化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (9): 1256-1263.DOI: 10.6023/A22050233 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2022-05-20
发布日期:2022-08-24
通讯作者:
刘春梅
基金资助:
Chunmei Liu( ), Yanjun Gao, Pengliang Chen
), Yanjun Gao, Pengliang Chen
Received:2022-05-20
Published:2022-08-24
Contact:
Chunmei Liu
Supported by:文章分享

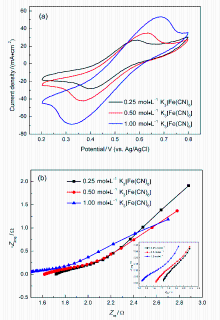
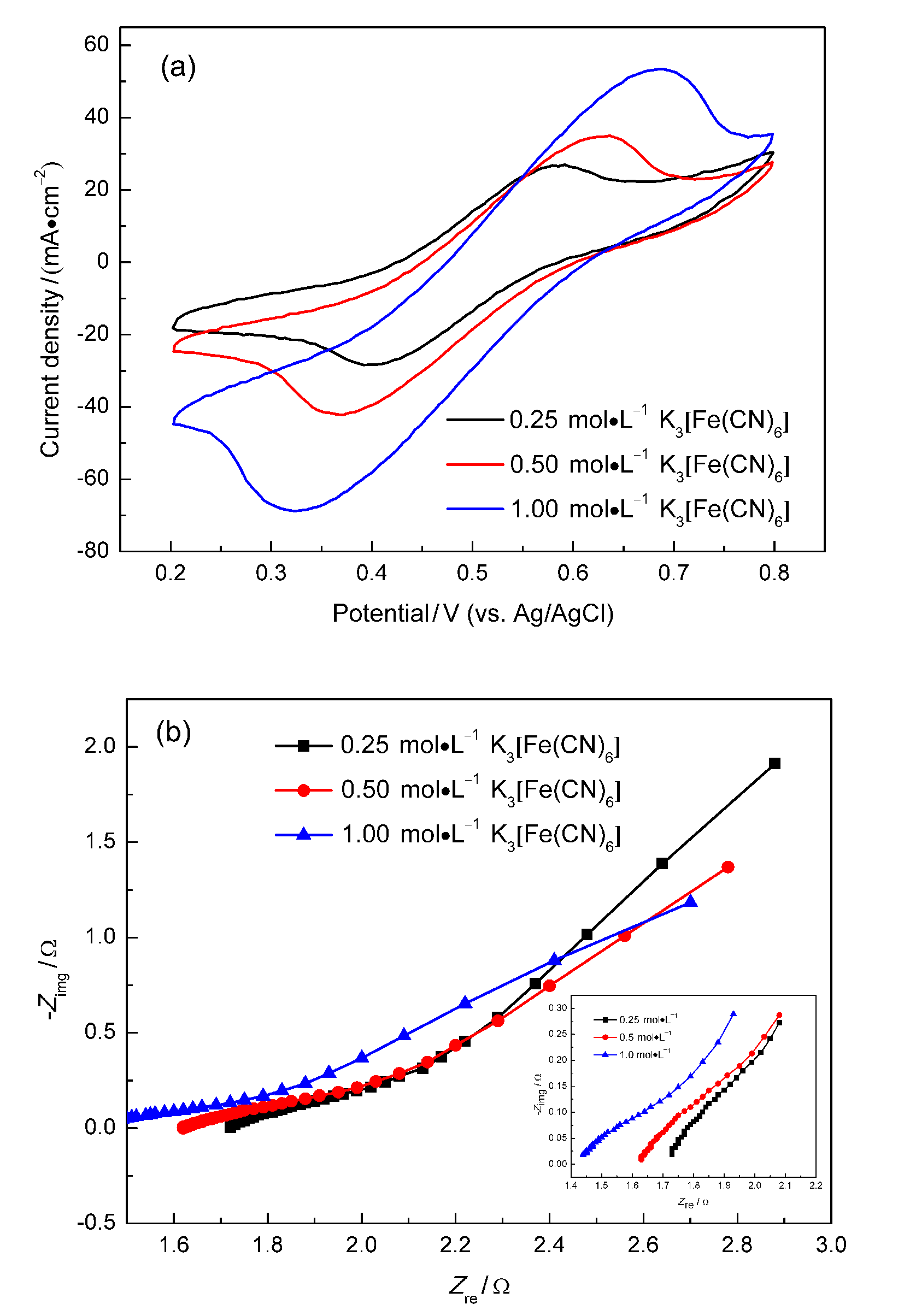
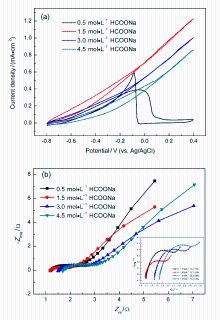
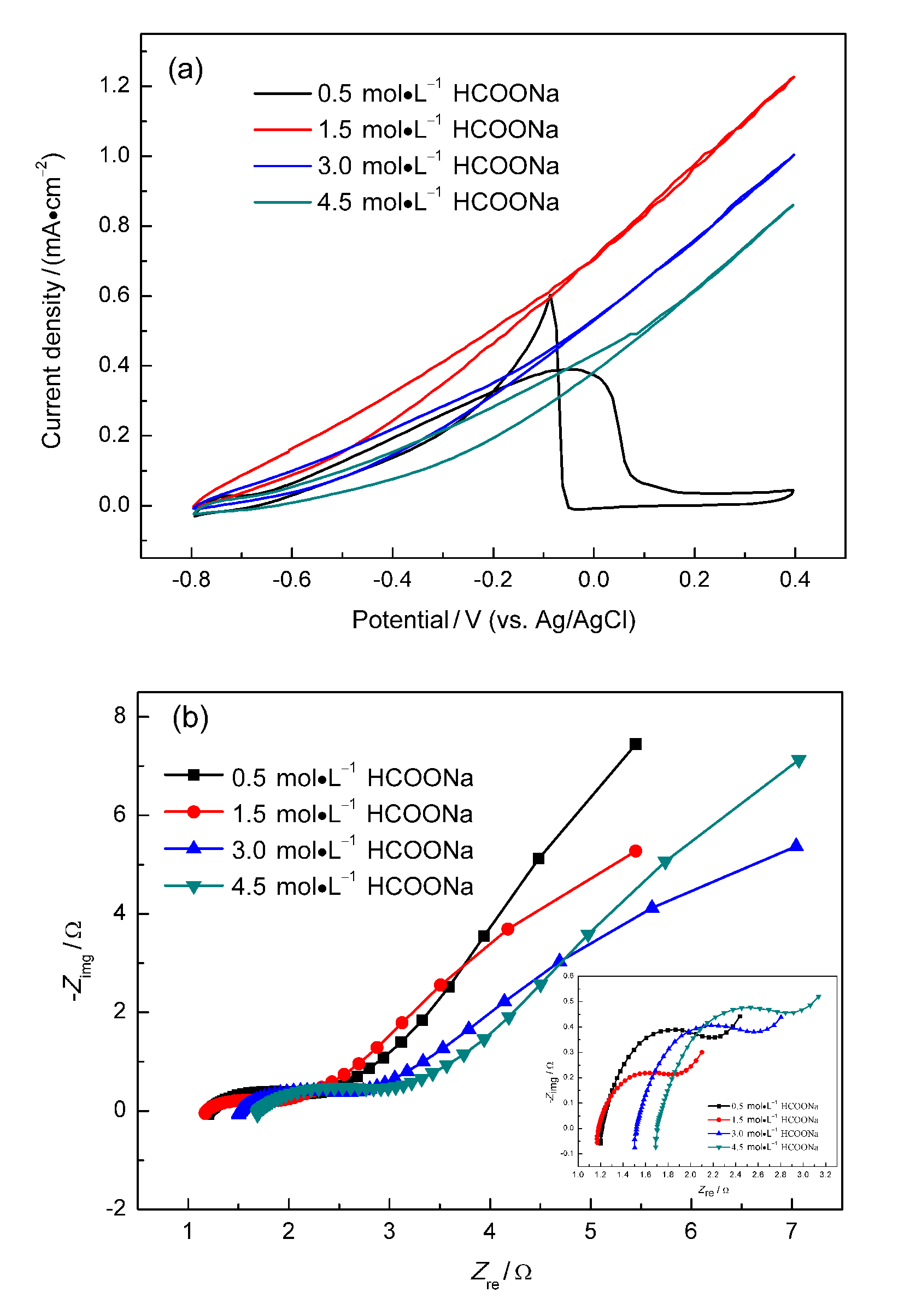
微流体燃料电池(MFC)利用两股流体在微通道内呈平行层流的特性, 无需传统燃料电池中的质子交换膜, 自动将燃料与氧化剂隔开. 本工作构建了阴阳极均为碱性介质且阴极无催化剂即可反应的直接甲酸钠/铁氰化钾MFC, 考察了反应物流速、氧化剂浓度、燃料浓度对该电池产电性能的影响. 实验结果表明, 在反应物流速为200 μL•min-1, 铁氰化钾氧化剂浓度为1 mol•L-1, 甲酸钠燃料浓度为1.5 mol•L-1时, 该微流体燃料电池性能达到最优, 其最高功率密度为123.93 mW•cm-2, 极限电流密度为220.93 mA•cm-2. 为了获得该电池的稳定运行性能, 对电池进行了恒电压放电实验. 结果表明, 该电池在2.25 h内可以持续较稳定地放电. 此外, 对该电池在开路状态下进行了电化学阻抗谱测试, 获得该电池内阻为18.4 Ω.
刘春梅, 高燕均, 陈鹏亮. 直接甲酸钠/铁氰化钾微流体燃料电池性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1256-1263.
Chunmei Liu, Yanjun Gao, Pengliang Chen. Performance Research of the Direct Sodium Formate/Potassium Ferricyanide Microfluidic Fuel Cell[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(9): 1256-1263.
| [1] |
Feng L. L.; Tang S. Y.; Chen Y.; Li S.; Li T. Y.; Li X. G. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 51, 1018.(in Chinese)
|
|
(冯利利, 汤思遥, 陈越, 李栓, 李彤岩, 李星国, 中国科学: 化学, 2021, 51, 1018.)
|
|
| [2] |
Zhong G. Y.; Wang H. J.; Yu H.; Peng F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 943.(in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17040183 |
|
(钟国玉, 王红娟, 余皓, 彭峰, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 943.)
doi: 10.6023/A17040183 |
|
| [3] |
Wang J.; Ding W.; Wei Z. D. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2021, 37, 2009094.(in Chinese)
|
|
(王健, 丁炜, 魏子栋, 物理化学学报, 2021, 37, 2009094.)
|
|
| [4] |
Tian H. X.; Qin P. L.; Li K.; Zhao Z. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 120813.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120813 |
| [5] |
Wang R.; Liu Z. K.; Yan C.; Qie L.; Huang Y. H. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2022, 38, 2203043.(in Chinese)
|
|
(汪茹, 刘志康, 严超, 伽龙, 黄云辉, 物理化学学报, 2022, 38, 2203043.)
|
|
| [6] |
Sharaf O. Z.; Orhan M. F. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2014, 32, 810.
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.01.012 |
| [7] |
Brushett F. R.; Jayashree R. S.; Zhou W. P.; Kenis P. J. A. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 30, 7099.
|
| [8] |
Zhao M.; Shi W. Y.; Wu B. B.; Liu W. M.; Liu J. G.; Xing D. M.; Yao Y. F.; Hou Z. J.; Ming P. W.; Zou Z. G. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 153, 254.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2014.12.024 |
| [9] |
Ferrigno R.; Stroock A. D.; Clark T. D.; Mayer M.; Whitesides G. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12930.
pmid: 12405803 |
| [10] |
Liu L. B.; Ye D. D.; Li J.; Zhu X.; Fu Q.; Zhang L.; Chen R.; Zhang Q. R. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 3821.(in Chinese)
doi: 10.1360/N972017-00304 |
|
(刘林波, 叶丁丁, 李俊, 朱恂, 付乾, 张亮, 陈蓉, 张倩茹, 科学通报, 2017, 62, 3821.)
|
|
| [11] |
Mu A. P.; Ye D. D.; Chen R.; Zhu X.; Liao Q. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2020, 71, 3278.(in Chinese)
|
|
(穆嫒萍, 叶丁丁, 陈蓉, 朱恂, 廖强, 化工学报, 2020, 71, 3278.)
|
|
| [12] |
Kundu A.; Jang J. H.; Gil J. H.; Jung C. R.; Lee H. R.; Kim S. H.; Ku B.; Oh Y. S. J. Power Sources 2007, 170, 67.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.03.066 |
| [13] |
Morse J. D. Int. J. Energy Res. 2007, 31, 576.
doi: 10.1002/er.1281 |
| [14] |
Choban E. R.; Markoski L. J.; Wieckowski A.; Kenis P. J. A. J. Power Sources 2004, 128, 54.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2003.11.052 |
| [15] |
Jayashree R. S.; Gancs L.; Choban E. R.; Primak A.; Natarajan D.; Markoski L. J.; Kenis P. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 16758.
pmid: 16316201 |
| [16] |
Zhi P.; Liu Z.; Jiao K.; Du Q. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 392, 139024.
|
| [17] |
Ma Q.; Duan Z.; Zhi P.; Ma J.; Du Q.; Jiao K.; Liu Z. Int. J. Green Energy 2022, https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2022.2075227.
|
| [18] |
Kjeang E.; Michel R.; Harrington D. A.; Sinton D.; Djilali N. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 54, 698.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2008.07.009 |
| [19] |
Kjeang E.; Brolo A. G.; Harrington D. A.; Djilali N.; Sinton D. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, B1220.
doi: 10.1149/1.2784185 |
| [20] |
López-Montesinos P. O.; Yossakda N.; Schmidt A.; Brushett F. R.; Pelton W. E.; Kenis P. J. A. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 196, 4638.
|
| [21] |
Zeng L.; Sun J.; Zhao T. S.; Ren Y. X.; Wei L. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45,12565.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.02.177 |
| [22] |
Liu C. M.; Liu L.; Wang X. T.; Xu B.; Lan W. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 13557.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.8b02994 |
| [23] |
Liu C. M.; Liao Q.; Zhu X.; Yang Y. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1756.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.7b04636 |
| [24] |
Lan Q.; Ye D. D.; Zhu X.; Chen R.; Liao Q.; Zhang T.; Zhou Y. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5623.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c00395 |
| [25] |
Nadal M.; Schuhmacher M.; Domingo J. Sci. Total Environ., 2004, 321, 59.
pmid: 15050385 |
| [26] |
Liu C. M.; Liu H. H.; Liu L. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 4557.
|
| [27] |
Rabaey K.; Lissens G.; Siciliano S. D.; Verstraete W. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1531.
doi: 10.1023/A:1025484009367 |
| [28] |
Ucar D.; Zhang Y.; Angelidaki I. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 643.
|
| [29] |
Krishnamurthy D.; Johansson E. O.; Lee J. W.; Kjeang E. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 10019.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.08.024 |
| [30] |
Yue L.; Li W.; Sun F.; Zhao L.; Xing L. Carbon 2010, 48, 3079.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2010.04.044 |
| [31] |
Yao C.; Zhang H.; Liu T.; Li X.; Liu Z. J. Power Sources 2012, 218, 455.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.06.072 |
| [32] |
Wang X. Y.; Yan J.; Yuan H. T.; Zhang Y. S.; Song D. Y. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 1999, 24, 973.
doi: 10.1016/S0360-3199(98)00130-X |
| [33] |
Amirdehi M. A.; Gong L.; Khodaparastasgarabad N.; Logan B. E.; Greener J. J. Power Sources 2021, 128, 54.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2003.11.052 |
| [34] |
Su X. Y. Ph.D. Dissertation, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, 2021.
|
| [35] |
Zhang H.; Xuan J.; Xu H.; Leung M. K. H.; Leung D. Y. C.; Zhang L.; Wang H. Z.; Wang L. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 1131.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.01.077 |
| [36] |
Zhang T.; Yu C.; Zhu X.; Ye D. D.; Yang Y.; Chen R.; Liao Q. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 1526.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c05947 |
| [1] | 朱婵, 海洋, 赵志刚, 阳耀月. Ni和P微量掺杂的Pd基催化剂对碱性介质中乙醇电氧化性能的增强效应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(1): 30-34. |
| [2] | 杨伟伟, 邸友莹, 孔玉霞, 金广鑫, 谭志诚. 水合邻苯二甲酸钠的合成、结构表征及热化学性质[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(04): 294-300. |
| [3] | 蔡良珍, 刘斌, 董于虎, 杜广延, 陶晓春. 铜(Ⅰ)催化亚铁氰化钾对含氮杂环溴化物的氰基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(21): 2523-2526. |
| [4] | 聂菲,吕九如. 铁氰化钾-钙黄绿素化学发光体系测定酮替芬的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(20): 2299-2302. |
| [5] | 林珩, 陈国良, 郑子山, 周建章, 陈声培, 林仲华. 碱性介质中甲醇在铂电极表面吸附和氧化的电化学原位FTIR反射光谱和EQCM研究[J]. 化学学报, 2005, 63(23): 2137-2140. |
| [6] | 李纲, 侯红卫, 李林科, 王宇飞, 孟祥茹, 朱玉, 樊耀亭. 二茂铁单甲酸根桥联的镧二聚体的合成、晶体结构及电化学性质[J]. 化学学报, 2004, 62(11): 1060-1064. |
| [7] | 杨维平,张琰图,章竹君. 高效液相色谱—化学发光法研究异烟肼和利福平[J]. 化学学报, 2003, 61(2): 303-306. |
| [8] | 张占军,李经建,武斌,刘忠范,蔡生民. 多孔硅于甲酸-甲酸钠溶液阳极偏压下的电致发光研究[J]. 化学学报, 2001, 59(10): 1587-1591. |
| [9] | 王相勤,邵春林,姚建铭,余立祥,余增亮. 低能离子与生物有机小分子相互作用机制的初步研究[J]. 化学学报, 2000, 58(4): 443-447. |
| [10] | 闫冰,陈志达. 稀土-六氰合铁氰根桥联配合物的晶体结构和磁化学[J]. 化学学报, 2000, 58(12): 1589-1595. |
| [11] | 王玉炉,王彩兰,李建平,王红,张自义,王晓阳. Galvinoxyl/K~3Fe(CN)~6/KOH复合体系相转移催化合成对称取代 偶氮苯[J]. 化学学报, 1999, 57(11): 1277-1282. |
| [12] | 韦寿连,卢建忠,江云宝,许金钩. 分子内扭转电荷转移的新荧光探针的研究[J]. 化学学报, 1998, 56(1): 37-40. |
| [13] | 唐紫超,石磊,黄荣彬,郑兰荪. 碳氮二元簇离子的激光产生与碰撞诱导解离研究[J]. 化学学报, 1997, 55(12): 1191-1197. |
| [14] | 钱卫军,金葆康,史汉生,于俊生,张祖训. 微盘电极上计时电流的数值模拟及其验证[J]. 化学学报, 1997, 55(11): 1108-1115. |
| [15] | 展树中,孟庆金,戴安邦. 氰桥配合物[LmCo^Ⅲ-μ-NC-Fe^Ⅱ(CN)~5]^-的合成与性质[J]. 化学学报, 1996, 54(3): 271-275. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||