化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (5): 520-526.DOI: 10.6023/A24010023 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2024-04-02
基金资助:Received:2024-01-20
Published:2024-04-02
Contact:
*E-mail: xiaobhuai@foxmail.com
Supported by:文章分享

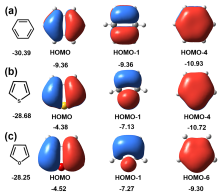
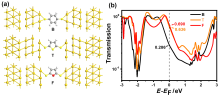
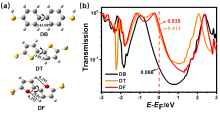
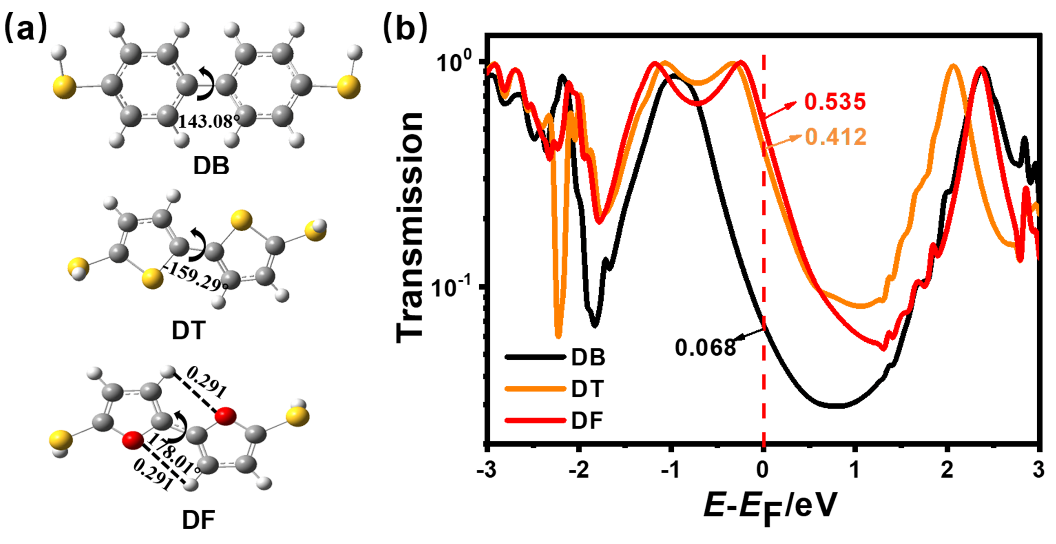
芳香性是有机化学中的重要概念, 传统芳香族化合物的芳香性通常源于π电子在环上下平面产生的高度离域, 而σ-芳香性则主要源于分子内σ键和轨道重叠, 两者均能影响分子的电子传输能力. 采用密度泛函理论结合非平衡格林函数(DFT+NEGF)方法对苯、噻吩和呋喃及其衍生物进行了芳香性和电子输运性质的系统研究. 计算结果表明, 苯、噻吩和呋喃分子的电子输运性质受π-芳香性和σ-芳香性影响, 其中σ-芳香性和电子传输正相关, 而π-芳香性和电子传输能力成负相关. 含有两个芳香环的联苯二巯基(DB)、联噻吩二巯基(DT)和联呋喃二巯基(DF)分子的电子传输能力受分子平面化影响较大, DF中呋喃环表现出比DT中噻吩环更大的NICS(1)zz值. 芳香性化合物具有更好的共平面趋势, 通过F原子修饰DT 和DF分子产生分子内F…S和F…O非共价相互作用的设计策略可以极大增加分子平面性和刚性. 同时, 含有分子内F…S和F…O相互作用的虚拟五元环具有平面σ-芳香性特征, 有效促进电子沿F…S和F…O路径进行传输, 从而提高电子传输能力. 本研究有助于进一步理解分子芳香性与电子传输能力之间的内在关系, 为未来设计更高效的电子器件提供策略.
王治业, 肖博怀. 利用平面σ-芳香性增强电子输运能力[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 520-526.
Zhiye Wang, Bohuai Xiao. Utilizing Planar σ-Aromaticity to Enhance Electron Transport Abilities[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(5): 520-526.




| [1] |
Zahedi, E.; Pangh, A. Superlattices Microstruct. 2011, 50, 386.
|
|
Yin, X.; Zang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Low Jonathan, Z.; Liu, Z.-F.; Cui, J.; Neaton Jeffrey, B.; Venkataraman, L.; Campos Luis, M. Sci. Adv. 2018, 3, eaao2615.
|
|
| [2] |
Ramos-Berdullas, N.; Graña, A. M.; Mandado, M. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2015, 134, 20.
|
| [3] |
Quinn, J. R.; Fross, F. W. Jr.; Venkataraman, L.; Hybertsen, M. S.; Breslow, R. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 6714.
|
| [4] |
Chen, W.; Li, H.; Widawsky, J. R.; Appayee, C.; Venkataraman, L.; Breslow, R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 918.
|
| [5] |
Mahendran, A.; Gopinath, P.; Breslow, R. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 4833.
|
| [6] |
Breslow, R.; Fross, F. W. Jr. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2008, 20, 374104.
|
| [7] |
Xie, Z.; Ji, X.-L.; Song, Y.; Wei, M.-Z.; Wang, C.-K. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2015, 639, 131.
|
| [8] |
Zdetsis, A. D.; Economou, E. N. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 29463.
|
| [9] |
Pauly, F.; Viljas, J. K.; Cuevas, J. C.; Schön, G. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 155312.
|
| [10] |
Yang, Y.; Gantenbein, M.; Alqorashi, A.; Wei, J.; Sangtarash, S.; Hu, D.; Sadeghi, H.; Zhang, R.; Pi, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, X.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Shi, J.; Hong, W.; Lambert, C. J.; Bryce, M. R. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 14965.
|
| [11] |
Zhang, G.-P.; Xie, Z.; Song, Y.; Wei, M.-Z.; Hu, G.-C.; Wang, C.-K. Org. Electron. 2017, 48, 29.
|
| [12] |
Emberly, E. G.; Kirczenow, G. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 188301.
|
| [13] |
Ke, S.; Baranger, H. U.; Yang, W. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 3482.
|
| [14] |
Zhu, C.-C.; Guo, K.-P.; Liu, W.-B.; He, Y.-B.; Li, Z.-M.; Gao, X.-C.; Deng, F.-J.; Wei, B. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 2095.
|
| [15] |
Yuan, S.; Dai, C.; Weng, J.; Mei, Q.; Ling, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, W. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 4535.
|
| [16] |
Yu, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H. Chem. J. Chinese U. 2009, 30, 33 (in Chinese).
|
|
(余翠, 赵健伟, 刘洪梅, 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30, 33.)
|
|
| [17] |
Ren, L.; Han, Y.; Hou, X.; Ni, Y.; Wu, J. Chem 2021, 7, 3442.
|
| [18] |
Alonso, M.; Herradón, B. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 3913.
|
| [19] |
Solà, M. Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 585.
|
| [20] |
Hua, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xia, H. Chinese J. Org. Chem. 2018, 38, 11 (in Chinese).
|
|
(华煜晖, 张弘, 夏海平, 有机化学, 2018, 38, 11.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201709009 |
|
| [21] |
Krygowski, T. M.; Stȩpień, B. T. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3482.
pmid: 16218559 |
| [22] |
Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, R.; Wu, D.; Tian, Z. Chem. J. Chinese U. 2015, 36, 9 (in Chinese).
|
|
(杨扬, 刘俊扬, 晏润文, 吴德印, 田中群, 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36, 9.)
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140941 |
|
| [23] |
Cheng, N.; Chen, F.; Durkan, C.; Wang, N.; He, Y.; Zhao, J. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 28860.
doi: 10.1039/c8cp05901b pmid: 30420983 |
| [24] |
Yuan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, T.; Chen, L.; Xu, W.; Duan, P.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Tang, C.; Yang, Y.; Huang, R.; Xiao, Z.; Hong, W. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 108404.
|
| [25] |
Xiao, B.; Dong, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, M.; Guo, J.; Qian, G.; Li, Y.; Chang, S. ChemPhysChem 2022, 23, e202100833.
|
| [26] |
Cheng, N.; Zhang, L.; Durkan, C.; Wang, N.; Du, B.; Zhao, J.; He, Y. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 21137.
|
| [27] |
He, Y.; Cheng, N.; Zhao, J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 893 (in Chinese).
|
|
(贺园园, 程娜, 赵健伟, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 893.)
doi: 10.6023/A17050195 |
|
| [28] |
Niu, X.; Qi, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2008, 66, 652 (in Chinese).
|
|
(牛秀明, 齐元华, 化学学报, 2008, 66, 652.)
|
|
| [29] |
Fallah-Bagher-Shaidaei, H.; Wannere, C. S.; Corminboeuf, C.; Puchta, R.; Schleyer, P. v. R. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 863.
pmid: 16494460 |
| [30] |
Wu, W.; Ma, B.; Wu, J. I-Chia; Schleyer, P. v. R.; Mo, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 9730.
|
| [31] |
Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Hao, Y.; Chen, H.; Su, P.; Wu, W.; Zhu, J. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 13, 3691.
|
| [32] |
Cai, Z.; Lo, W. Y.; Zheng, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, N.; Hu, Y.; Yu, L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10630.
|
| [33] |
Yan, R.; Jin, X.; Guan, S.; Zhang, X.; Pang, R.; Tian, Z..; Wu, D.; Mao, B. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 11820.
|
| [34] |
Kiguchi, M.; Fujii, S. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 90, 1.
|
| [35] |
Krygowski, T. M.; Cyrañski, M. K.; Czarnocki, Z.; Häfelinger, G.; Katritzky, A. R. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 1783.
|
| [36] |
Mishchenko, A.; Vonlanthen, D.; Meded, V.; Burkle, M.; Li, C.; Pobelov, I. V.; Bagrets, A.; Viljas, J. K.; Pauly, F.; Evers, F.; Mayor, M.; Wandlowski, T. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 156.
doi: 10.1021/nl903084b pmid: 20025266 |
| [37] |
Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zou, Y.; Li, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 257 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A16090495 |
|
(刘晔, 袁俊, 邹应萍, 李永舫, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 257.)
doi: 10.6023/A16090495 |
|
| [38] |
Milov, A. A.; Minyaev, R. M.; Minkin, V. I. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 12973.
|
| [39] |
Huang, H.; Yang, L.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T. J. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10291.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00084 pmid: 28671815 |
| [40] |
Cheng, Y.; Qi, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Wan, Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, R. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 3609.
|
| [41] |
Wang, Z.; Huang, M.; Dong, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, M.; Chang, S. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 2518.
|
| [42] |
Haque, A.; Alenezi, K. M.; Khan, M. S.; Wong, W.-Y.; Raithby, P. R. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 454.
|
| [43] |
Ma, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, M.; Guo, J.; Qian, G.; Chang, S. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 3298.
|
| [44] |
Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Tian, W.; Liu, D.; Ge, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 1509 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张敏, 刘子忠, 田维全, 刘东升, 葛湘巍, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 1509.)
|
|
| [45] |
Venkataraman, L.; Park, Y. S.; Whalley, A. C.; Nuckolls, C.; Hybertsen, M. S.; Steigerwald, M. L. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 502.
pmid: 17253760 |
| [1] | 来悦颖, 赵子豪, 郑书源, 袁望章. 具有同质多晶依赖性发射的非芳香性发光化合物[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(1): 93-99. |
| [2] | 周沃华, 陈蓉, 吴子文, 丁丹丹, 徐志广, 许旋, 罗一帆. [Cu2Pt(npa)4X2](X=Cl-,NCS-)金属串配合物电子传输性质的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(11): 1214-1218. |
| [3] | 寇东星, 刘伟庆, 胡林华, 陈双宏, 黄阳, 戴松元. 氧气氛烧结电极对染料敏化太阳电池微观性能影响机理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(08): 1149-1153. |
| [4] | 易平贵, 侯博, 汪朝旭, 刘峥军, 于贤勇, 徐百元. 杂苯C5H5X (X=N, P, As, Sb, Bi)芳香性的核独立化学位移(NICS)与异构体稳定化能(ISE)研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(01): 126-132. |
| [5] | 李会学, 王晓峰, 李志锋, 潘素娟. 石墨炔结构及性能的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(01): 75-80. |
| [6] | 张敏, 刘子忠, 田维全, 刘东升, 葛湘巍. C6FmH6-m (m=1~6)结构及芳香性的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(13): 1509-1516. |
| [7] | 刘子忠, 王宇婷, 田维全, 刘东升, 葛湘巍. E42-, [CoE4]+和[P4CoE4]- (E=N~Bi)结构和芳香性的理论预测[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(22): 2297-2304. |
| [8] | 梁锦霞, 张聪杰. 包含两个平面五配位碳原子C2+nB10-n (n=0~10)团簇的结构的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(01): 7-12. |
| [9] | 阿布力克木V,克热木. C36CH2各种可能异构体芳香性的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(9): 841-846. |
| [10] | 裴晓琴, 贾建峰, 武海顺. 2,8 (4,6)-二取代半瞬烯及其BCO衍生物的Cope重排[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(7): 579-583. |
| [11] | 李会学,唐惠安,杨声,萧泰. 电子传输材料噻二唑衍生物的密度泛函研究[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(20): 2229-2234. |
| [12] | 裴晓琴, 武海顺, 张晓清, 许兴友. 四同芳香性转烯及其羰基硼衍生物[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(14): 1357-1362. |
| [13] | 黄嘉驰, 杨立功, 莫雄, 施敏敏, 汪茫, 陈红征. 氟代位置对苝酰亚胺聚集态结构和电子传输性能的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(11): 1051-1056. |
| [14] | 魏孝强,朱卫国,杨爱丽,李龙章,谢名贵,杨刚,林祖伦,成建波. 方酸作桥联配体的双核铕螯合物的电致发光[J]. 化学学报, 2003, 61(3): 388-392. |
| [15] | 周立新,吴立明,李奕,李俊Qian. 1, 2-二硒方酸气相酸性和芳香性的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 1999, 57(10): 1107-1113. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
