化学学报 ›› 2012, Vol. 0 ›› Issue (05): 659-666 .DOI: 10.6023/A1104073 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
毛琼晶a, 彭政b, 陆胜勇a, 李晓东a, 严建华a
Mao Qiongjinga, Peng Zhengb, Lu Shengyonga, Li Xiaodonga, Yan Jianhuaa
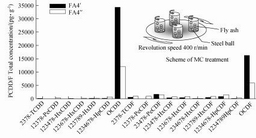
利用机械化学法进行含二噁英废弃物的无害化处置, 是一个值得关注的研究领域. 本研究以去除大部分二噁英及其它有机成分的医疗垃圾焚烧飞灰作为反应基质, 添加了八氯代二噁英和呋喃(OCDD/OCDF)后, 在自行研制的行星式球磨试验装置上进行了球磨机械化学法降解试验研究. 实验球磨两种飞灰分别采自某回转窑热解流化多段焚烧系统和某简易固定床焚烧系统的医疗垃圾焚烧炉布袋除尘器, 其中对于简易固定床焚烧处置的飞灰, OCDD 和OCDF 分别减少了64.7%和63.6%, 氯化度由6.86 降至5.53. 两种飞灰处理后, 平均粒径大幅缩小, 比表面积、孔容积显著增加,CaCO3 强度显著减弱. 实验证实飞灰本身的某些组分(CaCO3 等)在球磨机械化学处理过程中起到类似氧化钙(CaO)的脱氯还原剂作用, 且机械化学法降解二噁英的效果显著. 研究结果对实际医疗垃圾焚烧飞灰中二噁英类污染物的脱除具有指导意义.