化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (5): 445-452.DOI: 10.6023/A25030093 上一篇 下一篇
研究通讯
张一亮a,b, 武卫龙b, 许文磊b, 傅玉琴b,*( ), 郭辉b,*(
), 郭辉b,*( ), 卢志强a,b,*(
), 卢志强a,b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-03-26
发布日期:2025-04-23
基金资助:
Yiliang Zhanga,b, Weilong Wub, Wenlei Xub, Yuqin Fub,*( ), Hui Guob,*(
), Hui Guob,*( ), Zhiqiang Lua,b,*(
), Zhiqiang Lua,b,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-26
Published:2025-04-23
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
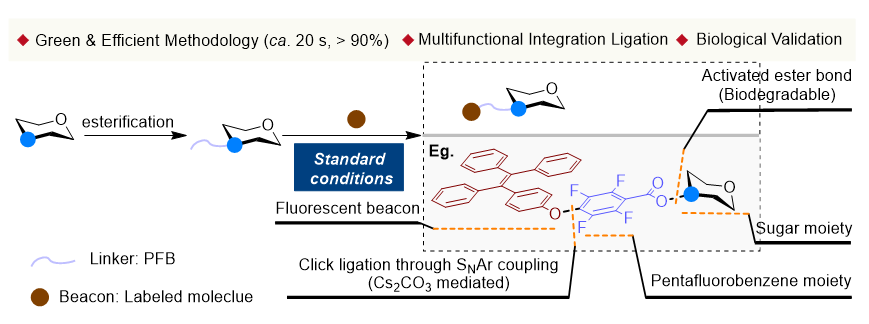
糖作为一种重要的功能性生物分子, 基于结构衍化以及结构改造往往可赋予该类分子多样化的生物识别作用及功能. 由于基于糖C3位点的结构衍生化可赋予其独特的、抑或潜在的生理及药学活性, 相关研究已成为糖化学研究的重要关注方向. 本研究通过模块化设计, 充分结合键合模式的生物学应用导向, 通过精准引入酯键(可控降解)、全氟芳基(疏水增效)及SNAr(位点专一性)三重复合功能基元, 设计和构建了具有多重响应潜质的糖C3分子骨架, 并采用绿色、温和、快速(主要过程最快20 s内完成)的方法, 实现了糖C3位点单元衍生化合成. 本工作还以所构建的代表性的糖衍生分子为例, 首次进行了基于糖C3衍生分子的糖-凝集素识别作用及信号响应初步研究.
张一亮, 武卫龙, 许文磊, 傅玉琴, 郭辉, 卢志强. 基于点击化学构建的功能化糖分子: 糖C3-OH的衍生化设计及高效合成[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(5): 445-452.
Yiliang Zhang, Weilong Wu, Wenlei Xu, Yuqin Fu, Hui Guo, Zhiqiang Lu. Click-Inspired Functionalization of Glycans: Rational Design and Efficient Synthesis of C3-OH Specific Derivatives[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(5): 445-452.


| Entrya | Base | Solvent (V/V) | Time | Aa-1 Yieldc/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cs2CO3 | THF | 12 h | 33.8 |
| 2 | Cs2CO3 | DMSO | 12 h | 71.5 |
| 3 | Cs2CO3 | DMF | 12 h | 42.6 |
| 4 | Cs2CO3 | THF/DMF (5∶1) | 12 h | 67.3 |
| 5 | Cs2CO3 | THF/NMP (5∶1) | 12 h | 55.2 |
| 6 | Cs2CO3 | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | 95.7 |
| 7 | DBU | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | NR |
| 8 | K2CO3 | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | 3.0 |
| 9 | NaHCO3 | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | 14.0 |
| 10 | NaOAc | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | 3.0 |
| 11 | Quinine | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | 60.7 |
| 12b | — | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | NR |
| 13d | Cs2CO3 | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 20 s | 92.9 |
| Entrya | Base | Solvent (V/V) | Time | Aa-1 Yieldc/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cs2CO3 | THF | 12 h | 33.8 |
| 2 | Cs2CO3 | DMSO | 12 h | 71.5 |
| 3 | Cs2CO3 | DMF | 12 h | 42.6 |
| 4 | Cs2CO3 | THF/DMF (5∶1) | 12 h | 67.3 |
| 5 | Cs2CO3 | THF/NMP (5∶1) | 12 h | 55.2 |
| 6 | Cs2CO3 | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | 95.7 |
| 7 | DBU | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | NR |
| 8 | K2CO3 | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | 3.0 |
| 9 | NaHCO3 | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | 14.0 |
| 10 | NaOAc | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | 3.0 |
| 11 | Quinine | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | 60.7 |
| 12b | — | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 12 h | NR |
| 13d | Cs2CO3 | THF/DMSO (5∶1) | 20 s | 92.9 |




| [1] |
For selected examples, see: (a)
pmid: 23281927 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/jm301677r pmid: 23281927 |
|
|
(c)
pmid: 23281927 |
|
| [2] |
For selected examples, see: (a)
pmid: 22955694 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/ja307355n pmid: 22955694 |
|
|
(c)
pmid: 22955694 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 22955694 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b00830 pmid: 22955694 |
|
|
(f)
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.098 pmid: 22955694 |
|
|
(g)
pmid: 22955694 |
|
| [3] |
(a)
pmid: 27160849 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2016.04.020 pmid: 27160849 |
|
| [4] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
|
(d)
|
|
|
(e)
|
|
|
(f)
|
|
| [5] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
|
(d)
|
|
|
(e)
|
|
|
(沈仁增, 曹鑫, 俞飚, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 278.)
doi: 10.6023/A17120544 |
|
|
(f)
|
|
|
(王昭, 郝凌云, 张小娟, 盛瑞隆, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 2379.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201903038 |
|
| [6] |
(a)
pmid: 3214839 |
|
(b)
pmid: 3214839 |
|
|
(c)
pmid: 3214839 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 3214839 |
|
|
(e)
pmid: 3214839 |
|
|
(f)
pmid: 3214839 |
|
|
(g)
pmid: 3214839 |
|
| [7] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
| [8] |
(a)
pmid: 29313666 |
|
(b)
pmid: 29313666 |
|
|
(c)
pmid: 29313666 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 29313666 |
|
|
(e)
pmid: 29313666 |
|
|
(f)
pmid: 29313666 |
|
|
(g)
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b03017 pmid: 29313666 |
|
|
(h)
doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00636 pmid: 29313666 |
|
| [9] |
the selective reference of sugar probe topic: (a)
pmid: 34165284 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00920 pmid: 34165284 |
|
|
(c)
pmid: 34165284 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 34165284 |
|
| [10] |
(a)
pmid: 16594719 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1126/science.7973629 pmid: 16594719 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1126/science.287.5460.2007 pmid: 16594719 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 16594719 |
|
|
(e)
pmid: 16594719 |
|
| [11] |
(a)
pmid: 16759798 |
|
(b)
pmid: 16759798 |
|
| [12] |
For fluorinated compounds in pharmaceuticals, see the following: (a)
pmid: 31846326 |
|
(b)
pmid: 31846326 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1021/cr300222d pmid: 31846326 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 31846326 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01692 pmid: 31846326 |
|
|
(f)
pmid: 31846326 |
|
|
(g)
pmid: 31846326 |
|
| [13] |
(a)
pmid: 17048824 |
|
(b)
pmid: 17048824 |
|
|
(c)
pmid: 17048824 |
|
|
(d)
pmid: 17048824 |
|
|
(e)
pmid: 17048824 |
|
|
(f)
pmid: 17048824 |
|
| [14] |
(a)
pmid: 30623945 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/c8ob02899k pmid: 30623945 |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||