化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (3): 264-274.DOI: 10.6023/A22110471 上一篇 下一篇
综述
投稿日期:2022-11-23
发布日期:2023-01-28
作者简介: |
刘康, 2016年6月毕业于湖北大学化学化工学院, 获理学学士学位; 2021年12月毕业于中国科学院高能物理研究所, 获理学博士学位; 2022年1月至今中国科学院高能物理研究所博士后. 目前主要研究方向: 低价锕系化学. |
 |
郭燕, 博士, 讲师. 2008年获宁夏大学学士学位; 2012年获宁夏大学硕士学位; 2020年获西北大学博士学位; 2020年9月加入宁夏大学化学化工学院从事教学科研工作; 2022年2月至今在中国科学院高能物理研究所从事博士后研究. 目前主要研究方向: 低价金属配合物的合成及磁性研究. |
 |
于吉攀, 副研究员. 2008年获江苏师范大学学士学位; 2011年获南开大学硕士学位; 2014年获清华大学博士学位; 2014年7月至2016年7月清华大学化学系博士后; 2016年7月加入中国科学院高能物理研究所核能放射化学实验室. 目前主要研究方向: 锕系元素化学. |
 |
石伟群, 研究员, 国家杰出青年科学基金获得者, 长期致力于核燃料循环化学与锕系元素化学相关基础研究, 在JACS、Angew. Chem、Chem、CCS Chem.、Nat. Commun.、Adv. Mater.、Environ. Sci. Technol.等国际知名期刊发表SCI 论文300余篇, 成果被国内外同行广泛关注和引用, 文章总引1万余次, H因子55 (Google Scholar). 分别担任期刊《Chinese Chemical Letters》、《Journal of Nuclear Fuel Cycle and Waste Technology》和《Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology》的编委与国际顾问编委, 中文期刊《核化学与放射化学》编委. 现为中国化学会核化学与放射化学专业委员会委员、中国核学会锕系物理与化学分会副理事长、中国有色金属学会熔盐化学与技术专业委员会副主任委员、中国核学会核化工分会理事兼副秘书长. |
基金资助:
Kang Liu, Yan Guo, Jipan Yu( ), Weiqun Shi(
), Weiqun Shi( )
)
Received:2022-11-23
Published:2023-01-28
Contact:
E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享
单分子磁体是一类由单个分子组成的磁性材料, 其磁性起源于单个分子的磁矩, 有望在超高密度存储、量子计算机、自旋电子学等领域得到应用. 由于锕系元素极大的旋轨耦合效应及5f轨道的延展性, 锕系单分子磁体越来越受到人们的关注, 期待未来磁学性能甚至能超越过渡及镧系金属. 然而, 目前对于锕系单分子磁体的弛豫机理及慢磁行为的影响因素仍尚未明确. 本综述总结了近10多年以来报道的锕系单分子磁体, 发现有效能垒的实验值和理论值极不相符, 一定程度限制了锕系单分子磁体的发展. 最后, 对未来的锕系单分子磁体研究方向进行了展望.
刘康, 郭燕, 于吉攀, 石伟群. 锕系单分子磁体研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(3): 264-274.
Kang Liu, Yan Guo, Jipan Yu, Weiqun Shi. Research Progress of Actinide Single Molecule Magnets[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(3): 264-274.


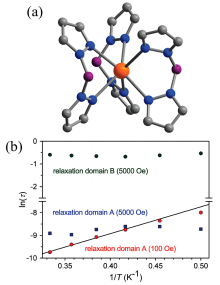









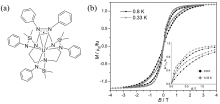
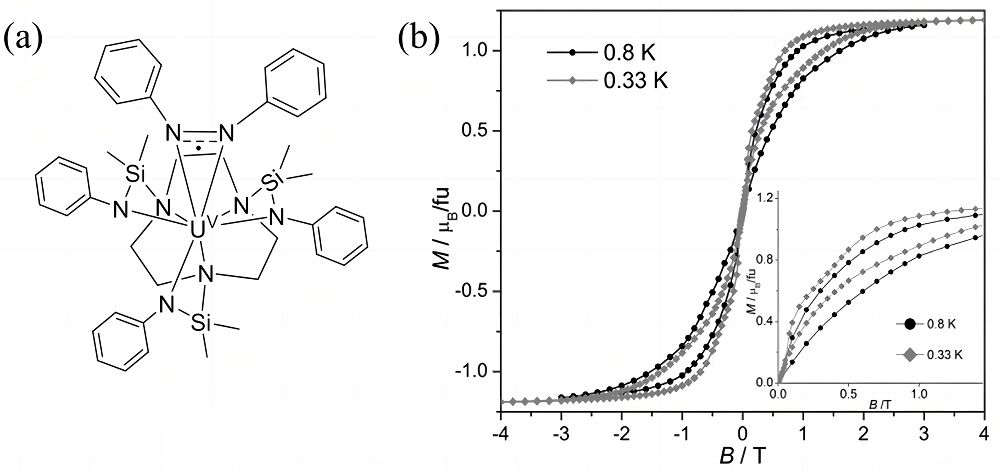
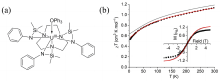



| 年份 | 化合物 | 对称性 | Hdc/Oe | (ΔE/kB)/K | τ0/s | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | U(Ph2BPz2)3 (1) | D3h | 1000 | 28.8 | 1×10−9 | [ |
| 2010 | U(H2BPz2)3 (2) | D3h | 100 | 11.5 | 1.2×10−6 | [ |
| 2012 | UTp3 (3) | D3h | 100 | 5.5 | 7.0×10−5 | [ |
| 2012 | [U(TpMe2)2I] (5) | C2v | 500 | 30.2 | 1.8×10−7 | [ |
| 2011 | [U(TpMe2)2(bipy)][I] (6) | C2 | 500 | 26.2 | 1.4×10−7 | [ |
| 2014 | [U(TpMe2)2(bipy)] (7) | C2 | 500 | 32.5 | 4.68×10−8 | [ |
| 2014 | U(BcMe)3 (9F) | C3h | 750 | 46 | [ | |
| 2015 | [U(O)(TrenTIPS)] (10) | C3v | 1000 | 21.5 | 2.6×10−7 | [ |
| 2013 | [UI3(THF)4] (11) | C2v | 2000 | 19 | 6.4×10−7 | [ |
| 2013 | U[(N(SiMe3)2]3 (12) | C3v | 2000 | 29 | 1.0×10−11 | [ |
| 2013 | [U(BIPMTMS)(I)2(THF)] (13) | C1 | 2000 | 23 | 2.9×10−7 | [ |
| 2014 | [K(18c6)][U(OSi(OtBu)3)4] (14) | Td | 0 | 26 | 2.6×10−7 | [ |
| 2014 | [K(18c6)][U(N(SiMe3)2)4] (15) | Td | 0 | 23 | 2.2×10−8 | [ |
| 2014 | [U(N(SiMe2tBu)2)3] (16) | D3h | 600 | 21.4 | 3.1×10−8 | [ |
| 2015 | [{(SiMe2NPh)3-tacn}UIV(η2-N2Ph2·)] (17) | C1 | 2500 | 17.6 | [ | |
| 2019 | [(η5-C5iPr5)2UI] (18) | C1 | [ | |||
| 2019 | [(η5-C5iPr5)2U][B(C6F5)4] (19) | C1 | [ | |||
| 2019 | [(η5-Cpi-Pr4)2UI] (20) | C2v | [ | |||
| 2019 | [(η5-Cpi-Pr4)2U][B(C6F5)4] (21) | C2v | [ | |||
| 2019 | [UIII{SiMe2NPh}3-tacn)(OPPh3)] (22) | C3 | 2000 | 25.1 | 7.8×10−7 | [ |
| 2020 | [(BDI)U(ODipp)2] (23) | C2v | 500 | 20.8 | 3.39×10−7 | [ |
| 2022 | [(η5-C5iPr5)2U][K(2.2.2-cryptand)] (24) | C1 | 0 | 20 | 1.1×10−7 | [ |
| 2011 | [U(BIPMTMS)(I)2(μ2-η6:η6-C6H5CH3)] (25) | C2v | [ | |||
| 2012 | [{[UO2(salen)]}2Mn(Py)3}6] (26) | C1 | 0 | 142 | 3.0×10−12 | [ |
| 2014 | {[UO2(salen)(py)][Mn(py)4](NO3)]}n (27) | C2v | 0 | 134 | 3.1×10−11 | [ |
| 2014 | UMn2TPA (29) | C2v | 0 | 81 | 5.0×10−10 | [ |
| 2015 | UFe2TPA (31) | C2v | 0 | 53.9 | 3.4×10−9 | [ |
| 2015 | UFe2BPPA (32) | C2v | 0 | 9.0 | 7.82×10−6 | [ |
| 2015 | UNi2BPPA (33) | C2v | 0 | 27.4 | 2.4×10−6 | [ |
| 2017 | UCo2BPPA (35) | C2v | 1500 | 30.5 | 2.9×10−9 | [ |
| 年份 | 化合物 | 对称性 | Hdc/Oe | (ΔE/kB)/K | τ0/s | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | U(Ph2BPz2)3 (1) | D3h | 1000 | 28.8 | 1×10−9 | [ |
| 2010 | U(H2BPz2)3 (2) | D3h | 100 | 11.5 | 1.2×10−6 | [ |
| 2012 | UTp3 (3) | D3h | 100 | 5.5 | 7.0×10−5 | [ |
| 2012 | [U(TpMe2)2I] (5) | C2v | 500 | 30.2 | 1.8×10−7 | [ |
| 2011 | [U(TpMe2)2(bipy)][I] (6) | C2 | 500 | 26.2 | 1.4×10−7 | [ |
| 2014 | [U(TpMe2)2(bipy)] (7) | C2 | 500 | 32.5 | 4.68×10−8 | [ |
| 2014 | U(BcMe)3 (9F) | C3h | 750 | 46 | [ | |
| 2015 | [U(O)(TrenTIPS)] (10) | C3v | 1000 | 21.5 | 2.6×10−7 | [ |
| 2013 | [UI3(THF)4] (11) | C2v | 2000 | 19 | 6.4×10−7 | [ |
| 2013 | U[(N(SiMe3)2]3 (12) | C3v | 2000 | 29 | 1.0×10−11 | [ |
| 2013 | [U(BIPMTMS)(I)2(THF)] (13) | C1 | 2000 | 23 | 2.9×10−7 | [ |
| 2014 | [K(18c6)][U(OSi(OtBu)3)4] (14) | Td | 0 | 26 | 2.6×10−7 | [ |
| 2014 | [K(18c6)][U(N(SiMe3)2)4] (15) | Td | 0 | 23 | 2.2×10−8 | [ |
| 2014 | [U(N(SiMe2tBu)2)3] (16) | D3h | 600 | 21.4 | 3.1×10−8 | [ |
| 2015 | [{(SiMe2NPh)3-tacn}UIV(η2-N2Ph2·)] (17) | C1 | 2500 | 17.6 | [ | |
| 2019 | [(η5-C5iPr5)2UI] (18) | C1 | [ | |||
| 2019 | [(η5-C5iPr5)2U][B(C6F5)4] (19) | C1 | [ | |||
| 2019 | [(η5-Cpi-Pr4)2UI] (20) | C2v | [ | |||
| 2019 | [(η5-Cpi-Pr4)2U][B(C6F5)4] (21) | C2v | [ | |||
| 2019 | [UIII{SiMe2NPh}3-tacn)(OPPh3)] (22) | C3 | 2000 | 25.1 | 7.8×10−7 | [ |
| 2020 | [(BDI)U(ODipp)2] (23) | C2v | 500 | 20.8 | 3.39×10−7 | [ |
| 2022 | [(η5-C5iPr5)2U][K(2.2.2-cryptand)] (24) | C1 | 0 | 20 | 1.1×10−7 | [ |
| 2011 | [U(BIPMTMS)(I)2(μ2-η6:η6-C6H5CH3)] (25) | C2v | [ | |||
| 2012 | [{[UO2(salen)]}2Mn(Py)3}6] (26) | C1 | 0 | 142 | 3.0×10−12 | [ |
| 2014 | {[UO2(salen)(py)][Mn(py)4](NO3)]}n (27) | C2v | 0 | 134 | 3.1×10−11 | [ |
| 2014 | UMn2TPA (29) | C2v | 0 | 81 | 5.0×10−10 | [ |
| 2015 | UFe2TPA (31) | C2v | 0 | 53.9 | 3.4×10−9 | [ |
| 2015 | UFe2BPPA (32) | C2v | 0 | 9.0 | 7.82×10−6 | [ |
| 2015 | UNi2BPPA (33) | C2v | 0 | 27.4 | 2.4×10−6 | [ |
| 2017 | UCo2BPPA (35) | C2v | 1500 | 30.5 | 2.9×10−9 | [ |
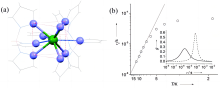

| [1] |
Sessoli R.; Gatteschi D.; Caneschi A.; Novak M. A. Nature 1993, 365, 141.
doi: 10.1038/365141a0 |
| [2] |
Sessoli R.; Tsai H. L.; Schake A. R.; Wang S.; Vincent J. B.; Folting K.; Gatteschi D.; Christou G.; Hendrickson D. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 1804.
doi: 10.1021/ja00058a027 |
| [3] |
Leuenberger M. N.; Loss D. Nature 2001, 410, 789.
doi: 10.1038/35071024 |
| [4] |
Bogani L.; Wernsdorfer W. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 179.
doi: 10.1038/nmat2133 pmid: 18297126 |
| [5] |
Mannini M.; Pineider F.; Sainctavit P.; Danieli C.; Otero E.; Sciancalepore C.; Talarico A. M.; Arrio M.-A.; Cornia A.; Gatteschi D.; Sessoli R. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 194.
doi: 10.1038/nmat2374 pmid: 19182788 |
| [6] |
Thiele S.; Balestro F.; Ballou R.; Klyatskaya S.; Ruben M.; Wernsdorfer W. Science 2014, 344, 1135.
doi: 10.1126/science.1249802 |
| [7] |
Wernsdorfer W.; Sessoli R. Science 1999, 284, 133.
pmid: 10102810 |
| [8] |
Ruiz E.; Cirera J.; Cano J.; Alvarez S.; Loose C.; Kortus J. Chem. Commun. 2008, 52.
|
| [9] |
Gould C. A.; McClain K. R.; Reta D.; Kragskow J. G. C.; Marchiori D. A.; Lachman E.; Choi E.-S.; Analytis J. G.; Britt R. D.; Chilton N. F.; Harvey B. G.; Long J. R. Science 2022, 375, 198.
doi: 10.1126/science.abl5470 |
| [10] |
Yu J.-P.; Liu K.; Wu Q.-Y.; Li B.; Kong X.-H.; Hu K.-Q.; Mei L.; Yuan L.-Y.; Chai Z.-F.; Shi W.-Q. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 2125.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v39.8 |
| [11] |
Wu Q.-Y.; Wang C.-Z.; Lan J.-H.; Chai Z.-F.; Shi W.-Q. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 15895.
doi: 10.1039/D0DT02909B |
| [12] |
Zhu Z.-H.; Tang J.-K. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 9469.
doi: 10.1039/D2CS00516F |
| [13] |
Zhu Z.-H.; Tang J.-K. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac194.
|
| [14] |
Tian H.-Q.; Zheng L.-M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 34. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19090330 |
|
(田海权, 郑丽敏, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 34.)
doi: 10.6023/A19090330 |
|
| [15] |
Ren M.; Zheng L.-M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 1091. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A15060376 |
|
(任旻, 郑丽敏, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 1091.)
doi: 10.6023/A15060376 |
|
| [16] |
Liddle S. T.; Slageren J. v. In Lanthanides and Actinides in Molecular Magnetism, Eds.: Layfield, R. A.; Murugesu, M., John Wiley & Sons, Weinheim, 2015, p. 315.
|
| [17] |
Meihaus K. R.; Long J. R. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 2517.
doi: 10.1039/c4dt02391a pmid: 25352033 |
| [18] |
McAdams S. G.; Ariciu A.-M.; Kostopoulos A. K.; Walsh J. P. S.; Tuna F. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 346, 216.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2017.03.015 |
| [19] |
Liddle S. T.; van Slageren J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6655.
doi: 10.1039/C5CS00222B |
| [20] |
Bates L. F.; Hughes D. Proc. Phys. Soc. B 1954, 67, 28.
doi: 10.1088/0370-1301/67/1/305 |
| [21] |
Brodsky M. B. AIP Conf. Proc. 1972, 5, 611.
|
| [22] |
Trzebiatowski W.; Sliwa A.; Stalinski B. Rocz. Chem. 1952, 26, 110.
|
| [23] |
Santini P.; Lémanski R.; Erdős P. Adv. Phys. 1999, 48, 537.
doi: 10.1080/000187399243419 |
| [24] |
Kindra D. R.; Evans W. J. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8865.
doi: 10.1021/cr500242w |
| [25] |
Rinehart J. D.; Long J. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 12558.
doi: 10.1021/ja906012u pmid: 19689136 |
| [26] |
Rinehart J. D.; Meihaus K. R.; Long J. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7572.
doi: 10.1021/ja1009019 pmid: 20465218 |
| [27] |
Meihaus K. R.; Rinehart J. D.; Long J. R. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 8484.
doi: 10.1021/ic201078r pmid: 21834501 |
| [28] |
Baldoví J. J.; Cardona-Serra S.; Clemente-Juan J. M.; Coronado E.; Gaita-Ariño A. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 938.
doi: 10.1039/C2SC21490C |
| [29] |
Rinehart J. D.; Long J. R. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 13572.
doi: 10.1039/c2dt31352a pmid: 22878433 |
| [30] |
Apostolidis C.; Kovács A.; Walter O.; Colineau E.; Griveau J.-C.; Morgenstern A.; Rebizant J.; Caciuffo R.; Panak P. J.; Rabung T.; Schimmelpfennig B.; Perfetti M. Chem.-Eur. J. 2020, 26, 11293.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v26.49 |
| [31] |
Coutinho J. T.; Antunes M. A.; Pereira L. C. J.; Bolvin H.; Marçalo J.; Mazzanti M.; Almeida M. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 13568.
doi: 10.1039/c2dt31421e pmid: 22878483 |
| [32] |
Coutinho J. T.; Antunes M. A.; Pereira L. C. J.; Marçalo J.; Almeida M. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 10262.
doi: 10.1039/C4CC04486J |
| [33] |
Antunes M. A.; Pereira L. C. J.; Santos I. C.; Mazzanti M.; Marçalo J.; Almeida M. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 9915.
doi: 10.1021/ic200705p pmid: 21916469 |
| [34] |
Meihaus K. R.; Minasian S. G.; Lukens W. W.; Kozimor S. A.; Shuh D. K.; Tyliszczak T.; Long J. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6056.
doi: 10.1021/ja501569t pmid: 24650296 |
| [35] |
King D. M.; Tuna F.; McMaster J.; Lewis W.; Blake A. J.; McInnes E. J. L.; Liddle S. T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4921.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v52.18 |
| [36] |
Moro F.; Mills D. P.; Liddle S. T.; van Slageren J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3430.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v52.12 |
| [37] |
Pereira L. C. J.; Camp C.; Coutinho J. T.; Chatelain L.; Maldivi P.; Almeida M.; Mazzanti M. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 11809.
doi: 10.1021/ic501520c pmid: 25354258 |
| [38] |
Goodwin C. A. P.; Tuna F.; McInnes E. J. L.; Liddle S. T.; McMaster J.; Vitorica-Yrezabal I. J.; Mills D. P. Chem.-Eur. J. 2014, 20, 14579.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201404864 pmid: 25241882 |
| [39] |
Antunes M. A.; Coutinho J. T.; Santos I. C.; Marçalo J.; Almeida M.; Baldoví J. J.; Pereira L. C. J.; Gaita-Ariño A.; Coronado E. Chem.-Eur. J. 2015, 21, 17817.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201503133 pmid: 26536849 |
| [40] |
Guo F.-S.; Chen Y.-C.; Tong M.-L.; Mansikkamäki A.; Layfield R. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10163.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.30 |
| [41] |
Boreen M. A.; Lussier D. J.; Skeel B. A.; Lohrey T. D.; Watt F. A.; Shuh D. K.; Long J. R.; Hohloch S.; Arnold J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 16629.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b02719 |
| [42] |
Coutinho J. T.; Perfetti M.; Baldoví J. J.; Antunes M. A.; Hallmen P. P.; Bamberger H.; Crassee I.; Orlita M.; Almeida M.; van Slageren J.; Pereira L. C. J. Chem.-Eur. J. 2019, 25, 1758.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201805090 pmid: 30403293 |
| [43] |
Boreen M. A.; Gould C. A.; Booth C. H.; Hohloch S.; Arnold J. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 7938.
doi: 10.1039/D0DT01599G |
| [44] |
Barluzzi L.; Giblin S. R.; Mansikkamäki A.; Layfield R. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 18229.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c06519 |
| [45] |
Mills D. P.; Moro F.; McMaster J.; van Slageren J.; Lewis W.; Blake A. J.; Liddle S. T. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 454.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.1028 |
| [46] |
Mougel V.; Chatelain L.; Pécaut J.; Caciuffo R.; Colineau E.; Griveau J.-C.; Mazzanti M. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 1011.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.1494 |
| [47] |
Mougel V.; Chatelain L.; Hermle J.; Caciuffo R.; Colineau E.; Tuna F.; Magnani N.; de Geyer A.; Pécaut J.; Mazzanti M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 819.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201307366 |
| [48] |
Chatelain L.; Walsh J. P. S.; Pécaut J.; Tuna F.; Mazzanti M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13434.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201407334 pmid: 25284018 |
| [49] |
Chatelain L.; Pécaut J.; Tuna F.; Mazzanti M. Chem.-Eur. J. 2015, 21, 18038.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201503637 pmid: 26464190 |
| [50] |
Chatelain L.; Tuna F.; Pécaut J.; Mazzanti M. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 5498.
doi: 10.1039/c6dt04558h pmid: 28094378 |
| [51] |
Guo F.-S.; Day B. M.; Chen Y.-C.; Tong M.-L.; Mansikkamäki A.; Layfield R. A. Science 2018, 362, 1400.
doi: 10.1126/science.aav0652 |
| [52] |
Magnani N.; Caciuffo R. Inorganics 2018, 6, 26.
doi: 10.3390/inorganics6010026 |
| [53] |
Magnani N.; Colineau E.; Eloirdi R.; Griveau J. C.; Caciuffo R.; Cornet S. M.; May I.; Sharrad C. A.; Collison D.; Winpenny R. E. P. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 197202.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.197202 |
| [54] |
Magnani N.; Apostolidis C.; Morgenstern A.; Colineau E.; Griveau J.-C.; Bolvin H.; Walter O.; Caciuffo R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1696.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201006619 pmid: 21308935 |
| [55] |
Magnani N.; Colineau E.; Griveau J. C.; Apostolidis C.; Walter O.; Caciuffo R. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8171.
doi: 10.1039/c4cc03400g |
| [56] |
Jung J.; Atanasov M.; Neese F. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 8802.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b00642 |
| [57] |
Belkhiri L.; Le Guennic B.; Boucekkine A. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 15.
doi: 10.3390/magnetochemistry5010015 |
| [58] |
Spivak M.; Vogiatzis K. D.; Cramer C. J.; Graaf C. d.; Gagliardi L. J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 1726.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.6b10933 |
| [59] |
Gaggioli C. A.; Gagliardi L. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 8098.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b00170 pmid: 29968473 |
| [60] |
Dey S.; Velmurugan G.; Rajaraman G. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 8976.
doi: 10.1039/C9DT01869G |
| [61] |
Singh S. K.; Cramer C. J.; Gagliardi L. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 6815.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c00105 |
| [62] |
Dey S.; Rajaraman G. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 1831.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c02646 |
| [63] |
Dey S.; Rajaraman G. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 6817.
doi: 10.1039/D2CC01356H |
| [1] | 万瑞辰, 伍思国, 刘俊良, 贾建华, 黄国璋, 李泉文, 童明良. 轴向卤离子配位调控金属冠醚铽(III)配合物的慢磁弛豫行为[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(5): 412-418. |
| [2] | 田海权, 郑丽敏. 环形镧系分子簇合物的组装与单分子磁体性质[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(1): 34-55. |
| [3] | 任旻, 郑丽敏. 稀土单分子磁体[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(11): 1091-1113. |
| [4] | 冯小佳, 李阳光, 张志明, 王恩波. 多酸构筑的单分子磁体[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(12): 1575-1588. |
| [5] | 郭鹏虎, 廖小芬, 冷际东, 童明良. 基于[Dy4(μ4-O)]四面体结构单元的八核和十核镝簇合物的合成、结构及其单分子磁体行为研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(02): 173-178. |
| [6] | 陶建清, 余智, 游效曾. 高温自旋交叉配合物Fe(mtt)2(NCS)2·2.5H2O的合成和磁性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2004, 62(5): 489-492. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||