化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (12): 1583-1591.DOI: 10.6023/A22070304 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
郭湾a, 胡聪意a, 甄淑君a, 黄承志b, 李原芳a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2022-07-13
发布日期:2022-11-04
通讯作者:
李原芳
基金资助:
Wan Guoa, Congyi Hua, Shujun Zhena, Chengzhi Huangb, Yuanfang Lia( )
)
Received:2022-07-13
Published:2022-11-04
Contact:
Yuanfang Li
Supported by:文章分享

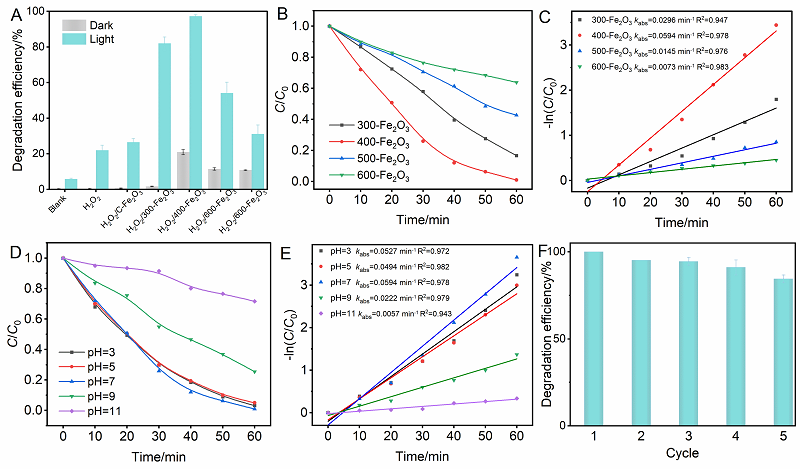
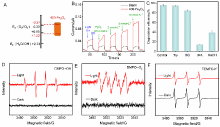
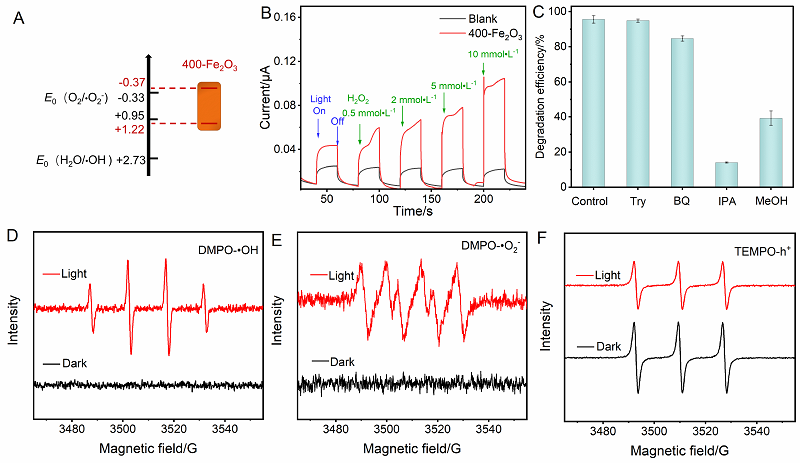
光催化剂在工业废水处理中发挥着重要作用. 本工作以室温下一步合成的片状铁基金属有机凝胶(Fe-based Metal-organic gel, Fe-MOG)为前驱体, 在不同温度下煅烧得到了片状(300-Fe2O3和400-Fe2O3)和球形(500-Fe2O3和600-Fe2O3)两种形貌的衍生三氧化二铁(Fe2O3). 通过一系列测试手段对衍生Fe2O3的晶体结构和光电性能进行了表征. 其中, 具有碳骨架结构的400-Fe2O3因其优良的电子传输性能和较高的光生电荷分离效率表现出优异的光催化活性, 可在中性条件下60 min内光降解97.5%的罗丹明B (Rh B), 并且在连续五次循环实验后其降解效率仍能达到85.3%. 本工作为开发和设计具有优异催化活性的半导体光催化剂提供了新的思路.
郭湾, 胡聪意, 甄淑君, 黄承志, 李原芳. 铁基金属有机凝胶衍生的三氧化二铁纳米片用于光芬顿降解罗丹明B[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(12): 1583-1591.
Wan Guo, Congyi Hu, Shujun Zhen, Chengzhi Huang, Yuanfang Li. Iron-based Metal-organic gel-derived Ferric oxide Nanosheets for Photo-Fenton Degradation of Rhodamine B[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(12): 1583-1591.
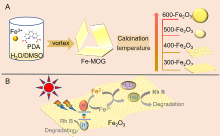
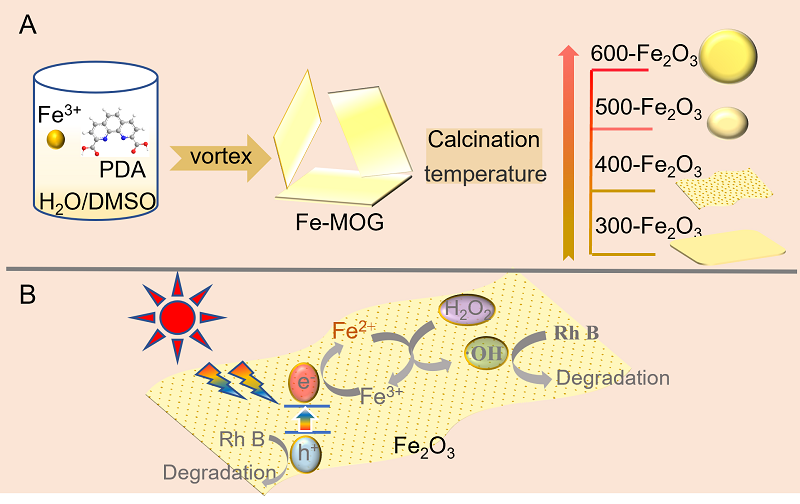
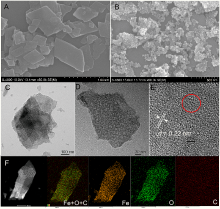

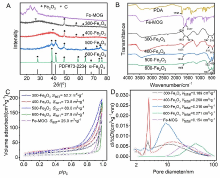

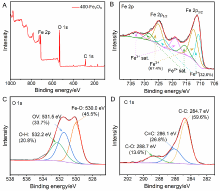
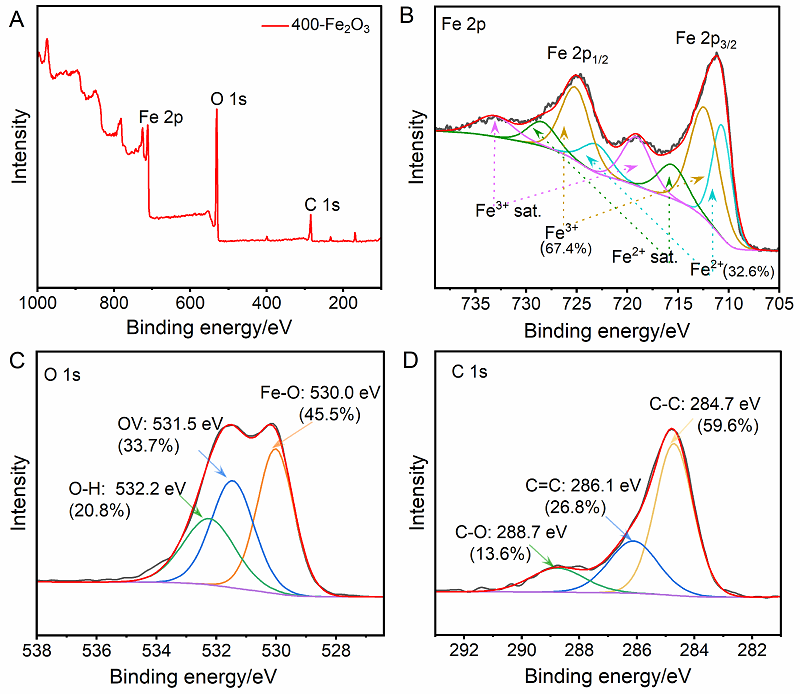
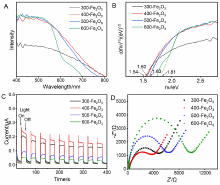

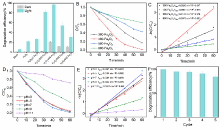
| [1] |
Xie, M.; Dai, F.; Li, J.; Dang, X.; Guo, J.; Lv, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, X. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 14370.
|
| [2] |
Zhao, J. J.; Zhang, Z. Z.; Chen, X. L.; Wang, B.; Deng, J. Y.; Zhang, D. Q.; Li, H. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 961. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 赵晶晶, 张正中, 陈小浪, 王蓓, 邓近远, 张蝶青, 李和兴, 化学学报 2020, 78, 961.)
doi: 10.6023/A20060244 |
|
| [3] |
Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.-P.; Wu, W. D.; Wu, Z. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 15513.
|
| [4] |
Cheng, M.; Lai, C.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Zhang, C.; Qin, L.; Hu, L.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, W. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 368, 80.
|
| [5] |
Mesquita, A. M.; Guimarães, I. R.; Castro, G. M. M. d.; Gonçalves, M. A.; Ramalho, T. C.; Guerreiro, M. C. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2016, 192, 286.
|
| [6] |
Bui, V. K. H.; Park, D.; Pham, T. N.; An, Y.; Choi, J. S.; Lee, H. U.; Kwon, O. H.; Moon, J. Y.; Kim, K. T.; Lee, Y. C. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11855.
|
| [7] |
Ma, Y. L.; Liu, R. X.; Meng, S. Y.; Niu, L. T.; Yang, Z. W.; Lei, Z. Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 153. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 马亚丽, 刘茹雪, 孟双艳, 牛力同, 杨志旺, 雷自强, 化学学报 2019, 77, 153.)
doi: 10.6023/A18090372 |
|
| [8] |
Sahoo, D. P.; Rath, D.; Nanda, B.; Parida, K. M. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 83707.
|
| [9] |
Yang, F.; Zhou, L.; Dong, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, S.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, A.; Chen, J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19803.
|
| [10] |
Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Walter, E.; Zong, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qafoku, O.; Wang, Z.; Rosso, K. M. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10197.
|
| [11] |
Sun, J.; Xia, W.; Zheng, Q.; Zeng, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, G.; Wang, P. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12339.
|
| [12] |
Wang, T.; Ge, T.; Zhang, Y. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 44, 100504.
|
| [13] |
Niu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, F.; Yang, L.; Chen, Z.; Bai, Z. Nano Energy 2021, 82, 105699.
|
| [14] |
Liu, H.; Li, J. Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, G. Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, L. F.; Qi, H.; Duo, S. W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1293. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 刘欢, 李京哲, 李平, 张广智, 徐迅, 张豪, 邱灵芳, 齐晖, 多树旺, 化学学报 2021, 79, 1293.)
doi: 10.6023/A21060265 |
|
| [15] |
Popov, N.; Ristić, M.; Bošković, M.; Perović, M.; Musić, S.; Stanković, D.; Krehula, S. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 161, 110372.
|
| [16] |
Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; McPherson, G. L.; John, V. T. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39049.
|
| [17] |
Xu, W.; Xue, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhong, C.; Mei, D. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2021, 291, 120129.
|
| [18] |
You, D.; Shi, H.; Xi, Y.; Shao, P.; Yang, L.; Yu, K.; Han, K.; Luo, X. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125359.
|
| [19] |
Wang, H.; Chen, B. H.; Liu, D. J. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008023.
|
| [20] |
Cao, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Feng, C.; Huang, C.; Li, Y. Talanta 2021, 221, 121616.
|
| [21] |
Wu, Q.; He, L.; Jiang, Z. W.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z. M.; Huang, C. Z.; Li, Y. F. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111704.
|
| [22] |
Wang, H.; Cheng, X.; Yin, F.; Chen, B.; Fan, T.; He, X. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 232, 114.
|
| [23] |
Liu, S. T.; Ji, H. F.; Pan, G. F. Chinese Ceramics 2021, 57, 53. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 刘书亭, 计海峰, 潘高峰, 中国陶瓷 2021, 57, 53.)
|
|
| [24] |
Yang, D. H.; Kong, L.; Zhong, M.; Zhu, J.; Bu, X. H. Small 2019, 15, 1804058.
|
| [25] |
Yang, C. P.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, Z. W.; Wang, X.; Huang, C. Z.; Li, Y. F. Talanta 2021, 228, 122261.
|
| [26] |
Zhao, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Bao, X.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 9820.
|
| [27] |
Xu, Z.; Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Pan, X.; Qin, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, G. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 4593.
|
| [28] |
Jain, S.; Shah, J.; Negi, N. S.; Sharma, C.; Kotnala, R. K. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 4743.
|
| [29] |
Wei, T. R.; Zhang, S. S.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, X. J. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2023, 39, 2207026. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 韦天然, 张书胜, 刘倩, 邱园, 罗俊, 刘熙俊, 物理化学学报, 2023, 39, 2207026.)
|
|
| [30] |
He, L.; Peng, Z. W.; Jiang, Z. W.; Tang, X. Q.; Huang, C. Z.; Li, Y. F. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 31834.
|
| [31] |
Shijina, K.; Illathvalappil, R.; Sumitha, N. S.; Sailaja, G. S.; Kurungot, S.; Nair, B. N.; Peer Mohamed, A.; Anilkumar, G. M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hareesh, U. S. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 18690.
|
| [32] |
Xiao, F.; Wang, F.; Fu, X.; Zheng, Y. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 2868.
|
| [33] |
Ouyang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Suib, S. L.; Yang, H. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 539, 135.
|
| [34] |
Yang, T.; Yu, D.; Petru, M. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2021, 286, 119859.
|
| [35] |
Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Chen, T.; Li, Z.; Hao, J. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 7370.
|
| [36] |
Wei, W.; Wei, Z.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Shi, R.; Ouyang, S.; Qi, Y.; Philips, D. L.; Yuan, H. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3199.
|
| [37] |
He, L.; Ni, Q.; Mu, J.; Fan, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Tang, W.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zou, J.; Yang, W.; Jacobson, O.; Zhang, F.; Huang, P.; Chen, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 6822.
|
| [38] |
Mimouni, I.; Bouziani, A.; Naciri, Y.; Boujnah, M.; El Belghiti, M. A.; El Azzouzi, M. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 7984.
|
| [39] |
Kim, C.; Chae, S.; Park, Y.; Choi, W. ACS EST Engg. 2022, 2, 232.
|
| [40] |
Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, F.; Luo, X.; Dionysiou, D. D. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122264.
|
| [41] |
Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, P.; Zheng, J.; Yang, M.; Huo, D.; Hou, C. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 383.
|
| [42] |
Liang, Q.; Yan, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Shi, H.; Huang, H.; Kang, Z. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 4279.
|
| [43] |
Zhang, Y.; Sun, A.; Xiong, M.; Macharia, D. K.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, L. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 129019.
|
| [44] |
Zhuang, J.; Tian, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, P.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, M. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 9519.
|
| [45] |
Clarizia, L.; Russo, D.; Di Somma, I.; Marotta, R.; Andreozzi, R. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2017, 209, 358.
|
| [46] |
Geng, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 280, 119409.
|
| [47] |
Hu, J.; Fan, W.; Ye, W.; Huang, C.; Qiu, X. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2014, 158-159, 182.
|
| [48] |
Xie, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Du, T.; Yang, C.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 131808.
|
| [49] |
He, J.; Yang, X.; Men, B.; Wang, D. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2016, 39, 97.
|
| [50] |
Wang, Z.; Mao, X.; Chen, P.; Xiao, M.; Monny, S. A.; Wang, S.; Konarova, M.; Du, A.; Wang, L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1030.
|
| [51] |
Zhao, P.; Feng, X.; Huang, D.; Yang, G.; Astruc, D. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 287, 114.
|
| [52] |
Xiao, R.; Zhao, C.; Zou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tian, L.; Xu, H.; Tang, H.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Z.; Yang, X. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2020, 268, 118382.
|
| [53] |
Chen, F.; He, A.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; Chen, H.; Geng, F.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134176.
|
| [54] |
Gazi, S.; Rajakumar, A.; Singh, N. D. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 894.
|
| [55] |
Zeng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Ni, J.; Tang, J.; Wen, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Cai, T. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138067.
|
| [56] |
He, L.; Jiang, Z. W.; Li, W.; Li, C. M.; Huang, C. Z.; Li, Y. F. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 28868.
|
| [1] | 马超, 武佳炜, 朱琳, 韩晓霞, 阮伟东, 宋薇, 王旭, 赵冰. g-C3N4/Ag纳米复合材料表面增强拉曼基底对婴幼儿糖果中的罗丹明B的痕量检测[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(10): 1024-1030. |
| [2] | 宋秋生, 周稳, 吴新民, 吴凡. P(NIPAM-co-RhBHA)-NP的双重荧光响应行为与影响机制[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(5): 435-440. |
| [3] | 崔素珍, 杨汉培, 孙慧华, 聂坤, 吴俊明. Fe对NaNbO3的晶格掺杂和同步异质结改性及其光催化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(12): 995-1002. |
| [4] | 李爱昌, 李健飞, 刘亚录, 张建平, 赵丽平, 卢艳红. 负偏压下(Ni-Mo)/TiO2膜电极光电催化降解罗丹明B的性能和机理[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(05): 815-821. |
| [5] | 黄文君, 吴文辉, 梁嘉香. 基于脱硫反应的硫脲基罗丹明B 汞离子荧光化学剂量计的合成及分子氢键的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(07): 873-880 . |
| [6] | 王崇太, 华英杰, 刘希龙, 吴春燕, 王会会, 赵欣欣, 刘晓旸. 铬取代杂多阴离子PWB11BOB39BCr(III)(HB2BO)4-可见光催化降解罗丹明B[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(04): 399-404. |
| [7] | 于书平, 席铭俊, 韩克飞, 汪中明, 朱红. 层状二氧化锰和2,2-联吡啶铁自组装膜的制备和光电性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(05): 374-378. |
| [8] | 王益林, 陆建平, 童张法, 陈璐. CdTe量子点与罗丹明B间的荧光共振能量转移研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(19): 2222-2226. |
| [9] | 杨丽琨,褚莹,刘阳,韩冬雪. 含有BaMoO4纳米粒子的反胶束溶液与罗丹明B的相互作用[J]. 化学学报, 2005, 63(1): 18-22. |
| [10] | 刘绍璞,刘忠芳,蒋治良,李明,龙秀芬. 镉(Ⅱ)-碘化物-碱性呫吨染料体系的倍频散射和二级散射及其 分析应用[J]. 化学学报, 2001, 59(11): 1864-1869. |
| [11] | 王喜庆,孙媛,龙英才. 罗丹明B内酯单晶的生长及晶体结构[J]. 化学学报, 2000, 58(9): 1173-1175. |
| [12] | 高莹,郑用熙. 表面活性剂双水相的性质及其应用 Ⅰ. 表面活性剂双水相的微环境性质[J]. 化学学报, 1996, 54(5): 491-496. |
| [13] | 郑肇生,景卫国. 增效试剂在动力学分析法中的应用研究Ⅱ: 锰(Ⅱ)-氨三乙酸-十二烷基硫酸钠-高碘酸钾-罗丹明B催化体系[J]. 化学学报, 1996, 54(10): 1016-1022. |
| [14] | 刘绍璞,刘忠芳,李明. 离子缔合物二级散射光谱的分析应用: 硒(IV)-碘化物-罗丹明B体系[J]. 化学学报, 1995, 53(12): 1178-1184. |
| [15] | 姜永才,沈世龙,吴世康. 利用光化学探针技术研究长链烷烃硫酸钠水溶液中预胶束的生成[J]. 化学学报, 1991, 49(1): 32-35. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||