化学学报 ›› 2011, Vol. 69 ›› Issue (20): 2479-2485. 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
周佳欣1,吴明红*,1,姚思德2
Zhou Jiaxin1 Wu Minghong*,1 Yao Side2
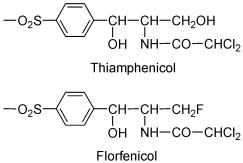
对甲砜霉素(THA)和氟苯尼考(FLO)的辐照降解进行了瞬态产物和稳态产物的分析. 利用脉冲辐解技术研究了THA/FLO水溶液在各种条件下与•OH, 和•H的反应机理, 研究表明: THA/FLO与•OH反应途径与pH有关: 中性条件下主要发生苯环上的加成反应, 其速率常数分别为为1.09×108 L•mol-1•s-1 (THA)和3.14×108 L•mol-1•s-1 (FLO)|碱性条件下, 则断裂产物在•OH催化下的去OH-反应. 的进攻导致THA/FLO脱Cl-和F-, 该反应中性条件比碱性条件更易进行. THA/FLO与•H发生加成反应, 生成较稳定的氢加成产物, 反应速率分别为3.52×107 L•mol-1•s-1 (THA)和2.43×108 L•mol-1•s-1 (FLO). 利用GC/MS对电子束辐照的稳态产物分析, 得出自由基反应生成的小分子碎片. 结合瞬态反应过程, 得出THA/FLO降解途径.