化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (1): 10-16.DOI: 10.6023/A24100296 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2024-10-07
发布日期:2024-11-29
基金资助:
Niu Zhanga, Shuran Hanb, Hongwei Maa, Pangkuan Chenb( )
)
Received:2024-10-07
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
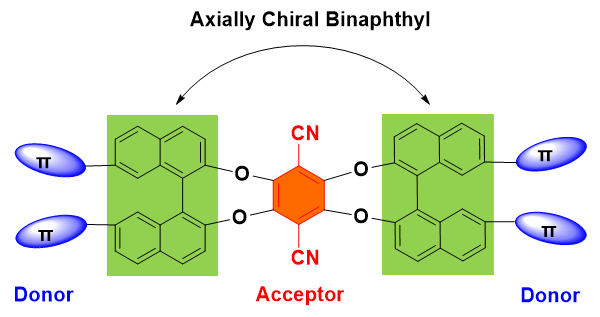
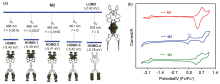
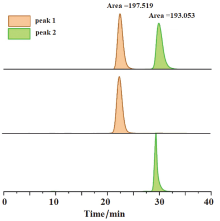
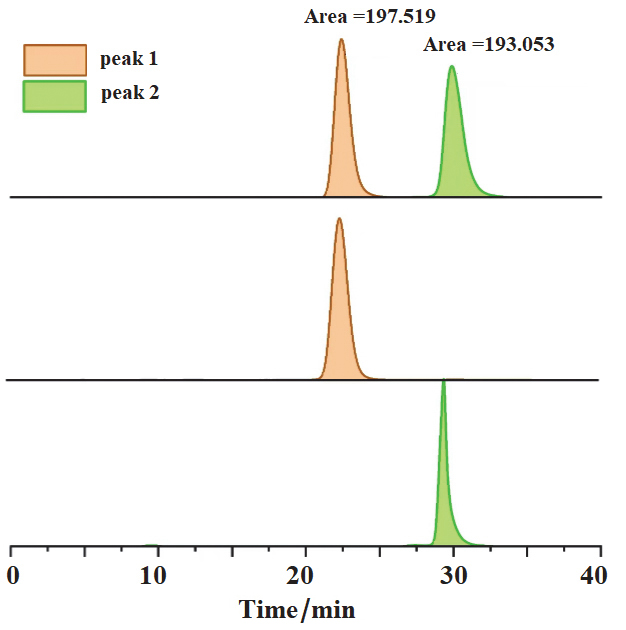
集手性与发光性能于一体的手性光电材料是手性科学前沿研究领域之一. 本工作中, 设计并合成了三个具有手性发光特性的新型有机小分子化合物M1, M2和M3, 这些分子的手性均来源于轴手性的联二萘酚骨架. 在联二萘酚手性单元的7,7'-位点进行结构修饰, 分别引入了二苯胺、对叔丁基二苯胺及叔丁基咔唑等电子给体(D)取代基. 三个手性分子的另一特征是它们都含有一个电子受体(A)基团, 即对苯二腈中心核结构. 通过核磁、高分辨质谱等手段对M1, M2和M3进行了结构确认, 并通过吸收光谱、荧光发射光谱、电化学和密度泛函理论(DFT)计算的方法对其电子结构进行表征. 采用手性高效液相色谱法对它们的外消旋体进行手性拆分, 并通过圆二色光谱(CD)和圆偏振发光光谱(CPL)表征了光学对映体的手性光学性能. 由于分子内推拉电子结构的存在, 以上目标分子均展现出可逆的变温荧光响应性能.
张妞, 韩书冉, 马宏伟, 陈磅宽. 基于联二萘酚的手性有机发光分子合成与性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(1): 10-16.
Niu Zhang, Shuran Han, Hongwei Ma, Pangkuan Chen. Synthesis and Characterization of Chiral Luminescent Materials Based on Binaphthol Scaffolds[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(1): 10-16.
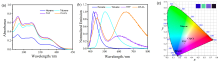

| λabsa/nm | λema/nm | ΦFb/% | τc/ns | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 375 | 435/600 | 8.0 | 20 |
| M2 | 351 | 549 | 8 | 97 |
| M3 | 373 | 435/576 | 4.4 | 12.7 |
| λabsa/nm | λema/nm | ΦFb/% | τc/ns | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 375 | 435/600 | 8.0 | 20 |
| M2 | 351 | 549 | 8 | 97 |
| M3 | 373 | 435/576 | 4.4 | 12.7 |



| [1] |
(a) Yang, X. F.; Gao, X. Q.; Zheng, Y. X.; Kuang, H.; Chen, C. F.; Liu, M. H.; Duan, P. F.; Tang, Z. Y. CCS Chem. 2023, 5, 2760.
|
|
(b) Xue, Y. T.; Shi, Y. F.; Chen, P. K. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2024, 12, 2303322.
|
|
|
(c) Di, J. Q.; Han, S. R.; Chen, P. Chin. J. Chem. 2025, 43, 219.
|
|
|
(d) Song, S. Q.; Han, X.; Huo, Z. Z.; Yip, C. F.; Hong, X. F.; Ding, M. N.; Zheng, Y. X. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 2257.
|
|
| [2] |
(a) Zhang, M.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Jin, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhuang, T.; Yu, S. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi9944.
|
|
(b) Furumi, S. Chem. Rec. 2010, 10, 394.
|
|
|
(c) Meng, G.; Zhou, J.; Han, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, C. F.; Zhang, D.; Duan, L. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2307420.
|
|
|
(d) Zhang, D.; Li, M.; Chen, C. F. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1331.
|
|
|
(f) Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y. P.; Zheng, Y. X. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 1097.
|
|
|
(g) Zhao, C. Y.; Ji, L. K.; Ouyang, G. H.; Liu, M. H. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 54, 1380 (in Chinese).
|
|
|
( 赵晨阳, 冀璐康, 欧阳光辉, 刘鸣华, 中国科学:化学, 2024, 54, 1380.)
|
|
| [3] |
(a) Ma, J. L.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, C. H. Chem.-Eur. J. 2019, 25, 15441.
|
|
(b) Li, M.; Li, S. H.; Zhang, D.; Cai, M.; Duan, L.; Fung, M. K.; Chen, C. F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2889.
|
|
|
(c) Zinna, F.; Voci, S.; Arrico, L.; Brun, E.; Homberg, A.; Bouffier, L.; Funaioli, T.; Lacour, J.; Sojic, N.; Di Bari, L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6952.
|
|
|
(d) Liang, Z. P.; Tang, R.; Qiu, Y. C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H. B.; Wu, Z. G. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1401 (in Chinese).
|
|
|
( 梁志鹏, 唐瑞, 邱雨晨, 王阳, 陆洪彬, 吴正光, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1401.)
doi: 10.6023/A21070355 |
|
|
(e) Ren, S. Z.; Liu, Z. F.; Li, P. H.; Liu, H. D.; Lu, M. S.; Wang, K.; Yao, J. N.; Dong, H. Y.; Yang, Q. Z.; Zhang, S. D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 64, e202415092.
|
|
|
(f) Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. F.; Li, M.; Gao, Q. Y.; Chen, C. F. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 740.
|
|
|
(g) Song, F.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, Z.; Qi, C.; Zhang, H.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, A.; Ma, D.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800062.
|
|
| [4] |
(a) Li, B.; Li, Y.; Chan, M. H. Y.; Yam, V. W. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 21676.
pmid: 35678629 |
|
(b) Schnable, D.; Schley, N. D.; Ung, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 10718.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c03791 pmid: 35678629 |
|
|
(c) Ouyang, G.; Rühe, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, M.; Liu, M.; Würthner, F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202206706.
pmid: 35678629 |
|
|
(d) Sun, Y. M.; Jiang, Y. Q.; Jiang, J.; Li, T. S.; Liu, M. H. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 366.
pmid: 35678629 |
|
|
(e) Gan, F. W.; Qiu, H. B. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 371 (in Chinese).
pmid: 35678629 |
|
|
( 干富伟, 邱惠斌, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 371.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202300006 pmid: 35678629 |
|
| [5] |
(a) Richardson, F. S.; Riehl, J. P. Chem. Rev. 1977, 77, 773.
|
|
(b) Arrico, L.; Bari, L. D.; Zinna, F. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 2920.
|
|
|
(c) Zinna, F.; Di Bari, L. Chirality 2015, 27, 1.
|
|
| [6] |
(a) Liu, D. H.; Sun, Z. B.; Zhao, Z. H.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, C. H. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 10179.
|
|
(b) Wu, Z. G.; Han, H. B.; Yan, Z. P.; Luo, X. F.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y. X.; Zuo, J. L.; Pan, Y. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900524.
|
|
|
(c) Liu, B.; Chen, P. K. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 929 (in Chinese).
|
|
|
( 刘斌, 陈磅宽, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 929.)
doi: 10.6023/A22030122 |
|
| [7] |
(a) He, Q.; Lin, H.; Weng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Lei, G.; Wang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Bai, F. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 1343.
pmid: 24524257 |
|
(b) Sánchez-Carnerero, E. M.; Moreno, F.; Maroto, B. L.; Agarrabeitia, A. R.; Ortiz, M. J.; Vo, B. G.; Muller, G.; Moya, S. D. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3346.
doi: 10.1021/ja412294s pmid: 24524257 |
|
| [8] |
(a) Sun, Z. B.; Liu, J. K.; Yuan, D. F.; Zhao, Z. H.; Zhu, X. Z.; Liu, D. H.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, C. H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4840.
|
|
(b) Xue, P. C.; Yao, B. Q.; Liu, X. H.; Sun, J. B.; Gong, P.; Zhang, Z. Q.; Qian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, R. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 1018.
|
|
| [9] |
(a) Horibe, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Hazeyama, T.; Takeda, K.; Ishihara, K. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 136770.
|
|
(b) MacLean, M. W.; Wood, T. K.; Wu, G.; Lemieux, R. P.; Crudden, C. M. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 5852.
|
|
| [10] |
(a) Zhang, K.; Zhao, J. Y.; Zhang, N.; Chen, J. F.; Wang, N.; Yin, X. D.; Zheng, X. Y.; Chen, P. K. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 1816.
|
|
(b) Tian, G. Q.; Chen, J. F.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Y. F.; Li, C. L.; Yin, X. D.; Liu, K. L.; Chen, P. K. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 15315.
|
|
|
(c) Zhang, K.; Hao, M. Y.; Jin, T. Y.; Shi, Y. F.; Tian, G. Q.; Li, C. L.; Ma, H. W.; Zhang, N.; Li, Q. S.; Chen, P. K. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 30, e202302950.
|
| [1] | 陶鹏, 郑小康, 王国良, 盛星浩, 姜贺, 李文桃, 靳继彪, 王瑞鸿, 苗艳勤, 王华, 黄维扬. 新型双极传输特性橙光铱(III)配合物的设计、合成及其电致发光★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 891-897. |
| [2] | 王志强, 白美丹, 张明, 张智强, 冯勋, 郑才俊. 基于新型电子受体1,3,5-三苯酰基苯的两种热活化延迟荧光材料的合成及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(2): 140-146. |
| [3] | 操强, 陈琦, 韩宝航. 有机多孔聚咔唑的制备及性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(6): 541-556. |
| [4] | 陈钊, 单威, 尹军, 余广鳌, 刘盛华. 新型四炔模块苯炔前体高效构建咔唑类衍生物[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(10): 1007-1012. |
| [5] | 谭芬, 陈加荣, 王萍, 肖文精. Sc(OTf)3/Bis(oxazoline)复合物催化的2-芳基-1,3-茚二酮与2-乙烯基吲哚的不对称Diels-Alder反应:高效构建四氢咔唑螺茚酮衍生物[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(7): 836-840. |
| [6] | 韩立志, 王卓, 华英杰, 任爱民, 刘艳玲*, 刘朋军. 9,9-二-(3-(9-苯咔唑基))-2,7-芘基芴的光电性质[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(05): 579-584 . |
| [7] | 孙玉姣, 王承建, 耿腾飞, 王仲孚, 黄琳娟. κ-卡拉胶寡糖AEC柱前衍生物的LC-ESI-MS/MSn分离分析[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(14): 1697-1704. |
| [8] | 高健, 刘煜, 谭华, 李亮, 曹韵波, 梁爱辉, 朱卫国. 1,2-亚乙基桥联咔唑和芳基噁二唑的双极传输材料的合成及光电性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(07): 661-666. |
| [9] | 朱召进, 徐景坤, 裴梅山, 卢宝阳, 马茶, 李龙, 申亮. 聚丙烯酸修饰咔唑的电化学聚合及表征[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(06): 564-570. |
| [10] | 王光荣a 李熙灿b 曾和平,. (E)-N-芳基-3-[2-(8-羟基喹啉基)-乙烯基]咔唑的合成、抗氧化活性及促进鼠骨髓间质干细胞增殖的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(9): 974-982. |
| [11] | 张安琪, 邹建华, 应磊, 陈奇良, 陈冰, 杨伟, 曹镛. 新型电磷光咔唑-co-吡啶共聚物的合成与发光性能[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(23): 2745-2749. |
| [12] | 刘红艳,易忠胜,莫凌云. 多氯咔唑系列化合物的热力学性质的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(14): 1626-1634. |
| [13] | 凡素华, 杨维春, 王科志. 一种含咔唑基团的混配型钌(II)配合物的合成、表征和酸碱性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(6): 690-696. |
| [14] | 甄红宇,罗潺,朱德喜,叶辉,刘旭. 基于不同辅助配体螯合电磷光聚合物的合成与性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(5): 557-562. |
| [15] | 刘然升, 曾文进, 杜斌, 候琼, 石伟, 孙明亮, 杨伟, 曹镛. 新型基于3,6-咔唑与噻吩衍生物的红光聚合物的合成与性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(9): 847-852. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||