化学学报 ›› 2011, Vol. 69 ›› Issue (20): 2359-2367. 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
冯丽娟,杨怀玉*,王福会
FENG Li-Juan, YANG Huai-Yu, WANG Fu-Hui
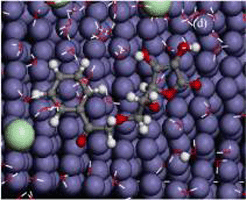
合成了一种苯甲酸抗坏血酸酯(AB), 利用腐蚀电化学和表面分析技术, 在含3.5% NaCl的饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中研究了化合物对钢筋的缓蚀性能, 结合量化计算和分子动力学模拟对其在铁表面的吸附行为和缓蚀作用机理进行了分析讨论. 结果表明, AB的添加可有效降低钢筋的腐蚀电流密度, 提高钢筋的耐蚀性能, 表明缓蚀剂对Cl-引起的钢筋腐蚀具有良好的抑制作用, 为阴极型缓蚀剂. 化合物通过吸附和与铁离子形成不溶性络合物, 可在钢筋表面形成一层保护膜, 进而阻碍介质中Cl-与金属表面的接触, 且吸附符合Langmuir等温吸附规律. 量化计算和分子模拟结果证明, 分子中内酯五元环和苯环既是亲核反应活性中心, 也是亲电反应中心, 化合物通过与铁原子间的共价键合而以平行于铁表面的方式吸附在金属表面.
中图分类号: