Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (6): 817-826.DOI: 10.6023/A22010055 Previous Articles Next Articles
Special Issue: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
Review
陈玉宛a,c, 周雯a,c, 李欣蔚a,b, 杨开广a,*( ), 梁振a, 张丽华a,*(
), 梁振a, 张丽华a,*( ), 张玉奎a
), 张玉奎a
发布日期:2022-07-07
通讯作者:
杨开广, 张丽华
作者简介: |
陈玉宛, 分析化学硕博连读生, 2017年7月毕业于内蒙古大学化学基地专业, 同年保送至中国科学院大连化学物理研究所, 师从杨开广、张丽华研究员. 主要研究方向为: 蛋白质复合物原位分析新技术新方法. |
 |
杨开广, 中国科学院大连化学物理研究所研究员, 博士生导师, 中国蛋白质组学会青年委员会委员; 中国生物材料学会血液净化材料分会委员会委员. 2017年入选第七批中科院“青年创新促进会”会员并获支持, 2021年获中科院“青年创新促进会”优秀会员. 曾承担国家重点研发计划、国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)、国家自然科学基金重大仪器专项、国家自然科学基金面上项目等科研项目. 一直从事蛋白质组学新技术新方法的研究. |
 |
张丽华, 中国科学院大连化学物理研究所研究员, 博士生导师, 1995年毕业于吉林大学化学系. 同年进入中国科学院大连化学物理研究所攻读博士学位, 师从张玉奎院士. 1999年赴德国国家环境与健康研究中心博士联合培养, 师从A. Kettrup教授. 2000年获得理学博士学位. 2001年~2003年3月, 在日本德岛大学马场嘉信教授研究室做博士后. 2003年4月回中国科学院大连化学物理研究所工作; 2005年晋升为研究员, 课题组长. 获得国家自然科学二等奖、辽宁省自然科学一等奖、中国分析测试协会CAIA一等奖和中国化学会青年化学奖等奖项. 2012年入选科技部“中青年科技创新领军人才”(万人计划). 2017年获国家杰出青年基金项目资助. 主要研究方向为: 蛋白质组定性定量及相互作用新技术新方法研究. |
基金资助:
Yuwan Chena,c, Wen Zhoua,c, Xinwei Lia,b, Kaiguang Yanga( ), Zhen Lianga, Lihua Zhanga(
), Zhen Lianga, Lihua Zhanga( ), Yukui Zhanga
), Yukui Zhanga
Published:2022-07-07
Contact:
Kaiguang Yang, Lihua Zhang
About author:Supported by:Share
Yuwan Chen, Wen Zhou, Xinwei Li, Kaiguang Yang, Zhen Liang, Lihua Zhang, Yukui Zhang. Research Progress of Protein-Protein Interaction Based on Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 817-826.
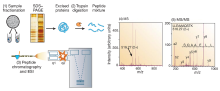


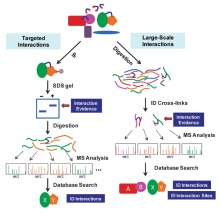


| 基于液质联用技术的蛋白质- 蛋白质相互作用检测方法 | 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的捕获原理 | 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的解析过程 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
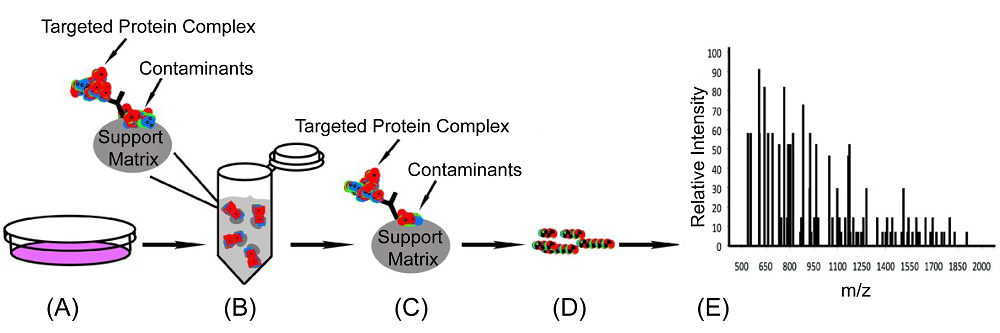
| 亲和纯化质谱(AP-MS) | 基于抗体的免疫共沉淀(IP)纯化 | 通过天然抗体对生物样本中的未修饰的天然蛋白质进行亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱解析内源性蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用. | [ |
| 基于表位标签(Epitope tag)标记的诱饵蛋白的亲和纯化(AP) | 通过在宿主生物体中高表达的融合目标蛋白的表位标签, 对目标蛋白进行亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱, 可解析数千种“诱饵蛋白”的相互作用. 通过在宿主生物体中以天然水平表达的融合目标蛋白的串联亲和标签(TAP), 对目标蛋白进行两次亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱, 可实现对天然表达水平的目标蛋白相互作用解析. | ||
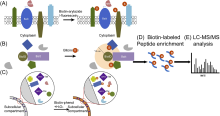
| 近程标记质谱(PDB-MS) | 基于酶催化的近程标记策略(生物素连接酶(BirA*/BioID), 辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)和抗坏血酸的过氧化物酶(APEX)融合的诱饵蛋白) | 通过HRP偶联的抗体或HRP融合蛋白表达于宿主细胞或生物体, 在芳基叠氮化物-生物素试剂存在情况下, 标记距离酶约200~300 nm范围内的蛋白质, 对生物素化的蛋白质亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱鉴定蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用. | [ |
| 通过混杂的生物素连接酶 BirA*融合诱饵蛋白, 在生物素和ATP存在下标记 (约16~24 h), 对其邻近蛋白质上(约10 nm)的伯胺(例: 赖氨酸侧链)生物素化, 对生物素化的蛋白质亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱鉴定蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用. | |||
| 通过工程改造的抗坏血酸过氧化物酶融合蛋白表达于宿主细胞和生物体, 在一定H2O2和生物素苯酚的条件下, 催化活细胞中短寿命、高反应性和不透膜自由基(生物素苯酚自由基)的产生, 然后以1 min的时间分辨率对活细胞线粒体内附近(<20 nm)的蛋白质中富电子氨基酸进行生物素化, 对生物素化的蛋白质亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱鉴定蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用. | |||
| 化学交联质谱(XL-MS) | 基于化学交联剂以共价键连接蛋白质的氨基酸残基 | 通过化学交联剂与空间距离较近的蛋白质残基位点间的化学反应生成新的共价键, 结合串联质谱鉴定交联肽的氨基酸序列和修饰的残基位点, 通过对分子间交联肽的解析鉴定蛋白质-蛋白质间相互作用信息. | [ |
| 共分级偶联质谱(CF‑MS) | 相同生化成分的蛋白质能在色谱中共流, 进而依赖相关算法从蛋白质的共定位和共聚集数据推断蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用 | 通过分子量/电荷/亲疏水性的差异, 将生物化学/生物物理性质相似的蛋白质在生理状态进行分离, 对每个馏分进行串联质谱鉴定, 通过算法对鉴定结果相似性进行评分(例: 蛋白质定量、质量控制、预处理和洗脱曲线), 最后推断分析蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用. | [ |
| 基于液质联用技术的蛋白质- 蛋白质相互作用检测方法 | 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的捕获原理 | 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的解析过程 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 亲和纯化质谱(AP-MS) | 基于抗体的免疫共沉淀(IP)纯化 | 通过天然抗体对生物样本中的未修饰的天然蛋白质进行亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱解析内源性蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用. | [ |
| 基于表位标签(Epitope tag)标记的诱饵蛋白的亲和纯化(AP) | 通过在宿主生物体中高表达的融合目标蛋白的表位标签, 对目标蛋白进行亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱, 可解析数千种“诱饵蛋白”的相互作用. 通过在宿主生物体中以天然水平表达的融合目标蛋白的串联亲和标签(TAP), 对目标蛋白进行两次亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱, 可实现对天然表达水平的目标蛋白相互作用解析. | ||
| 近程标记质谱(PDB-MS) | 基于酶催化的近程标记策略(生物素连接酶(BirA*/BioID), 辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)和抗坏血酸的过氧化物酶(APEX)融合的诱饵蛋白) | 通过HRP偶联的抗体或HRP融合蛋白表达于宿主细胞或生物体, 在芳基叠氮化物-生物素试剂存在情况下, 标记距离酶约200~300 nm范围内的蛋白质, 对生物素化的蛋白质亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱鉴定蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用. | [ |
| 通过混杂的生物素连接酶 BirA*融合诱饵蛋白, 在生物素和ATP存在下标记 (约16~24 h), 对其邻近蛋白质上(约10 nm)的伯胺(例: 赖氨酸侧链)生物素化, 对生物素化的蛋白质亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱鉴定蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用. | |||
| 通过工程改造的抗坏血酸过氧化物酶融合蛋白表达于宿主细胞和生物体, 在一定H2O2和生物素苯酚的条件下, 催化活细胞中短寿命、高反应性和不透膜自由基(生物素苯酚自由基)的产生, 然后以1 min的时间分辨率对活细胞线粒体内附近(<20 nm)的蛋白质中富电子氨基酸进行生物素化, 对生物素化的蛋白质亲和纯化, 结合串联质谱鉴定蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用. | |||
| 化学交联质谱(XL-MS) | 基于化学交联剂以共价键连接蛋白质的氨基酸残基 | 通过化学交联剂与空间距离较近的蛋白质残基位点间的化学反应生成新的共价键, 结合串联质谱鉴定交联肽的氨基酸序列和修饰的残基位点, 通过对分子间交联肽的解析鉴定蛋白质-蛋白质间相互作用信息. | [ |
| 共分级偶联质谱(CF‑MS) | 相同生化成分的蛋白质能在色谱中共流, 进而依赖相关算法从蛋白质的共定位和共聚集数据推断蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用 | 通过分子量/电荷/亲疏水性的差异, 将生物化学/生物物理性质相似的蛋白质在生理状态进行分离, 对每个馏分进行串联质谱鉴定, 通过算法对鉴定结果相似性进行评分(例: 蛋白质定量、质量控制、预处理和洗脱曲线), 最后推断分析蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用. | [ |
| [1] |
Fu, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Shao, X.; Cai, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 472. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20100489 |
|
(付浩浩, 陈淏川, 张宏, 邵学广, 蔡文生, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 472.)
doi: 10.6023/A20100489 |
|
| [2] |
Britt, H. M.; Cragnolini, T.; Thalassinos, K. Chem. Rev. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00356
|
| [3] |
Richards, A. L.; Eckhardt, M.; Krogan, N. J. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2021, 17, e8792.
doi: 10.15252/msb.20188792 pmid: 33434350 |
| [4] |
Fenn, J. B.; Mann, M.; Meng, C. K.; Wong, S. F.; Whitehouse, C. M. Science 1989, 246, 64.
pmid: 2675315 |
| [5] |
Karas, M.; Hillenkamp, F. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 2299.
doi: 10.1021/ac00171a028 pmid: 3239801 |
| [6] |
Aebersold, R.; Mann, M. Nature 2003, 422, 198.
doi: 10.1038/nature01511 |
| [7] |
Link, A. J.; Eng, J.; Schieltz, D. M.; Carmack, E.; Mize, G. J.; Morris, D. R.; Garvik, B. M.; Yates, J. R., 3rd, Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 676.
doi: 10.1038/10890 pmid: 10404161 |
| [8] |
Bian, Y.; Zheng, R.; Bayer, F. P.; Wong, C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Meng, C.; Zolg, D. P.; Reinecke, M.; Zecha, J.; Wiechmann, S.; Heinzlmeir, S.; Scherr, J.; Hemmer, B.; Baynham, M.; Gingras, A.-C.; Boychenko, O.; Kuster, B. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7 |
| [9] |
Dunham, W. H.; Mullin, M.; Gingras, A.-C. Proteomics 2012, 12, 1576.
doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100523 pmid: 22611051 |
| [10] |
Kim, D. I.; Roux, K. J. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 804.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.09.004 |
| [11] |
Chavez, J. D.; Mohr, J. P.; Mathay, M.; Zhong, X.; Keller, A.; Bruce, J. E. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2318.
doi: 10.1038/s41596-019-0181-3 pmid: 31270507 |
| [12] |
Wilkins, M. R.; Appel, R. D.; Williams, K. L.; Hochstrasser, D. F., Proteome Research: Concepts, Technology and Application, Second Edition, Eds.: Wilkins, M. R.; Zhang, L., Science Press, Beijing, 2010, p. 52.
|
| [13] |
Zhao, L.; Zhao, Q.; Shan, Y.; Fang, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, B.; Li, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 1097.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04161 |
| [14] |
Low, T. Y.; Syafruddin, S. E.; Mohtar, M. A.; Vellaichamy, A.; NS, A. R.; Pung, Y. F.; Tan, C. S. H. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 5325.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03856-0 |
| [15] |
Cox, J.; Mann, M. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1511 |
| [16] |
Eng, J. K.; Fischer, B.; Grossmann, J.; Maccoss, M. J. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 4598.
doi: 10.1021/pr800420s |
| [17] |
Rath, S.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, R.; Ast, T.; Chan, C.; Durham, T. J.; Goodman, R. P.; Grabarek, Z.; Haas, M. E.; Hung, W. H. W.; Joshi, P. R.; Jourdain, A. A.; Kim, S. H.; Kotrys, A. V.; Lam, S. S.; McCoy, J. G.; Meisel, J. D.; Miranda, M.; Panda, A.; Patgiri, A.; Rogers, R.; Sadre, S.; Shah, H.; Skinner, O. S.; To, T. L.; Walker, M. A.; Wang, H.; Ward, P. S.; Wengrod, J.; Yuan, C. C.; Calvo, S. E.; Mootha, V. K. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1541.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1011 |
| [18] |
Yang, B.; Wu, Y. J.; Zhu, M.; Fan, S. B.; Lin, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Chi, H.; Li, Y. X.; Chen, H. F.; Luo, S. K.; Ding, Y. H.; Wang, L. H.; Hao, Z.; Xiu, L. Y.; Chen, S.; Ye, K.; He, S. M.; Dong, M. Q. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 904.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2099 |
| [19] |
Anderson, G. A.; Tolic, N.; Tang, X.; Zheng, C.; Bruce, J. E. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 3412.
pmid: 17676784 |
| [20] |
Hoopmann, M. R.; Zelter, A.; Johnson, R. S.; Riffle, M.; MacCoss, M. J.; Davis, T. N.; Moritz, R. L. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2190.
doi: 10.1021/pr501321h pmid: 25812159 |
| [21] |
Teo, G.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Nesvizhskii, A. I.; Gingras, A. C.; Choi, H. J. Proteomics 2014, 100, 37.
doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.10.023 |
| [22] |
Combe, C. W.; Fischer, L.; Rappsilber, J. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2015, 14, 1137.
doi: 10.1074/mcp.O114.042259 |
| [23] |
Riffle, M.; Jaschob, D.; Zelter, A.; Davis, T. N. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2863.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00274 |
| [24] |
Schweppe, D. K.; Zheng, C.; Chavez, J. D.; Navare, A. T.; Wu, X.; Eng, J. K.; Bruce, J. E. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2716.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw232 pmid: 27153666 |
| [25] |
Malovannaya, A.; Lanz, R. B.; Jung, S. Y.; Bulynko, Y.; Le, N. T.; Chan, D. W.; Ding, C.; Shi, Y.; Yucer, N.; Krenciute, G.; Kim, B. J.; Li, C.; Chen, R.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; O'Malley, B. W.; Qin, J. Cell 2011, 145, 787.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.05.006 pmid: 21620140 |
| [26] |
Hopp, T. P.; Prickett, K. S.; Price, V. L.; Libby, R. T.; March, C. J.; Pat Cerretti, D.; Urdal, D. L.; Conlon, P. J. Nat. Biotechnol. 1988, 6, 1204.
doi: 10.1038/nbt1088-1204 |
| [27] |
Evan, G. I.; Lewis, G. K.; Ramsay, G.; Bishop, J. M. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1985, 5, 3610.
doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610-3616.1985 pmid: 3915782 |
| [28] |
Hochuli, E.; Bannwarth, W.; Döbeli, H.; Gentz, R.; Stüber, D. Nat. Biotechnol. 1988, 6, 1321.
doi: 10.1038/nbt1188-1321 |
| [29] |
Schmidt, T. G.; Skerra, A. Protein Eng. 1993, 6, 109.
pmid: 8433964 |
| [30] |
Smith, D. B.; Johnson, K. S. Gene 1988, 67, 31.
pmid: 3047011 |
| [31] |
Chalfie, M.; Tu, Y.; Euskirchen, G.; Ward, W. W.; Prasher, D. C. Science 1994, 263, 802.
pmid: 8303295 |
| [32] |
Uhlén, M.; Nilsson, B.; Guss, B.; Lindberg, M.; Gatenbeck, S.; Philipson, L. Gene 1983, 23, 369.
pmid: 6313477 |
| [33] |
Guruharsha, K. G.; Rual, J. F.; Zhai, B.; Mintseris, J.; Vaidya, P.; Vaidya, N.; Beekman, C.; Wong, C.; Rhee, D. Y.; Cenaj, O.; McKillip, E.; Shah, S.; Stapleton, M.; Wan, K. H.; Yu, C.; Parsa, B.; Carlson, J. W.; Chen, X.; Kapadia, B.; VijayRaghavan, K.; Gygi, S. P.; Celniker, S. E.; Obar, R. A.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. Cell 2011, 147, 690.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.047 pmid: 22036573 |
| [34] |
Rigaut, G.; Shevchenko, A.; Rutz, B.; Wilm, M.; Mann, M.; Seraphin, B. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 1030.
doi: 10.1038/13732 pmid: 10504710 |
| [35] |
Dunham, W. H.; Larsen, B.; Tate, S.; Badillo, B. G.; Goudreault, M.; Tehami, Y.; Kislinger, T.; Gingras, A. C. Proteomics 2011, 11, 2603.
doi: 10.1002/pmic.201000571 pmid: 21630450 |
| [36] |
Bendayan, M. Science 2001, 291, 1363.
pmid: 11233453 |
| [37] |
Mayer, G.; Bendayan, M. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1997, 45, 1449.
pmid: 9358846 |
| [38] |
Kim, D. I.; Birendra, K. C.; Zhu, W.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Doye, V.; Roux, K. J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2014, 111, E2453.
|
| [39] |
Kotani, N.; Gu, J.; Isaji, T.; Udaka, K.; Taniguchi, N.; Honke, K. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008, 105, 7405.
|
| [40] |
Miyagawa-Yamaguchi, A.; Kotani, N.; Honke, K. PLoS One 2014, 9, e93054.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093054 |
| [41] |
Roux, K. J.; Kim, D. I.; Burke, B. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2013, 74, 19.23.1.
|
| [42] |
Kim, D. I.; Jensen, S. C.; Noble, K. A.; Kc, B.; Roux, K. H.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Roux, K. J. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 1188.
doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-12-0844 |
| [43] |
Antonicka, H.; Lin, Z. Y.; Janer, A.; Aaltonen, M. J.; Weraarpachai, W.; Gingras, A. C.; Shoubridge, E. A. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 479.
doi: S1550-4131(20)30412-5 pmid: 32877691 |
| [44] |
Opitz, N.; Schmitt, K.; Hofer-Pretz, V.; Neumann, B.; Krebber, H.; Braus, G. H.; Valerius, O. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2017, 16, 2199.
doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.066654 |
| [45] |
Lin, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, W.; Fang, M.; Li, M.; Li, H. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 749.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00749 |
| [46] |
Gupta, G. D.; Coyaud, E.; Goncalves, J.; Mojarad, B. A.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Gheiratmand, L.; Comartin, D.; Tkach, J. M.; Cheung, S. W.; Bashkurov, M.; Hasegan, M.; Knight, J. D.; Lin, Z. Y.; Schueler, M.; Hildebrandt, F.; Moffat, J.; Gingras, A. C.; Raught, B.; Pelletier, L. Cell 2015, 163, 1484.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.065 |
| [47] |
Uezu, A.; Kanak, D. J.; Bradshaw, T. W.; Soderblom, E. J.; Catavero, C. M.; Burette, A. C.; Weinberg, R. J.; Soderling, S. H. Science 2016, 353, 1123.
doi: 10.1126/science.aag0821 |
| [48] |
Rhee, H. W.; Zou, P.; Udeshi, N. D.; Martell, J. D.; Mootha, V. K.; Carr, S. A.; Ting, A. Y. Science 2013, 339, 1328.
doi: 10.1126/science.1230593 |
| [49] |
Lam, S. S.; Martell, J. D.; Kamer, K. J.; Deerinck, T. J.; Ellisman, M. H.; Mootha, V. K.; Ting, A. Y. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 51.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3179 |
| [50] |
Branon, T. C.; Bosch, J. A.; Sanchez, A. D.; Udeshi, N. D.; Svinkina, T.; Carr, S. A.; Feldman, J. L.; Perrimon, N.; Ting, A. Y. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 880.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.4201 pmid: 30125270 |
| [51] |
Cho, K. F.; Branon, T. C.; Rajeev, S.; Svinkina, T.; Udeshi, N. D.; Thoudam, T.; Kwak, C.; Rhee, H. W.; Lee, I. K.; Carr, S. A.; Ting, A. Y. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2020, 117, 12143.
|
| [52] |
Chen, Z. L.; Cao, Y.; He, S. M. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2161.Q.20210728.1624.006.html.
|
|
(陈镇霖, 曹勇, 贺思敏, 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2021, 网络首发.)
|
|
| [53] |
Fan, S. B.; Wu, Y. J.; Yang, B.; Chi, H.; Meng, J. M.; Lu, S.; Zhang, K.; Wu, L.; Sun, R. X.; Dong, M. Q.; He, S. M. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 41, 1109. (in Chinese)
|
|
(樊盛博, 吴妍洁, 杨兵, 迟浩, 孟佳明, 卢珊, 张昆, 邬龙, 孙瑞祥, 董梦秋, 贺思敏, 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2014, 41, 1109.)
|
|
| [54] |
Tang, X.; Bruce, J. E. Mol. Biosyst. 2010, 6, 939.
doi: 10.1039/b920876c |
| [55] |
Bartolec, T. K.; Smith, D. L.; Pang, C. N. I.; Xu, Y. D.; Hamey, J. J.; Wilkins, M. R. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 1874.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03975 pmid: 31851481 |
| [56] |
Wheat, A.; Yu, C.; Wang, X.; Burke, A. M.; Chemmama, I. E.; Kaake, R. M.; Baker, P.; Rychnovsky, S. D.; Yang, J.; Huang, L. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2021, 118, e2023360118.
|
| [57] |
Schweppe, D. K.; Chavez, J. D.; Lee, C. F.; Caudal, A.; Kruse, S. E.; Stuppard, R.; Marcinek, D. J.; Shadel, G. S.; Tian, R.; Bruce, J. E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2017, 114, 1732.
|
| [58] |
Ryl, P. S. J.; Bohlke-Schneider, M.; Lenz, S.; Fischer, L.; Budzinski, L.; Stuiver, M.; Mendes, M. M. L.; Sinn, L.; O'Reilly, F. J.; Rappsilber, J. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 327.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00541 |
| [59] |
Linden, A.; Deckers, M.; Parfentev, I.; Pflanz, R.; Homberg, B.; Neumann, P.; Ficner, R.; Rehling, P.; Urlaub, H. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2020, 19, 1161.
doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA120.002028 |
| [60] |
Albanese, P.; Tamara, S.; Saracco, G.; Scheltema, R. A.; Pagliano, C. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1361.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15184-1 pmid: 32170184 |
| [61] |
Mann, M. Proteomics 2020, 20, 1900330.
doi: 10.1002/pmic.201900330 |
| [62] |
Havugimana, P. C.; Hart, G. T.; Nepusz, T.; Yang, H.; Turinsky, A. L.; Li, Z.; Wang, P. I.; Boutz, D. R.; Fong, V.; Phanse, S.; Babu, M.; Craig, S. A.; Hu, P.; Wan, C.; Vlasblom, J.; Dar, V. U.; Bezginov, A.; Clark, G. W.; Wu, G. C.; Wodak, S. J.; Tillier, E. R.; Paccanaro, A.; Marcotte, E. M.; Emili, A. Cell 2012, 150, 1068.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.011 pmid: 22939629 |
| [63] |
Skinnider, M. A.; Foster, L. J. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 806.
doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01194-4 pmid: 34211188 |
| [64] |
Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Fan, X.; Chen, P. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 406. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20110530 |
|
(汪欣, 张贤睿, 黄宗煜, 樊新元, 陈鹏, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 406.)
doi: 10.6023/A20110530 |
|
| [65] |
Liu, X.; Salokas, K.; Tamene, F.; Jiu, Y.; Weldatsadik, R. G.; Ohman, T.; Varjosalo, M. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1188.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03523-2 |
| [66] |
Leissing, F.; Misch, N. V.; Wang, X.; Werner, L.; Huang, L.; Conrath, U.; Beckers, G. J. M. Plant Physiology 2021, 187, 2381.
doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab446 pmid: 34609515 |
| [1] | Fan Haibo, Yang Rongjie, Li Xiangmei. Purity Analysis of Polyhedral Oligomeric Octa(nitrophenyl)silsesquioxane [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 70(16): 1737-1742. |
| [2] | Zhou Sisi, Ma Zengchun, Liang Qiande, Wang Yuguang, Tan Hongling, Xiao Chengrong, Zhang Boli, Gao Yue. UPLC/Q-TOF-MS Based Chemical Profiling Approach to Evaluate Chemical Composition of Augmentation Toxicity in Combination of Radix Aconiti and Pinellia Praeparata [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 70(03): 284-290. |
| [3] | WANG Chao, WANG Yu-Guang, LIANG Qian-De, RANG Wei-Qing, XIAO Cheng-Rong, GAO Yue. Analysis of Chemical Composition in Combination of Aconitum and Fritillaria by UPLC/Q-TOFMS with Multivariate Statistical Analysis [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(16): 1920-1928. |
| [4] | ZHOU Wan-Hong, WANG Ye, YU Ling, JIN Yong-Ming, ZHENG Sai-Jing. A Rapid LC-MS/MS Method for Determination of Nicotine and Its 9 Metabolites in Urine [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(07): 803-809. |
| [5] | YAN Jun, LIU Shu, PI Zi-Feng, SONG Feng-Rui, LIU Zhong-Ying, LIU Zhi-Qiang. Studies on Fingerprint Chromatograms of Anti-virus Component of Compound Indigowoad Root Granule by HPLC-UV and LC-ESI-MSn [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(02): 204-208. |
| [6] | . Identification of Anthocyanins and Flavonols in Extract of Blueberry by Using HPLC-ESI-MS/MS [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2009, 67(4): 318-322. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||