化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (2): 116-125.DOI: 10.6023/A21110528 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
陈祥松a, 帅蝶a, 姜泽东a, 杨晗a, 罗丹a, 倪辉a, 王力a,*( ), 陈丙年b,*(
), 陈丙年b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-11-22
发布日期:2022-01-10
通讯作者:
王力, 陈丙年
基金资助:
Xiangsong Chena, Die Shuaia, Zedong Jianga, Han Yanga, Dan Luoa, Hui Nia, Li Wanga( ), Bingnian Chenb(
), Bingnian Chenb( )
)
Received:2021-11-22
Published:2022-01-10
Contact:
Li Wang, Bingnian Chen
Supported by:文章分享
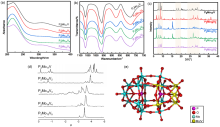
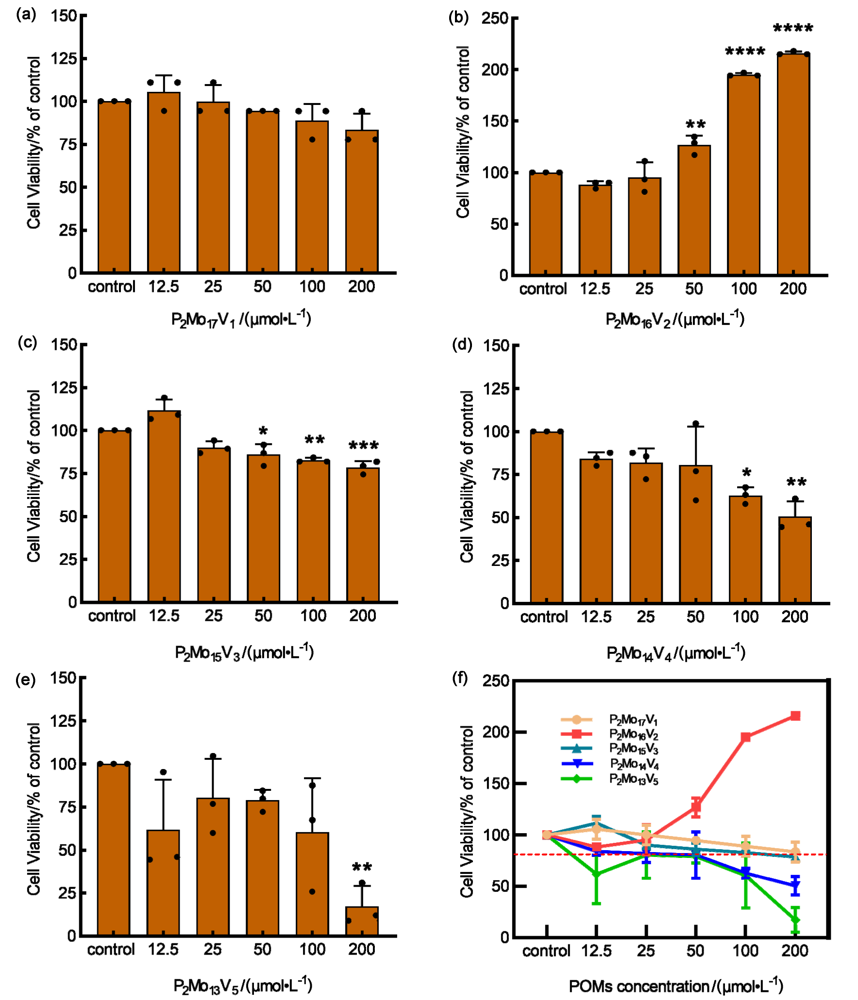
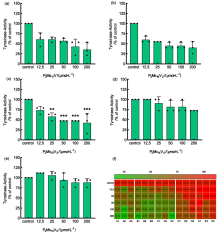
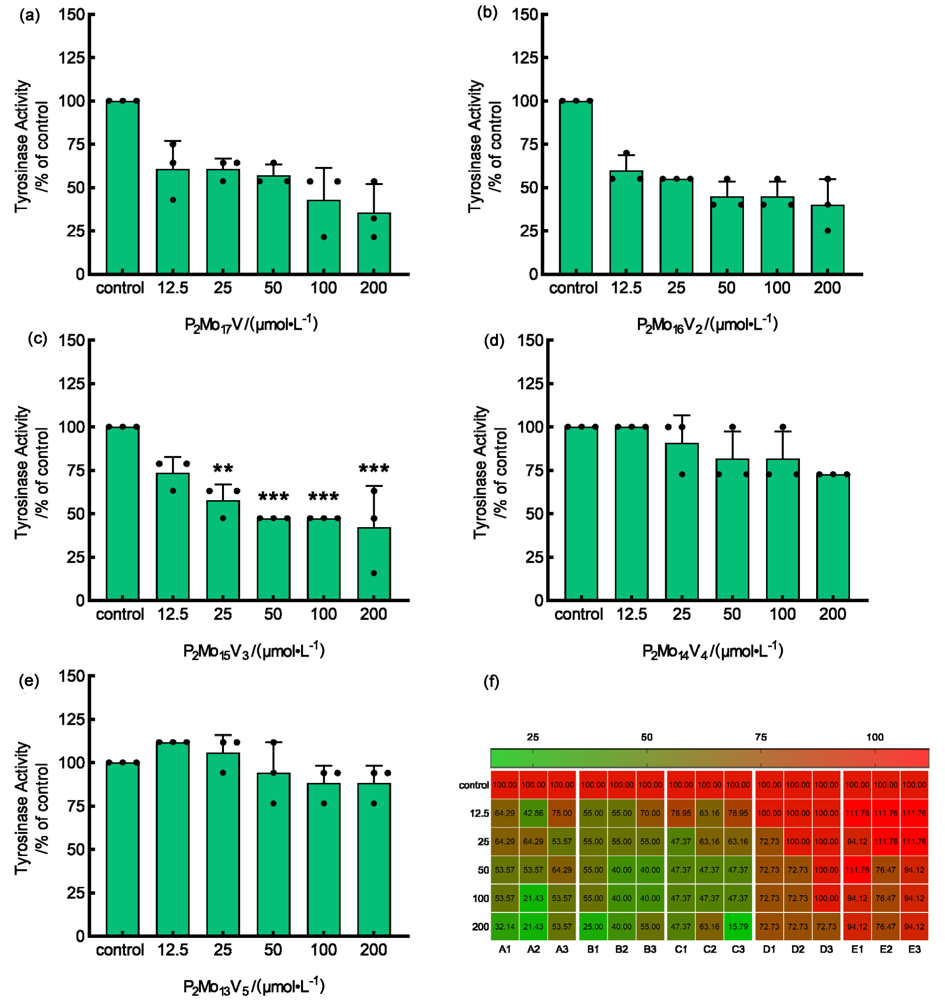
合成了五种多金属氧酸盐. 以B16小鼠黑色素瘤细胞为模型, 用噻唑蓝(MTT)法检测细胞存活率, 酶标法测定抗氧化活性和内黑色素含量及酪氨酸酶活性, 最后用分子对接模拟多金属氧酸盐和酪氨酸酶结合的机制. 研究结果表明, 两种磷钼酸(H7[P2Mo17VO62]和H8[P2Mo16V2O62])是高效的黑色素生成抑制剂, 在200 μmol/L的浓度下对黑色素合成的抑制率为74.40%和75.14%, 对细胞内酪氨酸酶活性的抑制率为35.71%和40.00%, 随着钒原子取代个数的增加, 两种抑制活性均逐渐降低. H7[P2Mo17VO62]和H8[P2Mo16V2O62]对细胞没有毒性. 两种多酸都有较好的1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)清除能力, IC50分别为1.683和2.800 mg/mL. 分子对接分数低于–146 kJ/mol. 综上所述, H7[P2Mo17VO62]和H8[P2Mo16V2O62]能抑制B16细胞黑色素的生成, 其机制与抑制酪氨酸酶的活性有关.
陈祥松, 帅蝶, 姜泽东, 杨晗, 罗丹, 倪辉, 王力, 陈丙年. H6[P2Mo18O62]的钒取代多金属氧酸盐对小鼠黑色素瘤细胞B16黑色素生成的调控及其机制研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 116-125.
Xiangsong Chen, Die Shuai, Zedong Jiang, Han Yang, Dan Luo, Hui Ni, Li Wang, Bingnian Chen. Study on the Regulation and Mechanism of the Vanadium Substituted Polyoxometalates of H6[P2Mo18O62] on Melanogenesis of Mouse Melanoma Cell B16[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(2): 116-125.


| 多酸 | IC50/(µmol•L–1) |
|---|---|
| P2Mo17V | >200 |
| P2Mo16V2 | >200 |
| P2Mo15V3 | >200 |
| P2Mo14V4 | >200 |
| P2Mo13V5 | 123.8±17.8 |
| 多酸 | IC50/(µmol•L–1) |
|---|---|
| P2Mo17V | >200 |
| P2Mo16V2 | >200 |
| P2Mo15V3 | >200 |
| P2Mo14V4 | >200 |
| P2Mo13V5 | 123.8±17.8 |




| 化合物 | 氢键和金属键 相关氨基酸 | 氢键 数量 | 大π键 | 对接分数(kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2Mo17V | His61, His94, His263, Asn259, Asn260 | 5 | His61, His263, Phe292 | –191 |
| P2Mo16V2 | His61, His9, His263, Asn244, Asn260 | 5 | His61, His263, Phe292 | –183 |
| P2Mo15V3 | His6, His94, His263, Asn259, Asn260 | 6 | 无 | –158 |
| P2Mo14V4 | His85, His259, Asn260 | 3 | His263 | –167 |
| P2Mo13V5 | His61, His94, His244, His259 | 6 | His263 | –146 |
| 化合物 | 氢键和金属键 相关氨基酸 | 氢键 数量 | 大π键 | 对接分数(kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2Mo17V | His61, His94, His263, Asn259, Asn260 | 5 | His61, His263, Phe292 | –191 |
| P2Mo16V2 | His61, His9, His263, Asn244, Asn260 | 5 | His61, His263, Phe292 | –183 |
| P2Mo15V3 | His6, His94, His263, Asn259, Asn260 | 6 | 无 | –158 |
| P2Mo14V4 | His85, His259, Asn260 | 3 | His263 | –167 |
| P2Mo13V5 | His61, His94, His244, His259 | 6 | His263 | –146 |
| 化合物 | NH4VO3 | NaH2PO4 | Na2MoO4•2H2O | pH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体积/mL | 用量/mol | 体积/mL | 用量/mol | 体积/mL | 用量/mol | ||||
| P2Mo17V | 100 | 0.0100 | 25 | 0.02 | 75 | 0.170 | 3.6 | ||
| P2Mo16V2 | 100 | 0.0200 | 25 | 0.02 | 100 | 0.160 | 3.8 | ||
| P2Mo15V3 | 150 | 0.0300 | 25 | 0.02 | 100 | 0.150 | 4.0 | ||
| P2Mo14V4 | 150 | 0.0400 | 25 | 0.02 | 75 | 0.140 | 4.2 | ||
| P2Mo13V5 | 120 | 0.0375 | 15 | 0.01 | 40 | 0.065 | 4.4 | ||
| 化合物 | NH4VO3 | NaH2PO4 | Na2MoO4•2H2O | pH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体积/mL | 用量/mol | 体积/mL | 用量/mol | 体积/mL | 用量/mol | ||||
| P2Mo17V | 100 | 0.0100 | 25 | 0.02 | 75 | 0.170 | 3.6 | ||
| P2Mo16V2 | 100 | 0.0200 | 25 | 0.02 | 100 | 0.160 | 3.8 | ||
| P2Mo15V3 | 150 | 0.0300 | 25 | 0.02 | 100 | 0.150 | 4.0 | ||
| P2Mo14V4 | 150 | 0.0400 | 25 | 0.02 | 75 | 0.140 | 4.2 | ||
| P2Mo13V5 | 120 | 0.0375 | 15 | 0.01 | 40 | 0.065 | 4.4 | ||
| [1] |
Zhang, J.-L.; Shi, C.-Z.; Shan, F.; Shi, N.-N.; Ye, W.; Zhuo, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Shi, Y.-X.; Peng, C. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127282.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127282 |
| [2] |
Kudo, M.; Kobayashi, N. K.; Tsuji, N. K. Plos One 2017, 12, e0171513.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171513 |
| [3] |
Zhang, Q.-J.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Ma, C.-H.; Xu, X.; Gu, W.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Wang, S.-F. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39, 2616. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201901053 |
|
( 张强健, 王芸芸, 赵雨珣, 马崇慧, 徐徐, 谷文, 杨益琴, 王石发, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 2616.)
|
|
| [4] |
Peng, H.-Y.; Wang, T.; Li, G.-R.; Huang, J. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2021, 42, 3357. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 彭海月, 汪婷, 李国瑞, 黄静, 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42, 3357.)
|
|
| [5] |
Machado, D.; Shishido, S. M.; Queiroz, K. C. S.; Oliveira, D. N.; Faria, A. L. C.; Catharino, R. R.; Spek, C. A.; Ferreira, C. V. PLoS One 2013, 8, e54269.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054269 |
| [6] |
Nasti, T. H.; Timares, L. Photochem. Photobiol. 2015, 91, 188.
doi: 10.1111/php.12335 |
| [7] |
Huang, L.; Liu, M.-Y.; Huang, H.-Y.; Wen, Y.-Q.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Wei, Y. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1858.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.8b00437 |
| [8] |
Shuai, D.; Zhao, M.-J. Chen, B.-N.; Wang, L. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2021, 42, 3579. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 帅蝶, 赵美娟, 陈丙年, 王力, 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42, 3579.)
|
|
| [9] |
Pillaiyar, T.; Namasivayam, V.; Manickam, M.; Jung, S. H. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7395.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00967 |
| [10] |
Lai, X. L.; Wichers, H. J.; Soler, L. M.; Dijkstra, B. W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9812.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.33 |
| [11] |
D'Mello, S. A. N.; Finlay, G. J.; Baguley, B. C.; Askarian-Amiri, M. E. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144.
doi: 10.3390/ijms17071144 |
| [12] |
Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Jung, S. H. Cell. Signalling 2017, 40, 99.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.09.004 |
| [13] |
Lai, X. L.; Wichers, H. J.; Soler, L. M.; Dijkstra, B. W. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 47.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201704410 |
| [14] |
Kanteev, M.; Goldfeder, M.; Fishman, A. Protein Sci. 2015, 24, 1360.
doi: 10.1002/pro.2734 |
| [15] |
Deri, B.; Kanteev, M.; Goldfeder, M.; Lecina, D.; Guallar, V.; Adir, N.; Fishman, A. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34993.
doi: 10.1038/srep34993 |
| [16] |
Fan, M.; Zhang, G.; Hu, X.; Xu, X.; Gong, D. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 226.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.07.010 |
| [17] |
Lee, S. Y.; Baek, N.; Nam, T. G. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 1.
|
| [18] |
Kim, M. S.; Bang, S. H.; Kim, J. H.; Shin, H. J.; Choi, J. H.; Chang, S. E. Ann. Dermatol. 2015, 27, 250.
doi: 10.5021/ad.2015.27.3.250 |
| [19] |
Lin, Z.-Q.; Xia, W.-L.; Liu, R.-Y.; Jiang, S.-H.; Ma, Z.-Q. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 2980. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202005006 |
|
( 林芷晴, 夏婉铃, 刘仁义, 姜少华, 马志强, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 2980.)
|
|
| [20] |
Chi, G.-X.; Xie, L.-F.; Zhao, M.-J.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Zheng, A.-P. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2020, 96, 1255.
doi: 10.1111/cbdd.v96.5 |
| [21] |
Kim, S. H.; Lee, S. Y.; Hong, C. Y.; Gwak, K. S.; Park, M. J.; Smith, D.; Choi, I. G. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 484.
doi: 10.1111/ics.2013.35.issue-5 |
| [22] |
Xiao, L.; Matsubayashi, K.; Miwa, N. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2007, 299, 245.
doi: 10.1007/s00403-007-0740-2 |
| [23] |
Chen, L.-Y.; Luque, R.; Li, Y.-W. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4614.
doi: 10.1039/C6CS00537C |
| [24] |
Gumerova, N. I.; Rompel, A. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 0112.
doi: 10.1038/s41570-018-0112 |
| [25] |
Feng, X.-J.; Li, Y.-G.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Wang, E.-B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 1575. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A13060664 |
|
( 冯小佳, 李阳光, 张志明, 王恩波, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 1575.)
|
|
| [26] |
Wei, Z.-Y.; Chang, Y.-L.; Yu, H.; Han, S.; Wei, Y.-G. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 725. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20050187 |
|
( 魏哲宇, 常亚林, 余焓, 韩生, 魏永革, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 725.)
|
|
| [27] |
Han, Z.-G.; Gao, Y.-Z.; Wang, J.-Y.; Hu, C.-W. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2009, 635, 2665.
|
| [28] |
Xia, Y.; Wei, Y.-G.; Guo, H.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2005, 63, 1931. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 夏芸, 魏永革, 郭洪猷, 化学学报, 2005, 63, 1931.)
|
|
| [29] |
Jiang, N.; Li, B.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Li, J.-M. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2014, 640, 2444.
doi: 10.1002/zaac.v640.12/13 |
| [30] |
Zhao, M.-J.; Chen, X.-S.; Chi, G.-X.; Shuai, D.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.-N.; Li, J. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 4320.
doi: 10.1039/D0QI00860E |
| [31] |
Zhao, Z.-F.; Zhou, B.-B.; Zheng, S.-T.; Su, Z.-H.; Wang, C.-M. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2009, 362, 5038.
doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2009.08.015 |
| [32] |
Wang, J.; Tao, Z.; Tian, T.; Qiu, J.; Qian, H.; Zha, Z.; Miao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129137.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129137 |
| [33] |
Xing, R.; Chen, B.-N.; Wang, F.; Zheng, A.-P.; Wang, L. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 177.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.003 |
| [34] |
Breibeck, J.; Gumerova, N. I.; Boesen, B. B.; Galanski, M.; Rompel, A. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5183.
|
| [35] |
Bijelic, A.; Aureliano, M.; Rompel, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2980.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.10 |
| [36] |
Wang, L.; Zhou, B.-B.; Liu, J.-R. Prog. Chem. 2013, 25, 1131.
|
| [37] |
She, S.; Bian, S.; Huo, R.; Chen, K.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hao, J.; Wei, Y. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33529.
doi: 10.1038/srep33529 |
| [38] |
Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, G.; Wei, Y. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 395.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2017.10.025 |
| [39] |
Liu, S.-X.; Wang, C.-L.; Yu, M.; Li, Y.-X.; Wang, E.-B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2005, 63, 1069. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 刘术侠, 王春玲, 于淼, 李玉新, 王恩波, 化学学报, 2005, 63, 1069.)
|
|
| [40] |
Liu, S.-X.; Wang, E.-B.; Zhai, H.-J.; Han, Z.-B.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Z.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2004, 62, 170. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 刘术侠, 王恩波, 翟宏菊, 韩正波, 曾毅, 李泽琳, 化学学报, 2004, 62, 170.)
|
|
| [41] |
Hu, J.-J.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.-N.; Chi, G.-X.; Zhao, M.-J.; Li, Y. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 3270.
doi: 10.1002/ejic.v2019.28 |
| [42] |
Li, D.; Gao, X.-Z.; Gu, J.-M.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Jin, Z.; Yan, D.-M.; Chen, Y.-G.; Zhu, X. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2016, 2016, 3239494.
|
| [43] |
Ni, D.-L.; Jiang, D.-W.; Kutyreff, C. J.; Lai, J.-H.; Yan, Y.-J.; Barnhart, T. E.; Yu, B.; Im, H. J.; Kang, L.; Cho, S. Y.; Liu, Z.-F.; Huang, P.; Engle, J. W.; Cai, W.-B. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5421.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07890-8 |
| [44] |
Li, S.-Y.; Jian, D.-W.; Ehlerding, E. B.; Rosenkrans, Z. T.; Engle, J. W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.-S.; Ni, D.-L.; Cai, W.-B. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13382.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b06780 |
| [45] |
Geng, J.; Li, M.; Ren, J.-S.; Wang, E.-B.; Qu, X.-G. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4184.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v50.18 |
| [46] |
Gao, N.; Sun, H.; Dong, K.; Ren, J.; Duan, T.; Xu, C.; Qu, X. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3422.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms4422 |
| [47] |
Li, M.; Xu, C.; Wu, L.; Ren, J.-S.; Wang, E.-B.; Qu, X.-G. Small 2013, 9, 3455.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v9.20 |
| [48] |
Xing, R.; Zheng, A.-P.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.-P.; Jiang, A. H. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 292.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.11.157 |
| [49] |
Xing, R.; Wang, F.; Dong, L.; Zheng, A.-P.; Wang, L.; Su, W.-J.; Lin, T. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 205.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.10.119 |
| [50] |
Wang, E.-B.; Hu, C.-W.; Zhou, Y.-X.; Liu, J.-F.; Zhao, S.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 1990, 48, 790. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 王恩波, 胡长文, 周延修, 刘景福, 赵世良, 化学学报, 1990, 48, 790.)
|
|
| [51] |
Tong, X.; Zhu, W.; Wu, Q.; Qian, X.; Liu, Z.; Yan, W.; Gong, J. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 7768.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.04.148 |
| [52] |
Liu, X.; Gong, W.; Luo, J.; Zou, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 362, 517.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.11.151 |
| [53] |
Liu, S.-X.; Wang, C.-M.; Li, D.-H.; Su, Z.-M.; Wang, E.-B.; Hu, N.-H.; Jia, H.-Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2004, 62, 1305. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 刘术侠, 王春梅, 李德慧, 苏忠民, 王恩波, 胡宁海, 贾恒庆, 化学学报, 2004, 62, 1305.)
|
|
| [54] |
Briand, L. E.; Thomas, H. J.; Baronetti, G. T. Appl. Catal.,A 2000, 201, 191.
doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00435-X |
| [55] |
Qian, X.; Tong, X.; Wu, Q.; He, Z.; Cao, F.; Yan, W. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 9897.
doi: 10.1039/c2dt30467h |
| [56] |
Luo, K.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, G.; Li, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128659.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.128659 |
| [57] |
Uchida, R.; Ishikawa, S.; Tomoda, H. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 141.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2013.12.008 |
| [1] | 李子奇, 刘力玮, 毛承晖, 周常楷, 夏旻祺, 沈桢, 郭月, 吴强, 王喜章, 杨立军, 胡征. 钴取代多金属氧酸盐作为可溶性介质提升锂硫电池性能[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 620-626. |
| [2] | 苏东芮, 任小康, 于沄淏, 赵鲁阳, 王天宇, 闫学海. 酪氨酸衍生物调控酶催化路径可控合成功能黑色素★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1486-1492. |
| [3] | 李瑶, 陈丙年, 罗丹, 雷珊, 王力. 多酸型α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的抗氧化性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1318-1326. |
| [4] | 夏雷, 程震, 朱华, 杨志. 124I原位标记有机黑色素纳米粒子的制备及初步分子影像研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(2): 172-178. |
| [5] | 李月, 姜宇晨, 蒋平平, 杜盛郁, 姜就胜, 冷炎. 多孔碳球封装纳米碳化钼催化剂无溶剂催化苄胺偶联反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(1): 66-71. |
| [6] | 徐婕, 魏雨晨, 伍智蔚, 易忠胜. 基于酸度诱导的HSA与BDE154的光谱和计算模拟研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(5): 408-414. |
| [7] | 宋芳源, 丁勇, 赵崇超. 多金属氧酸盐催化的水氧化研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(2): 133-144. |
| [8] | 李博, 周锐, 何谷, 郭丽, 黄维. 螺环吲哚类MDM2抑制剂的分子对接、定量构效关系和分子动力学模拟[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(10): 1396-1403. |
| [9] | 王媛, 蒋勇军, 张美青, 沈银. α-咔啉类GSK-3β抑制剂的合成、活性评价和分子对接研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(18): 1974-1978. |
| [10] | 林军, 李祖光, 邹建卫, 陆绍永. 基于HPPD 靶标酶的分子对接研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(11): 1309-1314. |
| [11] | 安康, 柴晓杰, 薛飞, 王媛, 张婷. VEGFR-2 与抑制剂Sunitinib 的分子对接及分子动力学研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(10): 1232-1236. |
| [12] | 吴琼, 康宏, 王欢欢, 高军, 朱瑞新, 康廷国. AT1 受体的中药活性成分筛选模型及其作用机理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(06): 796-802. |
| [13] | 许倩倩, 杨春. 多金属氧酸盐/TiO2 介孔杂化材料的合成及光催化性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 0(04): 392-398. |
| [14] | 高丽华, 张金凤, 孙庆玲, 王科志. 双偶极半菁染料/多金属氧酸盐自组装膜的制备及其光电转换性质[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 0(04): 441-444. |
| [15] | 詹冬玲, 王嵩, 韩葳葳, 刘景圣. 人参β-香树素合成酶同源模建及高通量虚拟筛选抑制剂的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(03): 217-222. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||