化学学报 ›› 2011, Vol. 69 ›› Issue (21): 2618-2626.DOI: 10.6023/A1101082B 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
陈学勇1,2,韦朝海*,1,邓秀琼1,夏芳1,于旭彪1
Chen Xueyong1,2 Wei Chaohai*,1 Deng Xiuqiong1 Xia Fang1 Yu Xubiao1
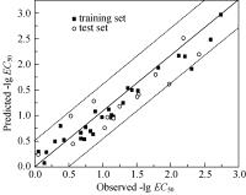
应用半经验方法AM1计算了42种硝基芳烃的19个量子化学和理化参数, 结合部分取自文献的分子结构符和梨形四膜虫的急性毒性数据, 采用偏最小二乘法回归分析建立了硝基芳烃对梨形四膜虫的毒性定量预测模型, 对该类化合物的急性毒性机理进行了讨论并对所建立模型与文献中相关报道的模型的评价指标进行了比较. 模型的内部交叉检验和外部测试检验结果均显示所获得模型具有较高的拟合精度和较好的预测效果(R2=0.946, =0.921, P=5.5×10-18, F=453.53, SD=0.171), 其评价指标优于文献中报道的其它模型结果. 模型变量重要性分析表明, ELUMO, a, , ET, MW, CSV及MR对硝基芳烃的毒性大小有较大的制约作用, 硝基芳烃对梨形四膜虫所表现出来的毒性随着ELUMO, ET, △E的增大而减少, 随a, , , △Hf,, MW, CSV及MR的增大而增大. 导致ET和△Hf对梨形四膜虫的毒性大小贡献的不同步, 被认为是由于硝基芳烃对梨形四膜虫多种致毒机制共存所造成.