化学学报 ›› 2011, Vol. 69 ›› Issue (21): 2589-2596.DOI: 10.6023/A1012275J 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
刘璐莎1,樊君*,1,胡春梅1,孙洋1,胡晓云2,赵英永3,魏嵩1,梁旭华1
Liu Lusha1 Fan Jun*,1 Hu Chunmei1 Sun Yang1 Hu Xiaoyun2 Zhao Yingyong3 Wei Song1 Liang Xuhua1
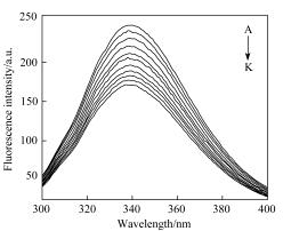
人血清白蛋白多种结合位点的存在使其成为许多药物可能的结合靶点. 土贝母皂苷具有广泛的生理和药理活性, 它与蛋白质相互作用机制的研究对于深入了解其药理药效具有重要的意义. 采用荧光光谱法研究了土贝母皂苷II (TBMSⅡ)与人血清白蛋白(HSA)之间的相互作用, 根据Stern-Volmer荧光淬灭方程计算得293, 298, 303, 308 K时TBMSⅡ与HSA相互作用的结合常数分别为1.002×105, 0.701×105, 0.514×105, 0.411×105 L•mol-1. 由实验计算出热力学参数焓变ΔH为-44.829 kJ•mol-1, 熵变ΔS为-57.497 J•mol-1•K-1, 表明分子间的氢键及疏水作用是TBMSⅡ-HSA复合物的主要作用力, 结合位点位于HSA的亚结构ⅡA, 这与分子模拟方法的结果相一致. 依据能量转移原理求得TBMSⅡ与HSA间的距离为4.95 nm|三维、同步荧光光谱及圆二色谱的结果表明TBMSⅡ的加入使HSA构象发生变化, α-螺旋结构有所下降.