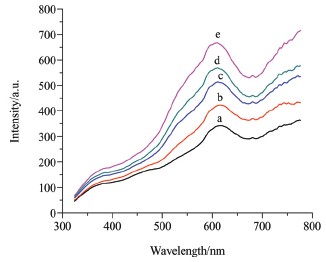
[1] Sanvicens, N.; Marco, M. P. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 425.  [2] Tongprasert, F.; Wanapirak, C.; Tongsong, T. Prenatal Diagn. 2011, 31, 430. [2] Tongprasert, F.; Wanapirak, C.; Tongsong, T. Prenatal Diagn. 2011, 31, 430.  [3] Cole, L. A.; Butler, S. A.; Khanlian, S. A.; Giddings, A.; Muller, C. Y.; Seckl, M. J.; Kohorn, E. I. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 102, 151. [3] Cole, L. A.; Butler, S. A.; Khanlian, S. A.; Giddings, A.; Muller, C. Y.; Seckl, M. J.; Kohorn, E. I. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 102, 151.  [4] Yang, H.-C.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Zhuo, Y. Colloids Surf., B 2011, 82, 463. [4] Yang, H.-C.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Zhuo, Y. Colloids Surf., B 2011, 82, 463.  [5] Chai, R.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Ou, C.-F.; Cao, S.-R.; Li, X.-L. Talanta 2008, 74, 1330. [5] Chai, R.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Ou, C.-F.; Cao, S.-R.; Li, X.-L. Talanta 2008, 74, 1330.  [6] Lim, T. K.; Matsunaga, T. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 1063. [6] Lim, T. K.; Matsunaga, T. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 1063.  [7] Yang, G.-M.; Yang, X.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Yang, Y.-H. Colloids Surf., A 2011, 389, 195. [7] Yang, G.-M.; Yang, X.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Yang, Y.-H. Colloids Surf., A 2011, 389, 195.  [8] Mao, L.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Zhuo, Y.; Yang, X. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 149, 226. [9] Li, R.; Wu, D.; Li, H.; Xu, C.-X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Cai, Y.-Y.; Wei, Q.; Du, B. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 414, 196. [10] Kim, H. S.; Pyun, J. C. Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 1043. [8] Mao, L.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Zhuo, Y.; Yang, X. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 149, 226. [9] Li, R.; Wu, D.; Li, H.; Xu, C.-X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Cai, Y.-Y.; Wei, Q.; Du, B. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 414, 196. [10] Kim, H. S.; Pyun, J. C. Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 1043.  [11] Luo, L.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Hou, L.-Y.; Wang, J.-L.; Tian, W. Talanta 2007, 72, 1293. [11] Luo, L.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Hou, L.-Y.; Wang, J.-L.; Tian, W. Talanta 2007, 72, 1293.  [12] Yan, X.; Huang, Z.-B.; He, M.; Liao, X.-M.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Yin, G.-F.; Gu, J.-W. Colloids Surf., B 2012, 89, 86. [12] Yan, X.; Huang, Z.-B.; He, M.; Liao, X.-M.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Yin, G.-F.; Gu, J.-W. Colloids Surf., B 2012, 89, 86.  [13] Nakamura, N.; Lim, T. K.; Jeong, J. M.; Matsunaga, T. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 439, 125. [14] Hudelist, G.; Wuelfing, P.; Czerwenka, K.; Knöfler, M.; Haider, S.; Fink-Retter, A.; Gschwantler-Kaulich, D.; Pfeiler, G.; Kubista, E.; Singer, C. F. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 191. [15] Jiang, Z.-L.; Zou, M.-J.; Liang, A.-H. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 387, 24. [16] Liang, A.-H.; Zou, M.-J.; Jiang, Z.-L. Talanta 2008, 75, 1214. [13] Nakamura, N.; Lim, T. K.; Jeong, J. M.; Matsunaga, T. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 439, 125. [14] Hudelist, G.; Wuelfing, P.; Czerwenka, K.; Knöfler, M.; Haider, S.; Fink-Retter, A.; Gschwantler-Kaulich, D.; Pfeiler, G.; Kubista, E.; Singer, C. F. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 191. [15] Jiang, Z.-L.; Zou, M.-J.; Liang, A.-H. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 387, 24. [16] Liang, A.-H.; Zou, M.-J.; Jiang, Z.-L. Talanta 2008, 75, 1214.  [17] Nakamura, K.; Satomura, S.; Matsuura, S. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 613. [18] Lv, M.-X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Q.-Y.; Chen, K.-M.; Feng, G.-Y. Chin. J. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 11, 174. (吕鸣详, 张杰, 申群英, 陈昆明, 冯光易, 中国生物医学工程学报, 1992, 11, 174.)[19] Robinson, G. A.; Hill, H. A.; Philo, R. D.; Gear, J. M.; Rattle, S. J.; Forrest, G. C. Clin. Chem. 1985, 31, 1449. [20] Guo, X.-Y.; Guan, Y.-P.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.-N.; Lan, H.-L.; Yang, Z.-H.; Lu, Z.-H. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2006, 7, 274. [21] Vaitukatitis, J. L.; Braunstein, G. D.; Ross, G. T. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1972, 113, 751. [22] Tung, N. H.; Chikae, M.; Ukita, Y.; Viet, P. H.; Takamura, Y. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1210. [23] Liang, A.-H.; Huang, Y.-J.; Jiang, Z.-L. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 383, 73. [24] Lin, S.-M.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Jiang, Z.-L.; Wen, G.-Q.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Liang, A.-H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2010, 68, 339. (凌绍明, 范燕燕, 蒋治良, 温桂清, 刘庆业, 梁爱惠, 化学学报, 2010, 68, 339.)[25] Jiang, Z.-L.; Sun, S.-J.; Liang, A.-H.; Huang, W.-X.; Qin, A.-M. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1389.[26] Li, J.-F.; Jiang, Z.-L.; Deng, A.-P. Chin. J. Chem. 2008, 26, 2297. [27] Jiang, Z.-L.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Liang, A.-H.; Wen, G.-Q.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Li, T.-S. Plasmonics 2010, 5, 375. [17] Nakamura, K.; Satomura, S.; Matsuura, S. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 613. [18] Lv, M.-X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Q.-Y.; Chen, K.-M.; Feng, G.-Y. Chin. J. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 11, 174. (吕鸣详, 张杰, 申群英, 陈昆明, 冯光易, 中国生物医学工程学报, 1992, 11, 174.)[19] Robinson, G. A.; Hill, H. A.; Philo, R. D.; Gear, J. M.; Rattle, S. J.; Forrest, G. C. Clin. Chem. 1985, 31, 1449. [20] Guo, X.-Y.; Guan, Y.-P.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.-N.; Lan, H.-L.; Yang, Z.-H.; Lu, Z.-H. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2006, 7, 274. [21] Vaitukatitis, J. L.; Braunstein, G. D.; Ross, G. T. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1972, 113, 751. [22] Tung, N. H.; Chikae, M.; Ukita, Y.; Viet, P. H.; Takamura, Y. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1210. [23] Liang, A.-H.; Huang, Y.-J.; Jiang, Z.-L. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 383, 73. [24] Lin, S.-M.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Jiang, Z.-L.; Wen, G.-Q.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Liang, A.-H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2010, 68, 339. (凌绍明, 范燕燕, 蒋治良, 温桂清, 刘庆业, 梁爱惠, 化学学报, 2010, 68, 339.)[25] Jiang, Z.-L.; Sun, S.-J.; Liang, A.-H.; Huang, W.-X.; Qin, A.-M. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1389.[26] Li, J.-F.; Jiang, Z.-L.; Deng, A.-P. Chin. J. Chem. 2008, 26, 2297. [27] Jiang, Z.-L.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Liang, A.-H.; Wen, G.-Q.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Li, T.-S. Plasmonics 2010, 5, 375.  [28] Jiang, C.-N.; Liang, A.-H.; Jiang, Z.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 714. (蒋彩娜, 梁爱惠, 蒋治良, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 714.)[29] Zhang, Y.; Liang, A.-H.; Zhou, L.-P.; Qin, H.-M.; Ouyang, H.-X.; Wang, P.-F.; Jiang, Z.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 2153. (张轶, 梁爱惠, 周莲平, 覃惠敏, 欧阳辉祥, 王鹏飞, 蒋治良, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 2153.)[30] Jiang, Z.-L.; Huang, Y.-J.; Liang, A.-H.; Pan, H.-C.; Liu, Q.-Y. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1674. Jiang, Z.-L.; Liao, X.-J.; Deng, A.-P.; Liang, A.-H.; Li, J.-S.; Pan, H.-C.; Li, J.-F.; Wang, S.-M.; Huang, Y.-J. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8681. [28] Jiang, C.-N.; Liang, A.-H.; Jiang, Z.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 714. (蒋彩娜, 梁爱惠, 蒋治良, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 714.)[29] Zhang, Y.; Liang, A.-H.; Zhou, L.-P.; Qin, H.-M.; Ouyang, H.-X.; Wang, P.-F.; Jiang, Z.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 2153. (张轶, 梁爱惠, 周莲平, 覃惠敏, 欧阳辉祥, 王鹏飞, 蒋治良, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 2153.)[30] Jiang, Z.-L.; Huang, Y.-J.; Liang, A.-H.; Pan, H.-C.; Liu, Q.-Y. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1674. Jiang, Z.-L.; Liao, X.-J.; Deng, A.-P.; Liang, A.-H.; Li, J.-S.; Pan, H.-C.; Li, J.-F.; Wang, S.-M.; Huang, Y.-J. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8681. |