化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (9): 1238-1249.DOI: 10.6023/A22050227 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
李小娟, 叶梓瑜, 谢书涵, 王永净, 王永好, 吕源财, 林春香*( )
)
投稿日期:2022-05-16
发布日期:2022-08-11
通讯作者:
林春香
基金资助:
Xiaojuan Li, Ziyu Ye, Shuhan Xie, Yongjing Wang, Yonghao Wang, Yuancai Lv, Chunxiang Lin( )
)
Received:2022-05-16
Published:2022-08-11
Contact:
Chunxiang Lin
Supported by:文章分享

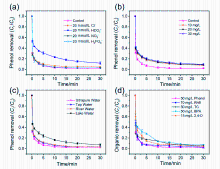
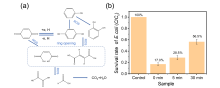
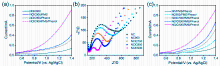
杂原子共掺杂碳材料在过硫酸盐活化领域具有广阔的应用前景. 本工作通过两步煅烧法合成了氮氯共掺杂ZIF-8衍生多孔碳材料(NClC), 并以苯酚为目标污染物, 考察其活化过一硫酸盐(PMS)的催化性能, 结果表明, 30 min内, 0.04 g/L NClC900活化0.3 g/L PMS可去除水中97.7%的苯酚(50 mg/L), 且总有机碳去除率可达72.4%; NClC900/PMS体系具备优异的酸碱耐受性(pH=3~9)和抗干扰能力, 无机阴离子和腐植酸对其影响较小, 且该体系还可有效去除水中的染料、抗生素、酚类及农药等有机污染物; 循环实验结果表明, NClC900在重复使用4次后其苯酚去除率可达72.1%; 猝灭实验、电子顺磁共振和电化学分析表明1O2和表面结合SO4•-是导致苯酚降解的主要活性物种, 而NClC900中的石墨N、C—Cl是产生1O2和表面结合SO4•-的关键活性位点.
李小娟, 叶梓瑜, 谢书涵, 王永净, 王永好, 吕源财, 林春香. 氮氯共掺杂多孔碳活化过一硫酸盐降解苯酚的性能及机理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1238-1249.
Xiaojuan Li, Ziyu Ye, Shuhan Xie, Yongjing Wang, Yonghao Wang, Yuancai Lv, Chunxiang Lin. Study on Performance and Mechanism of Phenol Degradation through Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Nitrogen/Chlorine Co-doped Porous Carbon Materials[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(9): 1238-1249.




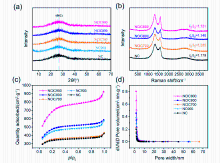
| Sample | SSAa/ (m2•g-1) | TPVb/ (cm3•g-1) | APS b/ nm | Vmicro c/ (cm3•g-1) | Vmeso c/ (cm3•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 1060.82 | 0.23 | 3.76 | 0.06 | 0.17 |
| NC900 | 1418.02 | 0.40 | 3.27 | 0.12 | 0.28 |
| NClC700 | 1101.09 | 0.24 | 3.49 | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| NClC800 | 1530.69 | 0.42 | 2.86 | 0.14 | 0.28 |
| NClC900 | 2259.60 | 0.84 | 2.96 | 0.25 | 0.59 |
| Sample | SSAa/ (m2•g-1) | TPVb/ (cm3•g-1) | APS b/ nm | Vmicro c/ (cm3•g-1) | Vmeso c/ (cm3•g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 1060.82 | 0.23 | 3.76 | 0.06 | 0.17 |
| NC900 | 1418.02 | 0.40 | 3.27 | 0.12 | 0.28 |
| NClC700 | 1101.09 | 0.24 | 3.49 | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| NClC800 | 1530.69 | 0.42 | 2.86 | 0.14 | 0.28 |
| NClC900 | 2259.60 | 0.84 | 2.96 | 0.25 | 0.59 |

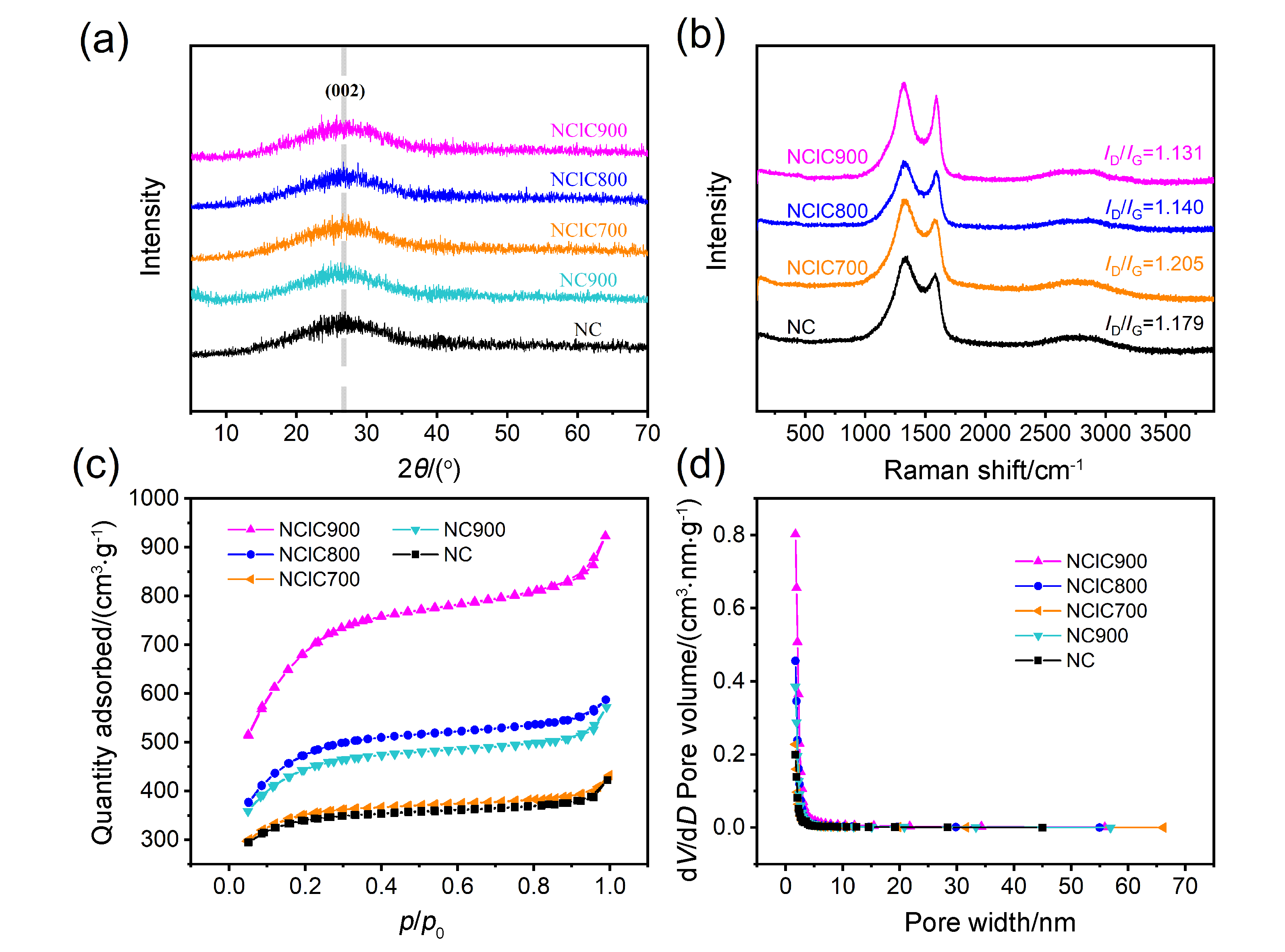
| Sample | C | N | O | Cl | Zn | C=O | 吡啶N | 吡咯N | 石墨N | 氧化N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 64.00 | 15.05 | 6.87 | — | 14.08 | 12.43 | 32.89 | 26.32 | 27.63 | 13.16 |
| NC900 | 77.85 | 7.15 | 7.55 | — | 7.45 | 11.51 | 36.21 | 5.17 | 43.10 | 15.52 |
| NClC700 | 62.94 | 12.36 | 7.51 | 1.53 | 15.66 | 11.73 | 46.51 | 13.49 | 28.84 | 11.16 |
| NClC800 | 68.57 | 8.35 | 10.36 | 2.31 | 10.41 | 8.39 | 42.73 | 10.26 | 34.62 | 12.39 |
| NClC900 | 83.59 | 4.33 | 7.09 | 1.10 | 3.59 | 10.26 | 31.46 | 6.57 | 46.95 | 15.02 |
| Sample | C | N | O | Cl | Zn | C=O | 吡啶N | 吡咯N | 石墨N | 氧化N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 64.00 | 15.05 | 6.87 | — | 14.08 | 12.43 | 32.89 | 26.32 | 27.63 | 13.16 |
| NC900 | 77.85 | 7.15 | 7.55 | — | 7.45 | 11.51 | 36.21 | 5.17 | 43.10 | 15.52 |
| NClC700 | 62.94 | 12.36 | 7.51 | 1.53 | 15.66 | 11.73 | 46.51 | 13.49 | 28.84 | 11.16 |
| NClC800 | 68.57 | 8.35 | 10.36 | 2.31 | 10.41 | 8.39 | 42.73 | 10.26 | 34.62 | 12.39 |
| NClC900 | 83.59 | 4.33 | 7.09 | 1.10 | 3.59 | 10.26 | 31.46 | 6.57 | 46.95 | 15.02 |




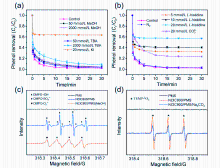

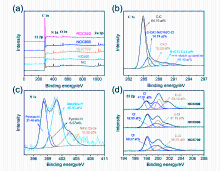
| 猝灭剂 | ROS | 抑制率/ % | ROS贡献值 (A) | ROS贡献率(A/T, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50/2000 mmol/L MeOH | (SO4•-+•OH)S | 2.6/2.6 | SO4•-S=1.3 | SO4•-S=0.9 |
| 50/2000 mmol/L TBA | •OHS+C | 1.3/5.7 | •OHS=1.3 •OHC=4.4 | •OHS=0.9 •OHC=3.1 |
| 20 mmol/L KI | (SO4•-+•OH)C | 61.2 | SO4•-C=56.8 | SO4•-C=40.6 |
| 20 mmol/L L-histidine | 1O2 | 55.0 | 1O2=55.0 | 1O2=39.3 |
| 20 mmol/L Na2CO3 | O2•- | 21.3 | O2•-=21.3 | O2•-=15.2 |
| 猝灭剂 | ROS | 抑制率/ % | ROS贡献值 (A) | ROS贡献率(A/T, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50/2000 mmol/L MeOH | (SO4•-+•OH)S | 2.6/2.6 | SO4•-S=1.3 | SO4•-S=0.9 |
| 50/2000 mmol/L TBA | •OHS+C | 1.3/5.7 | •OHS=1.3 •OHC=4.4 | •OHS=0.9 •OHC=3.1 |
| 20 mmol/L KI | (SO4•-+•OH)C | 61.2 | SO4•-C=56.8 | SO4•-C=40.6 |
| 20 mmol/L L-histidine | 1O2 | 55.0 | 1O2=55.0 | 1O2=39.3 |
| 20 mmol/L Na2CO3 | O2•- | 21.3 | O2•-=21.3 | O2•-=15.2 |

| [1] |
Ganiyu S. O.; Sable S.; Gamal El-Din M. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132492.
|
| [2] |
Liu L.; Chen Z.; Zhang J.; Shan D.; Wu Y.; Bai L.; Wang B. J Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102122.
|
| [3] |
Luo H.; Fu H.; Yin H.; Lin Q. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128044.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.128044 |
| [4] |
Chen X.; Oh W.; Lim T. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 941.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.049 |
| [5] |
Luo R.; Wu J.; Zhao J.; Fang D.; Liu Z.; Hu L. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112060.
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112060 |
| [6] |
Xie J.; Chen L.; Luo X.; Huang L.; Li S.; Gong X. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119887.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119887 |
| [7] |
Humphrey N.; Rodriguez R.; Arias G.; Thai E.; Muro E.; Merinov B. V.; Goddard W. A.; Yu T. H. J. Catal. 2020, 381, 295.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2019.10.022 |
| [8] |
Zhang C.; Bai J.; Ma L.; Lv Y.; Wang F.; Zhang X.; Yuan X.; Hu S. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 87, 215.
doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2018.06.013 |
| [9] |
Wu Q.; Liang J.; Yi J.; Shi P.; Huang Y.; Cao R. Science China Materials 2018, 62, 671.
doi: 10.1007/s40843-018-9364-5 |
| [10] |
Wang N.; Ma W.; Ren Z.; Zhang L.; Qiang R.; Lin K.-Y. A.; Xu P.; Du Y.; Han X. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1849.
doi: 10.1039/C8QI00256H |
| [11] |
Ferrari A. C.; Robertson J. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 14095.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.61.14095 |
| [12] |
Dresselhaus M. S.; Dresselhaus G.; Saito R.; Jorio A. Phys. Rep. 2005, 409, 47.
doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2004.10.006 |
| [13] |
Zhang M.; Luo R.; Wang C.; Zhang W.; Yan X.; Sun X.; Wang L.; Li J. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 12547.
doi: 10.1039/c9ta02931a |
| [14] |
Yang Y.; Jin H.; Zhang C.; Gan H.; Yi F.; Wang H. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 821, 153439.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153439 |
| [15] |
Tang L.; Liu Y.; Wang J.; Zeng G.; Deng Y.; Dong H.; Feng H.; Wang J.; Peng B. Appl. Catal., B 2018, 231, 1.
|
| [16] |
Huang B.; Jiang J.; Huang G.; Yu H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 8978.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA02282H |
| [17] |
Zhang J.; Chen P.; Gao W.; Wang W.; Tan F.; Wang X.; Qiao X.; Wong P. K. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 265, 118474.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118474 |
| [18] |
Chen F.; Cheng X.; Zhao Z.; Wang X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 941.(in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21030117 |
|
(陈峰, 程晓琴, 赵振新, 王晓敏, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 941.)
|
|
| [19] |
Wang G.; Chen S.; Quan X.; Yu H.; Zhang Y. Carbon 2017, 115, 730.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.01.060 |
| [20] |
Cheng Z.; Zheng K.; Lin G.; Fang S.; Li L.; Bi J.; Shen J.; Wu L. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2674.
doi: 10.1039/C9NA00089E |
| [21] |
Bianco G. V.; Sacchetti A.; Milella A.; Grande M.; D’orazio A.; Capezzuto P.; Bruno G. Carbon 2020, 170, 75.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.07.038 |
| [22] |
Ghanbari F.; Moradi M. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 41.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.064 |
| [23] |
Abdul Nasir Khan M.; Kwame Klu P.; Wang C.; Zhang W.; Luo R.; Zhang M.; Qi J.; Sun X.; Wang L.; Li J. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 363, 234.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.129 |
| [24] |
Ma W.; Wang N.; Tong T.; Zhang L.; Lin K. A.; Han X.; Du Y. Carbon 2018, 137, 291.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.05.039 |
| [25] |
Guan Y.; Ma J.; Ren Y.; Liu Y.; Xiao J.; Lin L.; Zhang C. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5431.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.06.023 |
| [26] |
Deng Z.; Yang X.; Xu W. Journal of Tongji University Natural Science, 2009, 37, 354.(in Chinese)
|
|
(邓子峰, 杨晓, 徐伟, 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 37, 354.)
|
|
| [27] |
Zhang L.; Kanki T.; Sano N.; Toyoda A. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 115, 395.
doi: 10.1007/s10661-006-7236-y |
| [28] |
Liang J.; Xu X.; Qamar Zaman W.; Hu X.; Zhao L.; Qiu H.; Cao X. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121908.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.121908 |
| [29] |
Wang Q.; Li L.; Luo L.; Yang Y.; Yang Z.; Li H.; Zhou Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 120891.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.170 |
| [30] |
Wu L.; Yu Y.; Zhang Q.; Hong J.; Wang J.; She Y. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 480, 717.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.034 |
| [31] |
Xi T.; Li X.; Zhang Q.; Liu N.; Niu S.; Dong Z.; Lyu C. Front. Env. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 11.
doi: 10.1007/s11783-020-1303-4 |
| [32] |
Cheng X.; Guo H.; Zhang Y.; Wu X.; Liu Y. Water Res. 2017, 113, 80.
doi: S0043-1354(17)30091-X pmid: 28199865 |
| [33] |
Duan W.; He J.; Wei Z.; Dai Z.; Feng C. Environ. Sci.: Nano 2020, 7, 2982.
doi: 10.1039/D0EN00848F |
| [34] |
Pang K.; Sun W.; Ye F.; Yang L.; Pu M.; Yang C.; Zhang Q.; Niu J. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127270.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127270 |
| [35] |
Gul I.; Sayed M.; Shah N. S.; Rehman F.; Khan J. A.; Gul S.; Bibi N.; Iqbal J. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 23368.
doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11497-2 |
| [36] |
Lyu L.; Yu G.; Zhang L.; Hu C.; Sun Y. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 747.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b04865 |
| [37] |
Li J.; He L.; Jiang J.; Xu Z.; Liu M.; Liu X.; Tong H.; Liu Z.; Qian D. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 353, 136579.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136579 |
| [38] |
Ma Y.; Liu R.; Meng S.; Niu L.; Yang Z.; Lei Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 153.(in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18090372 |
|
(马亚丽, 刘茹雪, 孟双艳, 牛力同, 杨志旺, 雷自强, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 153.)
|
|
| [39] |
Liu Y.; Miao W.; Fang X.; Tang Y.; Wu D.; Mao S. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122584.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122584 |
| [40] |
Guo W.; Yu J.; Dai Z.; Hou W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1203.(in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19080316 |
|
(郭文娟, 于洁, 代昭, 侯伟钊, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1203.)
doi: 10.6023/A19080316 |
| [1] | 蒋江民, 郑欣冉, 孟雅婷, 贺文杰, 陈亚鑫, 庄全超, 袁加仁, 鞠治成, 张校刚. 氟氮共掺杂多孔碳纳米片的制备及其储钾性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(4): 319-327. |
| [2] | 牛犇, 翟振宇, 郝肖柯, 任婷莉, 李从举. 基于ZIF-8/PAN复合薄膜的柔性丙酮气体传感器[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 946-955. |
| [3] | 郭彩霞, 马小杰, 王博. 金属有机框架基复合材料的制备及其光热性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(8): 967-985. |
| [4] | 陈锋, 程晓琴, 赵振新, 王晓敏. 分级多孔N, P共掺杂rGO改性隔膜增强锂硫电池的循环稳定性[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 941-947. |
| [5] | 穆春辉, 张艺馨, 寇伟, 徐联宾. 镍氮掺杂有序大孔/介孔碳负载银纳米颗粒用于高效电催化CO2还原[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 925-931. |
| [6] | 李旭飞, 闫保有, 黄维秋, 浮历沛, 孙宪航, 吕爱华. 金属有机骨架及其复合材料基于筛分复合效应的C2分离的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 459-471. |
| [7] | 陈杨, 杜亚丹, 王勇, 刘普旭, 李立博, 李晋平. UTSA-280的氨改性以及C2H4/C2H6分离性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 534-539. |
| [8] | 李宸, 陈凤华, 叶丽, 李伟, 于晗, 赵彤. B,N共掺杂的In2O3/TiO2制备与光催化产氢性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12): 1448-1454. |
| [9] | 武卓敏, 石勇, 李春艳, 牛丹阳, 楚奇, 熊巍, 李新勇. 双金属MOF-74-CoMn催化剂的制备及其CO选择性催化还原技术应用[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(8): 758-764. |
| [10] | 张贺, 李国良, 张可刚, 廖春阳. 金属有机骨架材料在吸附分离研究中的应用进展[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(9): 841-859. |
| [11] | 杨向平, 郭晓雪, 张成华, 王小萍, 杨勇, 李永旺. 金属有机骨架材料Fe-MIL-100诱导的铁基费托催化剂的合成及催化性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(4): 360-366. |
| [12] | 李绍周, 黄晓, 张华. 有机或金属-有机二维纳米材料的制备与应用[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(9): 913-923. |
| [13] | 韩若冰, 芦姗, 王艳杰, 张雪华, 吴强, 贺涛. SO4-和I-共掺杂的聚苯胺对电极在染料敏化太阳电池中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(10): 1061-1068. |
| [14] | 姜洪泉, 王巧凤, 李井申, 王庆元, 李振宇. N-P-TiO2纳米粒子的溶胶-水热制备及太阳光下光催化降解4-氯酚性能[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(20): 2173-2178. |
| [15] | 陈其凤, 史卫梅, 姜东, 徐耀, 吴东, 孙予罕. 可见光响应的镍硅共掺杂二氧化钛及其光催化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(04): 301-308. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||