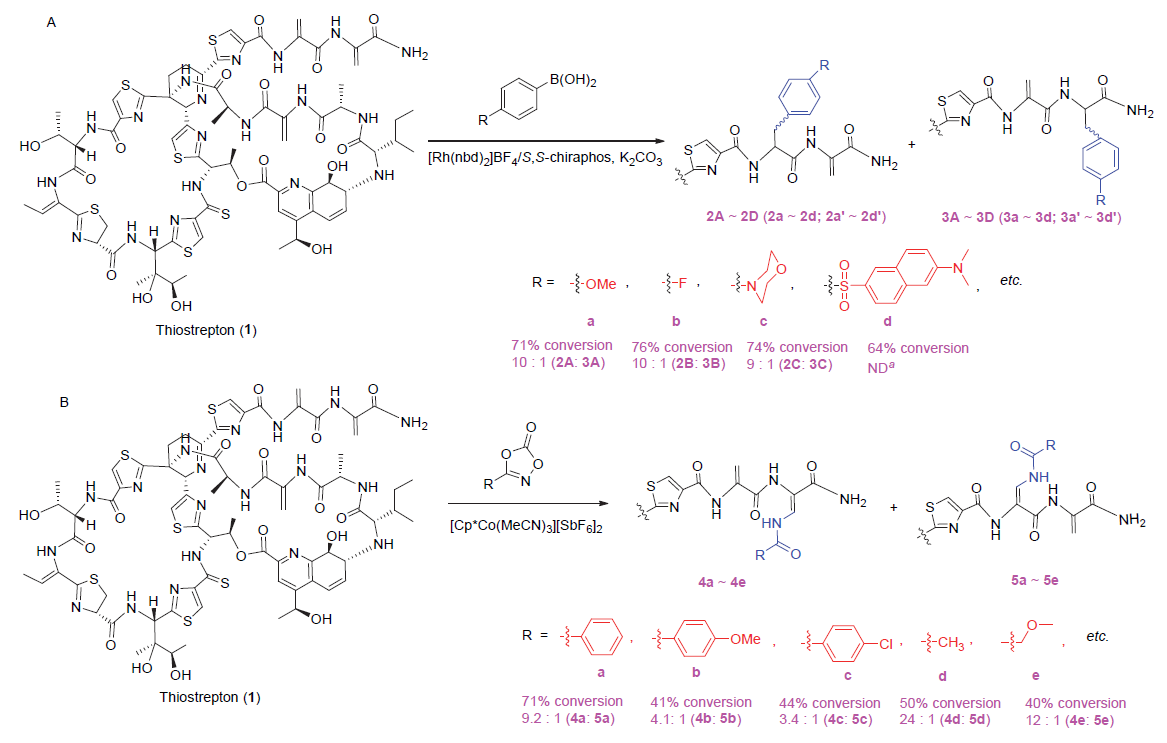
| Condition | Additive | Conversions to 2A+3B (2A∶3B) | d.r. (2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | 22% (10∶1) | 1∶1 |
| 2 | K2CO3 | 62% (5∶1) | 3∶1 |
| 3 | Na2CO3 | 84% (9∶1) | 4∶1 |
| 4 | KCl | 30% (8∶1) | 3∶1 |
| 5 | NaCl | 43% (8∶1) | 3∶1 |
| Condition | Additive | Conversions to 2A+3B (2A∶3B) | d.r. (2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | 22% (10∶1) | 1∶1 |
| 2 | K2CO3 | 62% (5∶1) | 3∶1 |
| 3 | Na2CO3 | 84% (9∶1) | 4∶1 |
| 4 | KCl | 30% (8∶1) | 3∶1 |
| 5 | NaCl | 43% (8∶1) | 3∶1 |
| Condition | Additive | Conversions | e.r. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | >99% | 83∶17 |
| 2 | K2CO3 | 95% | 10∶90 |
| 3 | Na2CO3 | 98% | 9∶91 |
| 4 | KCl | 18% | 15∶85 |
| 5 | NaCl | 42% | 21∶79 |
| Condition | Additive | Conversions | e.r. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | >99% | 83∶17 |
| 2 | K2CO3 | 95% | 10∶90 |
| 3 | Na2CO3 | 98% | 9∶91 |
| 4 | KCl | 18% | 15∶85 |
| 5 | NaCl | 42% | 21∶79 |
| Compound | MICa/(µg•mL–1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. faecalis | S. pneumoniae | S. pyogenes | |
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 2a | 1 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.004 |
| 2a’ | 0.5 | 1 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 2b | 1 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
| 2b’ | 2 | 2 | 0.015 | 0.008 |
| 2c | 4 | 2 | 0.015 | 0.015 |
| 2c’ | 2 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.004 |
| 2d | 32 | 4 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 2d’ | 64 | 4 | 0.015 | 0.015 |
| 4a | 2 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.002 |
| 4b | 2 | 2 | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| 4c | 0.5 | 0.25 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| 4d | 4 | 4 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| 4e | 1 | 1 | 0.015 | 0.00 |
| Compound | MICa/(µg•mL–1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. faecalis | S. pneumoniae | S. pyogenes | |
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 2a | 1 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.004 |
| 2a’ | 0.5 | 1 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 2b | 1 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
| 2b’ | 2 | 2 | 0.015 | 0.008 |
| 2c | 4 | 2 | 0.015 | 0.015 |
| 2c’ | 2 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.004 |
| 2d | 32 | 4 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 2d’ | 64 | 4 | 0.015 | 0.015 |
| 4a | 2 | 1 | 0.008 | 0.002 |
| 4b | 2 | 2 | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| 4c | 0.5 | 0.25 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| 4d | 4 | 4 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| 4e | 1 | 1 | 0.015 | 0.00 |
| Compound | Solubilitya/(μg•mL–1) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3.0±0.2 |
| 4a | <1.0 |
| 4c | <1.0 |
| 4d | 83±5 |
| 4e | 28±4 |
| Compound | Solubilitya/(μg•mL–1) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3.0±0.2 |
| 4a | <1.0 |
| 4c | <1.0 |
| 4d | 83±5 |
| 4e | 28±4 |
| Compound | MICa/(µg•mL–1) | Solubility/(µg•mL–1) in ddH2O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. faecalis | ||
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 6.4±0.1 |
| 7 | 2 | 2 | —b |
| 8 | 2 | 1 | —b |
| 10 | 64 | 64 | 169.7±2.6 (27×c) |
| Compound | MICa/(µg•mL–1) | Solubility/(µg•mL–1) in ddH2O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. faecalis | ||
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 6.4±0.1 |
| 7 | 2 | 2 | —b |
| 8 | 2 | 1 | —b |
| 10 | 64 | 64 | 169.7±2.6 (27×c) |
| NR1R2 | MICa/(µg•mL–1) | PD50b/(mg•kg–1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus A15090 | S. pneumo A28272 | E. faecalis A20688 | ||
| 35 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 2 | 1.65 |
| | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.06 | 4.35 |
| | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 5 |
| | 0.5 | 0.125 | 1 | >10 |
| NR1R2 | MICa/(µg•mL–1) | PD50b/(mg•kg–1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus A15090 | S. pneumo A28272 | E. faecalis A20688 | ||
| 35 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 2 | 1.65 |
| | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.06 | 4.35 |
| | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 5 |
| | 0.5 | 0.125 | 1 | >10 |
| Compound | MICa/(µg•mL–1) | Yield/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. faecalis | ATCC 25923 | ||
| Nosiheptide (47) | 0.0078 | 0.031 | 0.062 | — |
| 56 | <0.0039 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 91 |
| 57 | <0.0039 | 0.0078 | 0.030 | 87 |
| 58 | 0.015 | 0.031 | 0.031 | 90 |
| 59 | <0.0039 | 0.015 | 0.031 | 83 |
| 60 | <0.0039 | 0.015 | 0.031 | 92 |
| Compound | MICa/(µg•mL–1) | Yield/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. faecalis | ATCC 25923 | ||
| Nosiheptide (47) | 0.0078 | 0.031 | 0.062 | — |
| 56 | <0.0039 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 91 |
| 57 | <0.0039 | 0.0078 | 0.030 | 87 |
| 58 | 0.015 | 0.031 | 0.031 | 90 |
| 59 | <0.0039 | 0.015 | 0.031 | 83 |
| 60 | <0.0039 | 0.015 | 0.031 | 92 |
| [1] |
Furusawa, C.; Horinouchi, T.; Maeda, T. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 54, 45.
doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2018.01.026 |
| [2] |
Arias, C. A.; Murray, B. E. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 266.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2761 |
| [3] |
Isenman, H.; Fisher, D. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 577.
doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000311 |
| [4] |
Su, T. L. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1948, 29, 473.
|
| [5] |
Nicolaou, K. C.; Dethe, D. H.; Chen, Y. K. Chem. Commun. 2008, 23, 2632.
|
| [6] |
Just-Baringo, X.; Bruno, P.; Ottesen, L. K.; Cañedo, L. M.; Albericio, F.; Álvarez, M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7818.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201302372 |
| [7] |
Okumura, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Shin, C. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1999, 72, 1561.
doi: 10.1246/bcsj.72.1561 |
| [8] |
Wang, N.; Saidhareddy, P.; Jiang, X. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 246.
doi: 10.1039/C8NP00093J |
| [9] |
Liao, Y.; Jiang, X. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 8862.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c03370 |
| [10] |
Luo, X.; Zambaldo, C.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xuan, W.; Wang, C.; Reed, S. A.; Yang, P.-Y.; Wang, R. E.; Javahishvili, T. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2016, 113, 3615.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1602733113 |
| [11] |
Bowers, A. A.; Acker, M. G.; Koglin, A.; Walsh, C. T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7519.
doi: 10.1021/ja102339q |
| [12] |
Bowers, A. A.; Acker, M. G.; Young, T. S.; Walsh, C. T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10313.
doi: 10.1021/ja302820x |
| [13] |
Zhang, Q.; Chen, D.; Lin, J.; Liao, R.; Tong, W.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21287.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.224832 pmid: 21454624 |
| [14] |
Duan, L.; Wang, S.; Liao, R.; Liu, W. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 443.
doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.02.008 |
| [15] |
Wang, S.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, W. Org. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 106.
doi: 10.1039/C4QO00288A |
| [16] |
Bagley, M. C.; Dale, J. W.; Merritt, E. A.; Xiong, X. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 685.
pmid: 15700961 |
| [17] |
Hensens, O. D.; Albers-Schonberg, G. J. Antibiot. 1983, 36, 814.
pmid: 6885636 |
| [18] |
Miyairi, N.; Mlyoshi, T.; Aoki, H.; Kohsaka, M.; Ikushima, H.; Kunugita, K.; Sakai, H.; Imanaka, H. J. Antibiot. 1970, 23, 113.
pmid: 5453305 |
| [19] |
Donovick, R.; Pagano, J.; Stout, H.; Weinstein, M. Antibiot. Annu. 1955, 3, 554.
|
| [20] |
Shoji, J. I.; Hinoo, H.; Wakisaka, Y.; Koizumi, K.; Mayama, M.; Matsuura, S.; Matsumoto, K. J. Antibiot. 1976, 29, 366.
pmid: 819410 |
| [21] |
Benazet, F.; Cartier, M.; Florent, J.; Godard, C.; Jung, G.; Lunel, J.; Mancy, D.; Pascal, C.; Renaut, J.; Tarridec, P. Experientia 1980, 36, 414.
pmid: 7379912 |
| [22] |
Li, J.; Qu, X.; He, X.; Duan, L.; Wu, G.; Bi, D.; Deng, Z.; Liu, W.; Ou, H. Y. PLoS One 2012, 7, e45878.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045878 |
| [23] |
Xing, Y.; Draper, D. E. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 1581.
pmid: 8634289 |
| [24] |
Harms, J. M.; Wilson, D. N.; Schluenzen, F.; Connell, S. R.; Fucini, P. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 26.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.009 |
| [25] |
Anborgh, P. H.; Parmeggiani, A. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 779.
doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08009.x pmid: 2009857 |
| [26] |
Parmeggiani, A.; Krab, I. M.; Okamura, S.; Nielsen, R. C.; Nissen, P. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 6846.
pmid: 16734421 |
| [27] |
Zheng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Gao, Q.; Liu, W. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 1002.
doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.06.019 |
| [28] |
Bhat, U. G.; Halasi, M.; Gartel, A. L. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6593.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006593 |
| [29] |
Rogers, M. J.; Cundliffe, E.; Mccutchan, T. F. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 715.
pmid: 9517961 |
| [30] |
Key, H. M.; Miller, S. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15460.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b08775 |
| [31] |
Scamp, R. J.; Deramon, E.; Paulson, E. K.; Miller, S. J.; Ellman, J. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 890.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201911886 |
| [32] |
Richter, M. F.; Drown, B. S.; Riley, A. P.; Garcia, A.; Shirai, T.; Svec, R. L.; Hergenrother, P. J. Nature 2017, 545, 299.
doi: 10.1038/nature22308 |
| [33] |
Bruijn, A. D.; Roelfes, G. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 11314.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201803144 |
| [34] |
Vries, R. H. D.; Viel, J. H.; Oudshoorn, R.; Kuipers, O. P.; Roelfes, G. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 12698.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201902907 |
| [35] |
Mortensen, M.; Husmann, R.; Veri, E.; Bolm, C. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1002.
doi: 10.1039/b816769a pmid: 19421578 |
| [36] |
Rémond, E.; Martin, C.; Martinez, J.; Cavelier, F. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 11654.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00122 |
| [37] |
Pujals, S.; Fernández-Carneado, J.; Kogan, M. J.; Martinez, J.; Cavelier, F.; Giralt, E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8479.
doi: 10.1021/ja060036c |
| [38] |
Zhan, B.-B.; Fan, J.; Jin, L.; Shi, B.-F. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 11058.
|
| [39] |
Vries, R. H. D.; Viel, J. H.; Kuipers, O. P.; Roelfes, G. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 11058.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC05026A |
| [40] |
Stubelius, A.; Lee, S.; Almutairi, A. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 3108.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00292 |
| [41] |
Vries, R. H. D.; Viel, J. H.; Kuipers, O. P.; Roelfes, G. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3946.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202011460 |
| [42] |
Jonker, H.; Baumann, S.; Wolf, M. A.; Schoof, S.; Hiller, D.; Schulte, K. W.; Kirschner, K. N.; Schwalbe, P.; Arndt, H. D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3308.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201003582 |
| [43] |
Hegde, N. S.; Sanders, D.; Rodriguez, R.; Balasubramanian, S. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 829.
|
| [44] |
Clough, J.; Chen, S.; Gordon, E. M.; Hackbarth, C.; Lam, S.; Trias, J.; White, R. J.; Candiani, G.; Donadio, S.; Romanò, G.; Ciabatti, R.; Jacobs, J. W. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 3409.
doi: 10.1016/S0960-894X(03)00811-4 |
| [45] |
LaMarche, M. J.; Leeds, J. A.; Dzink-Fox, J.; Mullin, S.; Patane, M. A.; Rann, E. M.; Tiamfook, S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 3210.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.04.048 pmid: 21550238 |
| [46] |
LaMarche, M. J.; Leeds, J. A.; Amaral, K.; Brewer, J. T.; Bushell, S. M.; Dewhurst, J. M.; Dzink-Fox, J.; Gangl, E.; Goldovitz, J.; Jain, A. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8099.
doi: 10.1021/jm200938f pmid: 21999529 |
| [47] |
LaMarche, M. J.; Leeds, J. A.; Amaral, A.; Brewer, J. T.; Bushell, S. M.; Deng, G.; Dewhurst, J. M.; Ding, J.; Dzink-Fox, J.; Gamber, G. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 2376.
|
| [48] |
Fabbretti, A.; He, C.-G.; Gaspari, E.; Maffioli, S.; Brandi, L.; Spurio, R.; Sosio, M.; Jabes, D.; Donadio, S. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4560.
doi: 10.1128/AAC.05155-14 pmid: 25987631 |
| [49] |
LaMarche, M. J.; Leeds, J. A.; Dzink-Fox, J.; Gangl, E.; Krastel, P.; Neckermann, G.; Palestrant, D.; Patane, M. A.; Rann, E. M.; Tiamfook, S. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6934.
doi: 10.1021/jm300783c pmid: 22812377 |
| [50] |
Bower, J.; Drysdale, M.; Hebdon, R.; Jordan, A.; Lentzen, G.; Matassova, N.; Murchie, A.; Powles, J.; Roughley, S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 2455.
doi: 10.1016/S0960-894X(03)00495-5 |
| [51] |
Naidu, B. N.; Sorenson, M. E.; Bronson, J. J.; Pucci, M. J.; Clark, J. M.; Ueda, Y. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 2069.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.02.046 |
| [52] |
Naidu, B. N.; Sorenson, M. E.; Matiskella, J. D.; Li, W.; Sausker, J. B.; Zhang, Y.; Connolly, T. P.; Lam, K. S.; Bronson, J. J.; Pucci, M. J. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 3545.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.03.079 |
| [53] |
Xu, L.; Farthing, A. K.; Shi, Y.-J.; Meinke, P. T.; Liu, K. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 7447.
doi: 10.1021/jo071115p |
| [54] |
Xu, L.; Farthing, A. K.; Dropinski, J. F.; Meinke, P. T.; McCallum, C.; Leavitt, P. S.; Hickey, E. J.; Colwell, L.; Barrett, J.; Liu, K. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3531.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.04.144 |
| [55] |
Sokolovsky, M.; Wilchek, M.; Patchornik, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1202.
doi: 10.1021/ja01060a048 |
| [56] |
Regueiro-Ren, A.; Ueda, Y. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 8699.
pmid: 12444665 |
| [57] |
Xu, L.; Farthing, A. K.; Dropinski, J. F.; Meinke, P. T.; McCallum, C.; Hickey, E.; Liu, K. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 366.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.10.065 |
| [58] |
Regueiro-Ren, A.; Naidu, B. N.; Zheng, X.; Hudyma, T. W.; Connolly, T. P.; Matiskella, J. D.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, O. K.; Sorenson, M. E.; Pucci, M. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 171.
pmid: 14684322 |
| [59] |
Connolly, T. P.; Regueiro-Ren, A.; Leet, J. E.; Springer, D. M.; Goodrich, J.; Huang, X.; Pucci, M. J.; Clark, J. M.; Bronson, J. J.; Ueda, Y. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 550.
|
| [60] |
Somei, M.; Tsuchiya, M. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 3145.
doi: 10.1248/cpb.29.3145 |
| [61] |
Fan, Y.; Chen, H.; Mu, N.; Wang, W.; Zhu, K.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 31, 115970.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115970 |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||