化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (3): 386-394.DOI: 10.6023/A21110536 上一篇 下一篇
综述
投稿日期:2021-11-27
发布日期:2021-12-16
通讯作者:
曾庆乐
作者简介: |
王一丁, 成都理工大学2019 级硕士生. 本科毕业于成都理工大学, 硕士阶段师从曾庆乐教授, 主要从事钯催化环化反应和不对称催化反应. |
 |
李福海, 成都理工大学2018级硕士生, 本科毕业于四川理工学院(今更名为四川轻化工大学), 硕士阶段师从曾庆乐教授, 主要从事有机合成方法学和有机硒化学的研究. |
 |
曾庆乐, 教授, 博士生导师, 四川省有突出贡献的优秀专家, 1970年出生于福建省漳州市平和县, 1994年在福建师范大学获得理学学士学位, 1997年在中国科学院兰州化学物理研究所获得理学硕士学位, 2002年在中国科学院成都有机化学研究所获得理学博士学位. 2006年5月入职成都理工大学. 2008年至2009年在美国麻省理工学院做访问科学家. 主要研究方向包括有机合成方法学、(手性)有机硫化学、矿产资源化学和环境治理材料. |
基金资助:
Yiding Wang, Fuhai Li, Qingle Zeng( )
)
Received:2021-11-27
Published:2021-12-16
Contact:
Qingle Zeng
About author:Supported by:文章分享
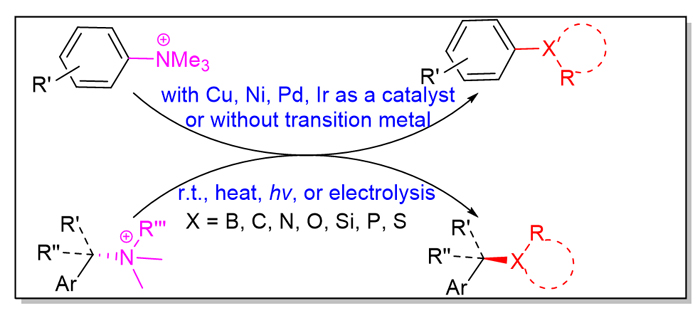
胺类种类繁多, 原料易得. 胺类的C—N键键能较大, 一般需要通过活化再进行断裂. 近些年发展了多种氨基的活化方法, 其中把胺类转化为季铵盐的活化方法, 制备容易、存放稳定, 具有一定优势. 最近十年左右, 芳香胺和苄胺衍生的季铵盐通过C—N键断裂、构建各种C—X键的研究取得了巨大的研究进展. 本综述主要论述了最近几年需要和不需要过渡金属催化的季铵盐通过C—N键断裂构建C—X键的反应. 通过C—N键断裂, 季铵盐可以构建C—B键、C—C键、C—N键、C—O键、C—Si键、C—P键、C—S键、C—Se键等, 合成硼酸酯、芳烃、烷烃、醚类、胺类、硅烷、膦、硫醚、二硫化物、硒醚、二硒化物等化合物. 而且, 如果是采用手性苄胺衍生的季铵盐, 还可以得到多种高对映体纯的手性有机化合物; 季铵盐的手性在产物中保持良好, 并且, 对所有反应都发生SN2型的构型翻转.
王一丁, 李福海, 曾庆乐. 季铵盐C—N键断裂构建C—X键的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 386-394.
Yiding Wang, Fuhai Li, Qingle Zeng. Advances in Formation of C—X Bonds via Cleavage of C—N Bond of Quaternary Ammonium Salts[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 386-394.
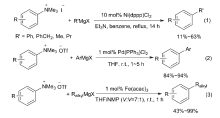
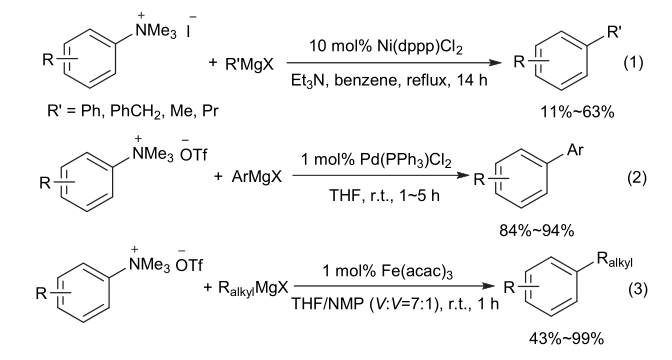
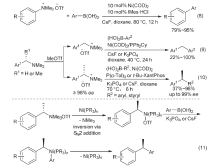
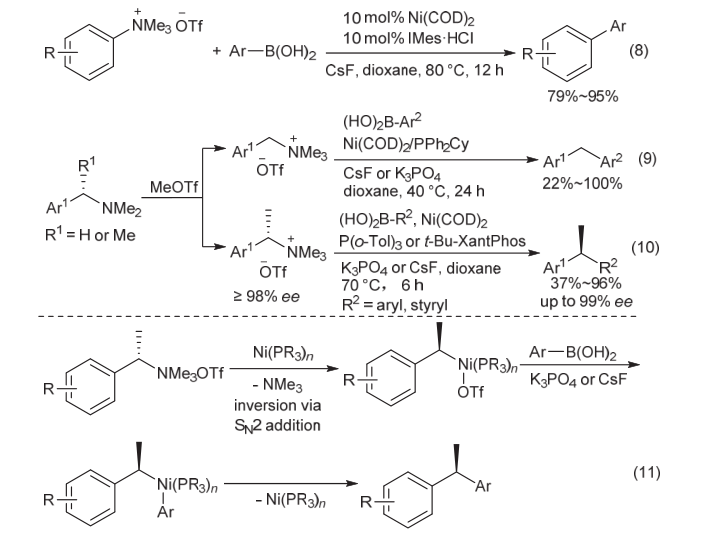
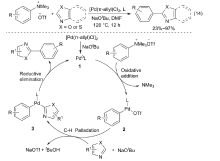
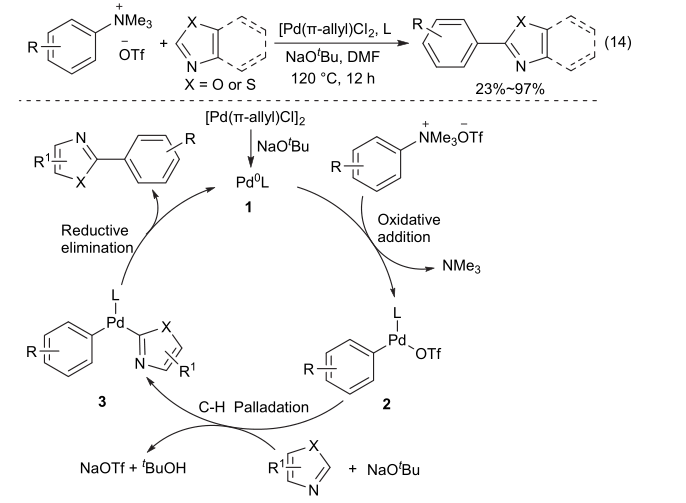
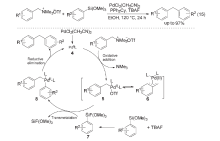
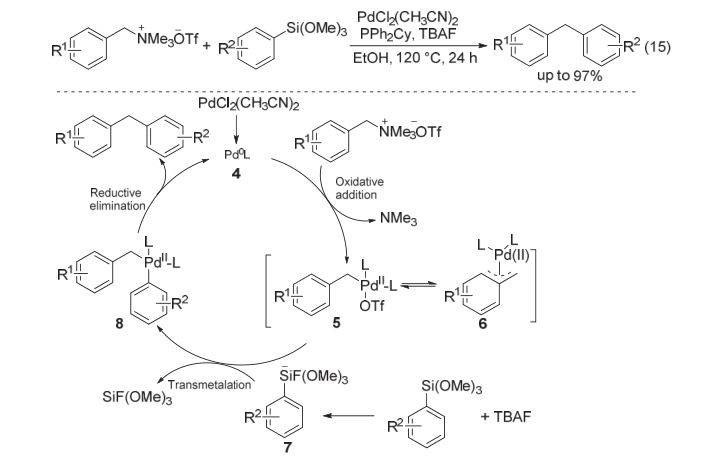
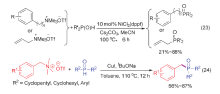
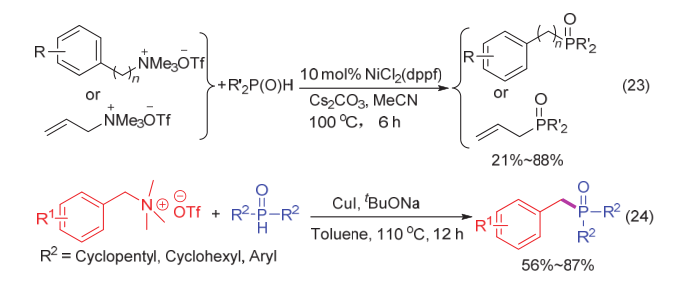
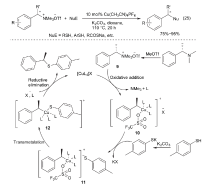
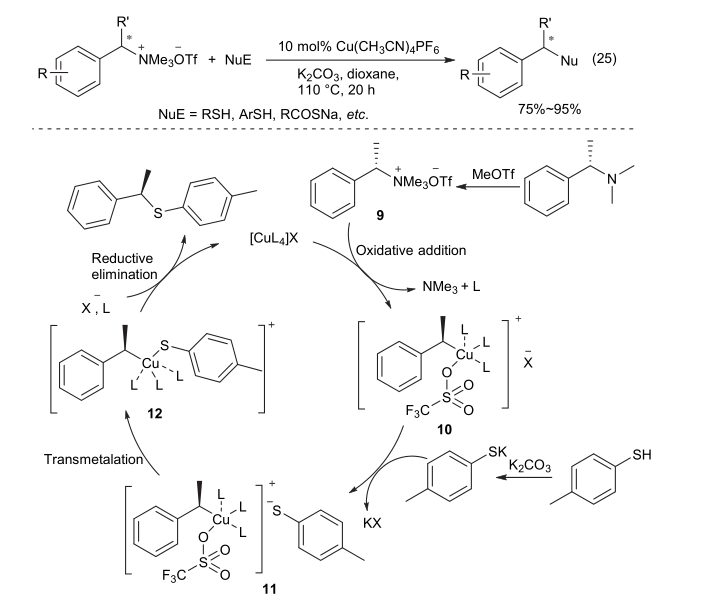
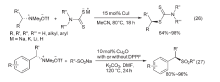
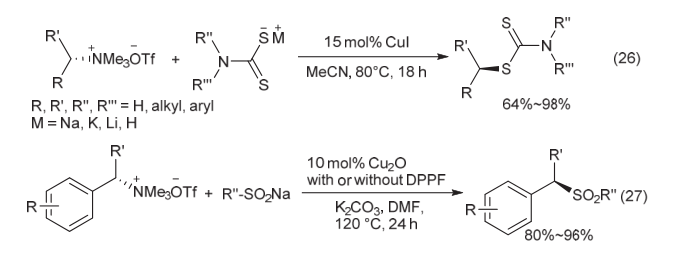
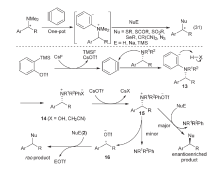

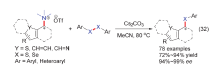



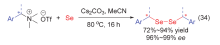
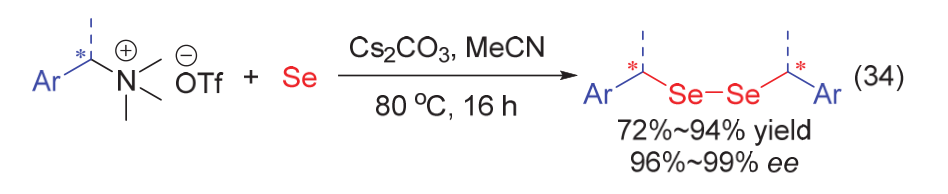
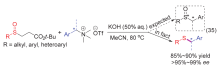
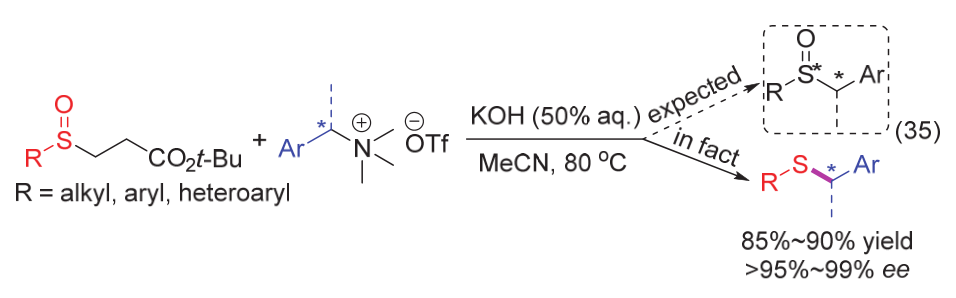

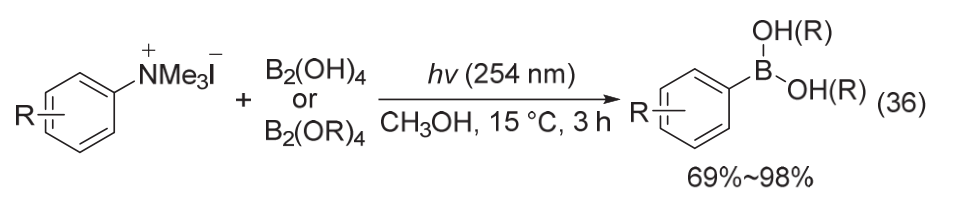
| [1] |
Hartwig, J. F. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 852.
doi: 10.1021/ar970282g |
| [2] |
Ley, S. V.; Thomas, A. W. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 5400.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773 |
| [3] |
Schlummer, B.; Scholz, U. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 1599.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.200404216 |
| [4] |
Ouyang, K.; Hao, W.; Zhang, W. X.; Xi, Z. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12045.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00386 |
| [5] |
Wang, Q.; Su, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1257.
doi: 10.1039/C5CS00534E |
| [6] |
Wang, Z. X.; Yang, B. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 1057.
doi: 10.1039/C9OB02667C |
| [7] |
Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Xia, J. B. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 38, 1949. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201803013 |
|
(李刚, 陈烨, 夏纪宝, 有机化学, 2018, 38, 1949.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201803013 |
|
| [8] |
Song, M. M.; Zhang, Z. G.; Zheng, D.; Li, X.; Liang, R.; Zhao, X. N.; Shi, L.; Zhang, G. S. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 2433. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202001007 |
|
(宋蒙蒙, 张志国, 郑丹, 李祥, 梁蕊, 赵旭娜, 时蕾, 张贵生, 有机化学, 2020, 40, 2433.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202001007 |
|
| [9] |
Menggen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Bao, Y. S. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 38, 902. (in Chinese)
|
|
(孟根其其格, 乌云, 包永胜, 有机化学, 2018, 38, 902.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201710034 |
|
| [10] |
Zhao, Y.; Li, S. H.; Zhang, M. M.; Liu, F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 916. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19040121 |
|
(赵勇, 李施宏, 张苗苗, 刘峰, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 916.)
doi: 10.6023/A19040121 |
|
| [11] |
Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Ouyang, K.; Zhang, W. X. Green Synth. Catal. 2021, 2, 87.
|
| [12] |
Wang, C. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 683.
doi: 10.1248/cpb.c20-00196 |
| [13] |
Bao, H.; Qi, X.; Tambar, U. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1206.
doi: 10.1021/ja110500m |
| [14] |
Wenkert, E.; Han, A. L.; Jenny, C. J. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commnu. 1988, 975.
|
| [15] |
Reeves, J. T.; Fandrick, D. R.; Tan, Z.; Song, J. J.; Lee, H.; Yee, N. K.; Senanayake, C. H. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4388.
doi: 10.1021/ol1018739 |
| [16] |
Guo, W. J.; Wang, Z. X. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 9580.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2013.09.039 |
| [17] |
Xie, L. G.; Wang, Z. X. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4901.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v50.21 |
| [18] |
Ogawa, H.; Yang, Z. K.; Minami, H.; Kojima, K.; Saito, T.; Wang, C.; Uchiyama, M. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 3988.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b01058 |
| [19] |
Wang, D. Y.; Kawahata, M.; Yang, Z. K.; Miyamoto, K.; Komagawa, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Wang, C.; Uchiyama, M. Nature Commun. 2016, 7, 12937.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms12937 |
| [20] |
Yang, Z. K.; Wang, D. Y.; Minami, H.; Ogawa, H.; Ozaki, T.; Saito, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Wang, C.; Uchiyama, M. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 15693.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201603436 |
| [21] |
Blakey, S. B.; MacMillan, D. W. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6046.
pmid: 12785821 |
| [22] |
Maity, P.; Shacklady-McAtee, D. M.; Yap, G. P. A.; Sirianni, E. R.; Watson, M. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 280.
doi: 10.1021/ja3089422 |
| [23] |
Chen, Q.; Gao, F.; Tang, H.; Yao, M.; Zhao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Dang, Y.; Cao, C. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 3730.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b00218 |
| [24] |
Xu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Han, C.; Hu, W.; Xiao, T.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, J. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 12192.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b01877 |
| [25] |
Zhu, F.; Tao, J. L.; Wang, Z. X. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 4926.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02458 |
| [26] |
Han, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, S.; Wang, K.; Chen, K.; Zhao, J. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 16308.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b02554 |
| [27] |
Moragas, T.; Gaydou, M.; Martin, R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5053.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v55.16 |
| [28] |
Liao, L. L.; Cao, G. M.; Ye, J. H.; Sun, G. Q.; Zhou, W. J.; Gui, Y. Y.; Yan, S. S.; Shen, G.; Yu, D. G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 17338.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b08792 pmid: 30518213 |
| [29] |
Yu, W.; Yang, S.; Xiong, F.; Fan, T.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, T. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 3099.
doi: 10.1039/C8OB00488A |
| [30] |
Rand Alexander, W.; Montgomery, J. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 5338.
doi: 10.1039/c9sc01083a pmid: 31191891 |
| [31] |
Scharfbier, J.; Gross, B. M.; Oestreich, M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1577.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.4 |
| [32] |
Zhang, X. Q.; Wang, Z. X. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 1448.
doi: 10.1039/c3ob41989d |
| [33] |
Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Li, N.; Xue, X.; He, Z.; Zeng, Q. Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 1679.
|
| [34] |
Yang, B.; Wang, Z. X. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 1500.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b02926 pmid: 30628791 |
| [35] |
Li, N.; Chen, F.; Wang, G.; Zeng, Q. Monatsch. Chem. 2020, 151, 99.
doi: 10.1007/s00706-019-02535-y |
| [36] |
O'Connor, S. E.; Grosset, A.; Janiak, P. Fund. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 13, 145.
pmid: 10226758 |
| [37] |
Sobal, G.; Menzel, E. J.; Sinzinger, H. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 61, 373.
pmid: 11172743 |
| [38] |
Zeng, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Cai, Y.; Weng, W.; Zhao, Y. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2005, 347, 1933.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1615-4169 |
| [39] |
Zhang, L.; Tan, M.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, Q. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 2778.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2018.06.008 |
| [40] |
Jiang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, Q. Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 1213.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-019-9499-5 |
| [41] |
Feng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Yang, L.; Kuchukulla, R. R.; Zeng, Q. Synlett 2021, 32, 224.
doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1707319 |
| [42] |
Jiang, W.; Li, N.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, Q. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 9899.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b03032 |
| [43] |
Chen, H.; Jiang, W.; Zeng, Q. Chem. Rec. 2020, 20, 1269.
doi: 10.1002/tcr.v20.11 |
| [44] |
Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, W.; Yang, H.; Zeng, Q. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2020, 9, 773.
doi: 10.1002/ajoc.v9.5 |
| [45] |
Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, W.; Zeng, Q. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 152320.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2020.152320 |
| [46] |
Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; He, Z.; Zeng, Q. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 1216.
doi: 10.1002/tcr.v21.5 |
| [47] |
Zhang, H.; Hagihara, S.; Itami, K. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 16796.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v21.47 |
| [48] |
Hu, J.; Sun, H.; Cai, W.; Pu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 14.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b02557 |
| [49] |
Basch, C. H.; Cobb, K. M.; Watson, M. P. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 136.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b03455 |
| [50] |
Gui, Y.; Tian, S. K. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1554.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00365 |
| [51] |
Li, F.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.; He, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, Q. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 13029.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC05633B |
| [52] |
Tang, Q.; Li, F.; Chen, F.; Yin, X.; Tang, Y.; Zeng, Q. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2021, 10, 1687.
doi: 10.1002/ajoc.v10.7 |
| [53] |
Chen, F.; Li, F.; Zeng, Q. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 2021, 5605.
doi: 10.1002/ejoc.v2021.41 |
| [54] |
Zhang, Q.; Feng, H.; Yang, H.; He, Z.; Zeng, Q. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 7806.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c00615 |
| [55] |
Yang, L.; Wang, B.; Yin, X.; Zeng, Q. Chem. Rec. 2021, DOI: 10.1002/tcr.202100242.
doi: 10.1002/tcr.202100242 |
| [56] |
Mfuh, A. M.; Doyle, J. D.; Chhetri, B.; Arman, H. D.; Larionov, O. V. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2985.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b01376 |
| [57] |
Wang, D. Y.; Yang, Z. K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, A.; Uchiyama, M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3641.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201712618 |
| [58] |
Wang, D. Y.; Wen, X.; Xiong, C. D.; Zhao, J. N.; Ding, C. Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhou, H.; Wang, C.; Uchiyama, M.; Lu, X. J.; Zhang, A. iScience 2019, 15, 307.
doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.04.038 |
| [59] |
Yang, D. T.; Zhu, M.; Schiffer, Z. J.; Williams, K.; Song, X.; Liu, X.; Manthiram, K. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 4699.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b00818 |
| [1] | 王凯凯, 贺军辉. 基于季铵盐改性SiO2空心球的抗菌/减反增透双功能薄膜的制备和研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(10): 807-812. |
| [2] | 王纪伟, 李莹, 徐艳玲, 李杨, 申凯华. 新型甲基吲哚季铵盐的制备及其光电性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(11): 1278-1282. |
| [3] | 汪丽敏, 吴金跃, 蒋育澄, 胡满成, 李淑妮, 翟全国. 手性苄基甲基亚砜的氯过氧化物酶催化定向合成[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 0(04): 465-470. |
| [4] | 宋伟伟, 张静, 杜敏. 新型不对称双季铵盐缓蚀剂在HCl中对Q235钢的缓蚀行为[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(16): 1851-1857. |
| [5] | 仇明华, 谢文林, 刘凤萍, 陈东初. 一种磺酰胺类碳酸酐酶II抑制剂3D-QSAR分析新方法[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(24): 2581-2589. |
| [6] | 王艳玉, 童威, 邵爽, 雷群芳, 方文军, 林瑞森. N-烷基-N-(2-羟乙基)-N,N-二甲基溴化铵与十二烷基硫酸钠复配系统的双水相[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(05): 379-383. |
| [7] | 杨芳,黎钢,刘荣,张彬,刘洋,王中旭. 壬基酚聚氧乙烯醚型Gemini季铵盐表面活性剂的合成 及其表面性质的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(8): 723-728. |
| [8] | 王桂香 贡雪东 肖鹤鸣. 高能化合物热解机理和撞击感度的理论研究-苯和苯胺类硝基衍生物[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(7): 711-716. |
| [9] | 王战辉,丁双阳,张素霞,沈建忠. 分子模拟技术研究17种磺胺类药物与抗体亲和力构效关系[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(23): 2613-2619. |
| [10] | . 新型氮二烷基吗啉盐酸盐离子液体的合成及其性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(20): 2289-2294. |
| [11] | 梁晓飞,王汉杰,罗浩,田惠,支敏,王永兰,常津. 生物降解多功能缓释微球的制备与表征[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(19): 2178-2183. |
| [12] | 石明娟,崔华. 苯酚和苯胺类化合物对鲁米诺电致化学发光的增强和抑制作用[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(22): 2555-2562. |
| [13] | 刘敏, 孙德志, 林瑞森, 曲秀葵, 王旭, 李玲. 人血清白蛋白与季铵盐双子表面活性剂的相互作用[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(2): 123-128. |
| [14] | 杨红伟, 朱谱新, 冯玉军, 陈志, 周栋梁, 吴大诚. 季铵盐三聚表面活性剂在空气-水界面上单分子膜的崩溃压和分子极限面积[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(18): 2081-2084. |
| [15] | 冯长君,杨伟华,沐来龙,杨春峰. N,N-二甲基-2-溴苯乙胺类衍生物对大鼠生物活性的三维构效关系研究[J]. 化学学报, 2006, 64(12): 1213-1217. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||