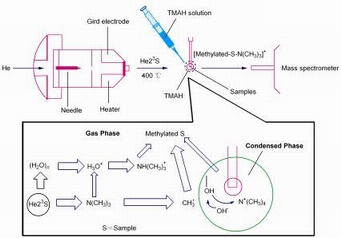
| [1] Cody, R. B.; Laramee, J. A.; Durst, H. D. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 2297.[2] Jones, R. W.; Cody, R. B.; McClelland, J. F. J. Forensic Sci. 2006, 51, 915.[3] Cody, R. B. Anal. Chem. 2008, 81, 1101.[4] Haefliger, O. P.; Jeckelmann, N. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 1361.[5] Harris, G. A.; Galhena, A. S.; Fernaandez, F. M. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4508.[6] Eberherr, W.; Buchberger, W.; Hertsens, R.; Klampfl, C. W. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5792.[7] Petucci, C.; Diffendal, J.; Kaufman, D.; Mekonnen, B.; Terefenko, G.; Musselman, B. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5064.[8] Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1496.[9] Kubec, R.; Cody, R. B.; Dane, A. J.; Musah, R. A.; Schraml, J.; Vattekkatte, A.; Block, E. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1121.[10] Fernández, F. M.; Cody, R. B.; Green, M. D.; Hampton, C. Y.; McGready, R.; Sengaloundeth, S.; White, N. J.; Newton, P. N. ChemMedChem 2006, 1, 702.[11] Curtis, M. E.; Jones, P. R.; Sparkman, O. D.; Cody, R. B. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20, 2082.[12] Song, F.-R.; Yan, C.-Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Liu, S.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2009, 67, 1103. (宋凤瑞, 闫存玉, 刘宁, 刘志强, 刘淑莹, 化学学报, 2009, 67, 1103.)[13] Liu, R. N.; Yue, H.; Krechmer, J.; Jiao, L.; Liu, C. C.; Musselman, B.; Liu, S.-Y. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22 (Supplement 1), 88.[14] Fabbri, D.; Helleur, R. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1999, 49, 277. |