化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (12): 1518-1525.DOI: 10.6023/A21070343 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2021-07-24
发布日期:2021-10-09
通讯作者:
贺宇飞, 李殿卿
基金资助:
Min Zhao, Xue Wang, Yanan Liu, Yufei He( ), Dianqing Li
), Dianqing Li
Received:2021-07-24
Published:2021-10-09
Contact:
Yufei He, Dianqing Li
Supported by:文章分享
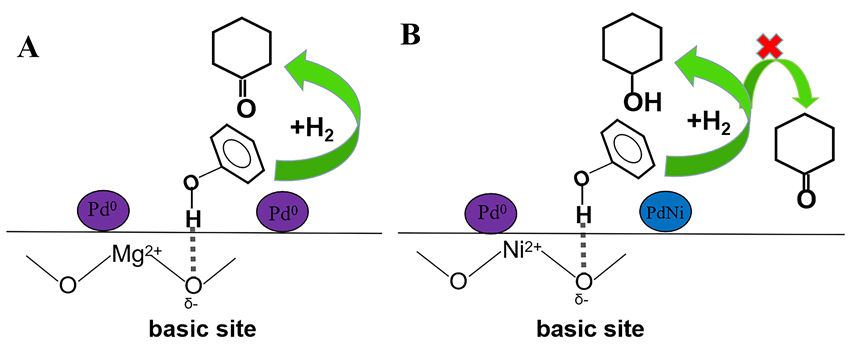
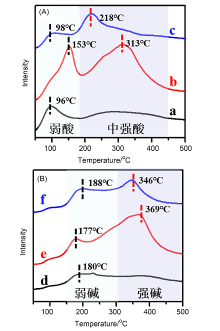
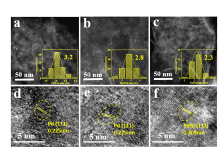
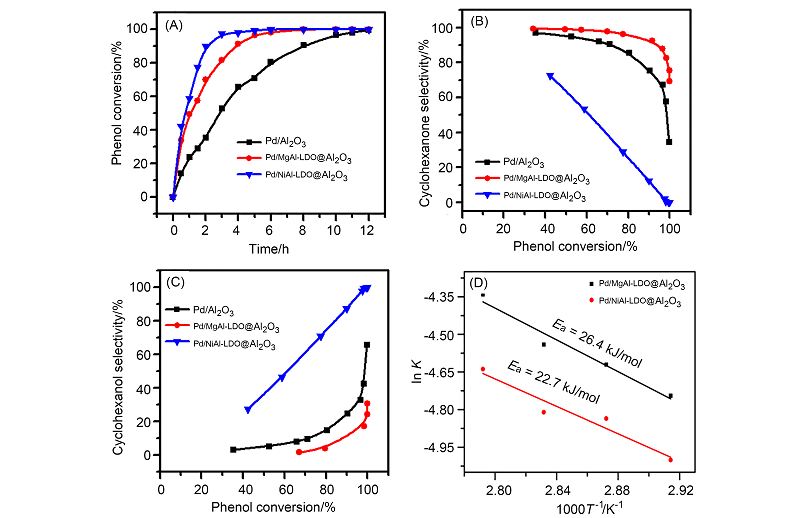
环己酮是合成尼龙等材料的重要中间体, 但苯酚直接加氢反应制备环己酮容易生成环己醇而降低收率. 采用原位生长策略制备Pd/MgAl-LDO@Al2O3催化剂, 并用于苯酚选择性加氢反应, 获得的催化剂在高底物比条件具有良好的催化性能, 相较于Pd/Al2O3催化剂, Pd/MgAl-LDO@Al2O3催化剂使苯酚转化率显著增加, 苯酚转化率在97%时环己酮选择性可达88%. 利用X射线衍射(XRD)、程序升温脱附(TPD)、高分辨透射电子显微镜(HRTEM)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等手段对催化剂结构进行表征发现在氧化铝上原位生长类水滑石结构能够优化催化剂孔结构并提高活性组分分散度, 且增加了载体表面碱位点的强度, 碱位点的存在影响了苯酚的吸附形式, 从而大幅增加环己酮的选择性. 此外, 当将Ni引入层状结构时, 通过NaBH4的还原可获得PdNi合金结构. 动力学研究表明, 由于PdNi合金的形成, Pd/NiAl-LDO@Al2O3催化剂苯酚加氢反应的能垒低于Pd/MgAl-LDO@Al2O3, 同时合金结构导致环己酮选择性的明显降低.
赵敏, 王雪, 刘雅楠, 贺宇飞, 李殿卿. 苯酚加氢制环己酮用高效Pd/MgAl-LDO@Al2O3催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(12): 1518-1525.
Min Zhao, Xue Wang, Yanan Liu, Yufei He, Dianqing Li. Preparation of Efficient Pd/MgAl-LDO@Al2O3 Catalyst for Phenol Hydrogenation to Cyclohexanone[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(12): 1518-1525.
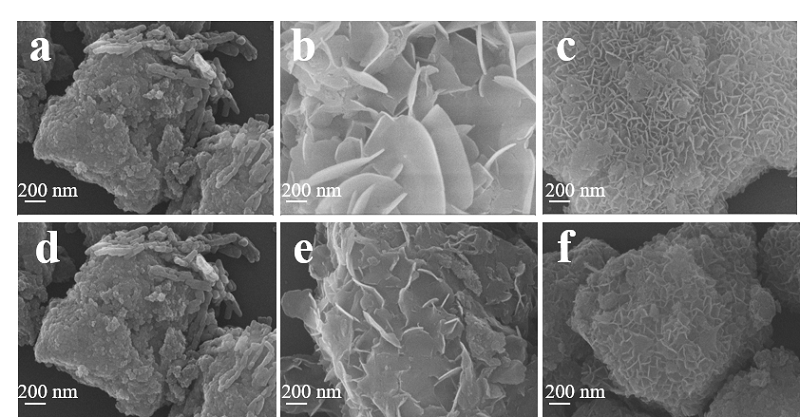
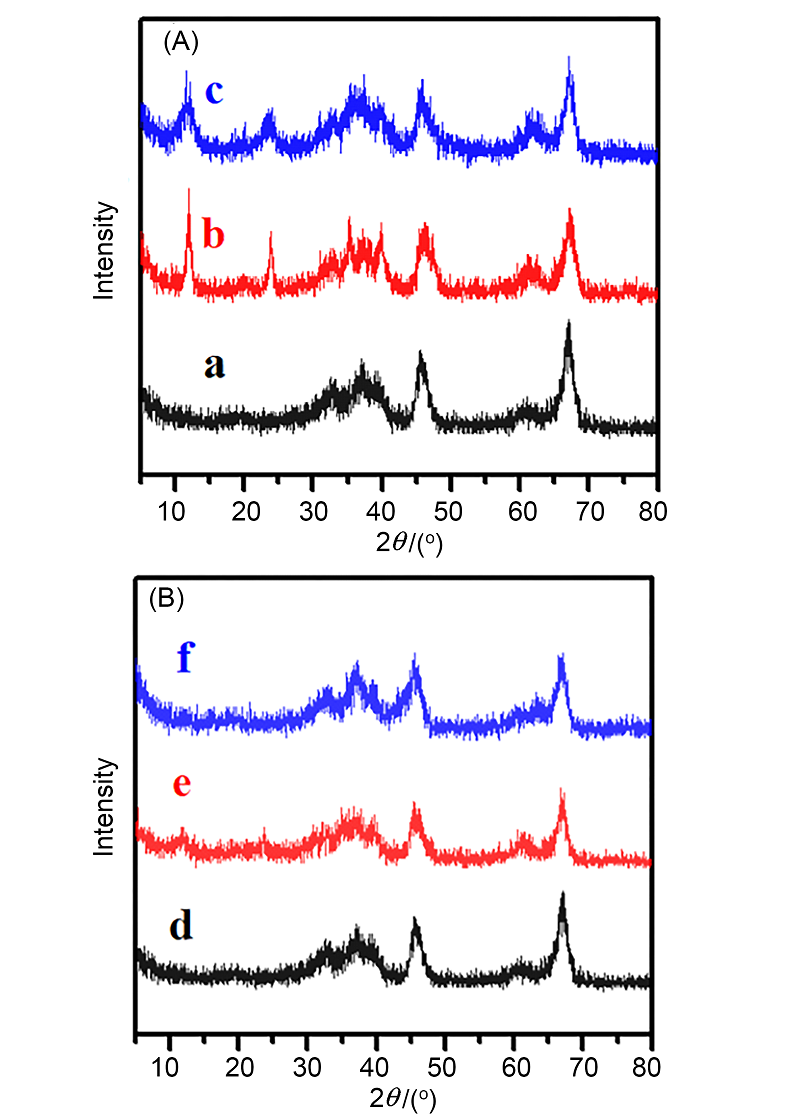

| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2•g–1) | 孔容/(cm3•g–1) | 平均孔径/nm | 负载量/% | 分散度/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/Al2O3 | 107 | 0.19 | 5.8 | 0.90 | 26.1 |
| Pd/MgAl-LDO@Al2O3 | 139 | 0.34 | 9.8 | 0.83 | 33.2 |
| Pd/NiAl-LDO@Al2O3 | 148 | 0.27 | 7.1 | 0.87 | 35.9 |
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2•g–1) | 孔容/(cm3•g–1) | 平均孔径/nm | 负载量/% | 分散度/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/Al2O3 | 107 | 0.19 | 5.8 | 0.90 | 26.1 |
| Pd/MgAl-LDO@Al2O3 | 139 | 0.34 | 9.8 | 0.83 | 33.2 |
| Pd/NiAl-LDO@Al2O3 | 148 | 0.27 | 7.1 | 0.87 | 35.9 |




| [1] |
Li, B. L.; Liu, R. Y.; Liang, R. X.; Jia, Y. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 448 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A17020080 |
|
( 李保乐, 刘人荣, 梁仁校, 贾义霞, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 448.)
doi: 10.6023/A17020080 |
|
| [2] |
Weng, X.; Dong, J.; She, T. T.; Bai, G. Y. Journal of Hebei University 2018, 3, 239 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 温昕, 董洁, 舍添添, 白国义, 河北大学学报, 2018, 3, 239.)
|
|
| [3] |
Shore, S. G.; Ding, E.; Park, C.; Keane, M. A. Catal. Commun. 2002, 3, 77.
doi: 10.1016/S1566-7367(02)00052-3 |
| [4] |
Sikhwivhilu, L. M.; Coville, N. J.; Naresh, D.; Chary, K. Appl. Catal. A, 2007, 324, 52.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2007.03.004 |
| [5] |
Neri, G.; Visco, A. M.; Donato, A.; Milone, C.; Malentacchi, M.; Gubitosa, G. Appl. Catal. A, 1994, 110, 49.
doi: 10.1016/0926-860X(94)80104-5 |
| [6] |
Chary, K. V. R.; Naresh, D.; Vishwanathan, V.; Sadakane, M.; Ueda, W. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 471.
doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2006.07.017 |
| [7] |
Scirè, S.; Minicò, S.; Crisafulli, C. Appl. Catal. A, 2002, 235, 21.
doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(02)00237-5 |
| [8] |
Gonzalez-Velasco, J. R.; Gonzalez-Marcos, M. P.; Arnaiz, S.; Gutierrez-Ortiz, J. I.; Gutierrez-Ortiz, M. A. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 1031.
doi: 10.1021/ie00043a004 |
| [9] |
Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Li, H. R.; Su, D. S.; Antonietti, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 42, 939.
|
| [10] |
Souza, P. M. D.; Rabelo-Neto, R. C.; Borges, L. E. P.; Jacobs, G.; Davis, B. H.; Sooknoi, T.; Resasco, D.; Nornoha, F. B. ACS Catal. 2015, 4, 1318.
doi: 10.1021/cs500312z |
| [11] |
Makowski, P.; Cakan, R. D.; Antonietti, M.; Goettmann, F.; Titirici, M. M. Chem. Commun. 2008, 39, 999.
|
| [12] |
Li, H.; Liu, J. L.; Li, H. X. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2321.
doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2007.11.080 |
| [13] |
Xiang, Y. Z.; Ma, L.; Lu, C. S.; Zhang, Q. F.; Li, X. N. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 939.
doi: 10.1039/b803217c |
| [14] |
Liu, H. Z.; Jiang, T.; Han, B. X.; Liang, S. G.; Zhou, Y. X. Science 2009, 326, 1250.
doi: 10.1126/science.1179713 |
| [15] |
Li, X. Z.; Cheng, L.; Wang, X. Y. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 45, 1249.
doi: 10.1007/s11164-018-3687-3 |
| [16] |
Cavani, F.; Trifirò, F.; Vaccari, A. Catal. Today 1991, 11, 173.
doi: 10.1016/0920-5861(91)80068-K |
| [17] |
Yu, J.; Yang, Y. S.; Wei, M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1129 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A19070260 |
|
( 余俊, 杨宇森, 卫敏, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1129.)
doi: 10.6023/A19070260 |
|
| [18] |
Debecker, D. P.; Gaigneaux, E. M.; Busca, G. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 3920.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v15:16 |
| [19] |
Sivasamy, A.; Cheah, K. Y.; Fornasiero, P.; Kemausuor, F.; Zinoviev, S.; Miertus, S. ChemSusChem 2010, 2, 278.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v2:4 |
| [20] |
Sikhwivhilu, L.; Coville, N.; Naresh, D.; Chary, K. V. R.; Vishwanathan, V. Appl. Catal. A, 2007, 324, 52.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2007.03.004 |
| [21] |
Veloso, C. O.; Pérez, C. N.; Souza, B. M. D.; Lima, E. C.; Dias, A. G.; Monteiro, J. L. F.; Henriques, C. A. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2008, 107, 23.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.05.036 |
| [22] |
Brindley, G. W.; Kikkawa, S. Clay. Clay Miner. 1980, 28, 87.
doi: 10.1346/CCMN |
| [23] |
Mahata, N.; Vishwanathan, V. Catal. Today 1999, 49, 65.
doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00409-X |
| [24] |
Zhong, J. W.; Chen, J. Z.; Chen, L. M. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 3555.
doi: 10.1039/C4CY00583J |
| [25] |
Yuan, X. Q.; Li, B. T.; Li, B.; Wang, X. J. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 211, 106581.
doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2020.106581 |
| [26] |
Chowdhury, S. R.; Maiyalagan, T.; Bhattachraya, S. K.; Gayen, A. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 342, 136028.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136028 |
| [27] |
Rai, R. K.; Gupta, K.; Behrens, S.; Li, J.; Xu, Q.; Singh, S. K. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 1806.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.v7.12 |
| [1] | 刘洵, 江辉波, 荆凯强, 徐忠宁, 郭国聪. Zn2+通过电子转移提升CO酯化反应Pd基催化剂性能[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 691-696. |
| [2] | 李保乐, 刘人荣, 梁仁校, 贾义霞. 钯/氨基酸共催化环己酮分子内α-烯基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(5): 448-452. |
| [3] | 邹雪, 王鸿梅, 陆燕, 黄超群, 夏磊, 陈小景, 沈成银, 储焰南. 电喷雾萃取电离-三重四极杆质谱快速检测PVC医疗器械中残留环己酮的方法研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(8): 851-855. |
| [4] | 薛晓金, 孙琼, 王妍, 吕康乐, 许宜铭. 氟离子对二氧化钛选择性光催化氧化环己烷的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(06): 471-475. |
| [5] | 李静霞,黄靓,戴维林,范康年. 高活性MgO/SnO2复合金属氧化物催化剂的合成及在双氧水选择氧化环己酮制ε-己内酯反应中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(1): 5-9. |
| [6] | 韩卫华, 李浩然, 邓东顺, 王勇. 硼氢化钠还原潜手性酮反应机理的量子化学研究[J]. 化学学报, 2006, 64(16): 1723-1729. |
| [7] | 郭明林. 十聚钨酸季铵盐催化H2O2氧化环己醇为环己酮[J]. 化学学报, 2004, 62(19): 1956-1958. |
| [8] | 毛东森,卢冠忠,陈庆龄,谢在库,张玉贤. 改性钛锆复合氧化物催化环己酮肟气相Beckmann重 排反应[J]. 化学学报, 2001, 59(7): 1139-1144. |
| [9] | 李平,卢冠忠,罗勇,代亚男. TS分子筛的催化氧化性能研究5: 环己酮氨肟化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2000, 58(2): 204-208. |
| [10] | 郭灿城,张晓兵,侯连伯,徐建兵,郝旭东,郭广明,梁本熹,陈新斌. 金属卟啉催化环己烷羟基化反应中环己酮的形成机理研究[J]. 化学学报, 1998, 56(5): 489-494. |
| [11] | 郭灿城. 金属卟啉的合成及其对细胞色素P-450的模拟 12.μ-氧-双铁(Ⅲ) 卟啉系列化合物对环已烷的单充氧催化物作用[J]. 化学学报, 1994, 52(4): 367-372. |
| [12] | 蒋本国,叶秀林. 4-(1,2-亚乙二氧基)环己酮及其2-甲醛和2-羧酸酯的烯胺和烯醇反应的研究[J]. 化学学报, 1993, 51(12): 1214-1220. |
| [13] | 铁宏,马振坤,李良助,张滂. 几个烯胺的邻硝基苯甲酰化和在酸水解中发生的重排[J]. 化学学报, 1990, 48(7): 720-725. |
| [14] | 陈方平,章咏华. 用于非水介质分析的新型离子选择电极: 水膜电极的设想及验证[J]. 化学学报, 1989, 47(2): 174-177. |
| [15] | 赵振国,张兰辉,林. 硅胶自环己烷中吸附环己酮和苯甲酸[J]. 化学学报, 1988, 46(1): 53-56. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||