化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (9): 979-986.DOI: 10.6023/A24070217 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2024-07-15
发布日期:2024-09-05
基金资助:Received:2024-07-15
Published:2024-09-05
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
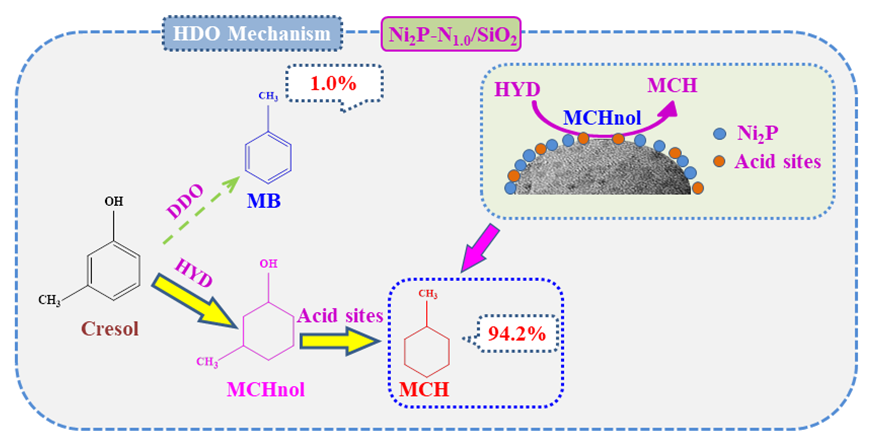
采用浸渍法制备了一系列N修饰的Ni2P-Nx/SiO2催化剂, 通过X射线衍射(XRD)、N2物理吸脱附(BET)、H2-程序升温还原(H2-TPR)、NH3-程序升温脱附(NH3-TPD)、吡啶红外(Py-FTIR)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等表征手段对催化剂的结构进行分析, 系统地研究了Ni/N物质的量比对催化剂理化性质的影响. 以间甲酚为模型化合物, 研究了Ni/N物质的量比、反应温度、反应时间及反应压力对催化剂加氢脱氧(HDO)性能的影响. 结果表明, 适量N修饰可以促进更小活性颗粒的形成, 提高活性组分的分散性, 进而提高催化剂的催化活性. Ni/N比为1时制备的Ni2P-N1.0/SiO2催化剂具有最优异的HDO活性, 在250 ℃、3 MPa、1 h条件下, 间甲酚转化率为93.2%, 目标产物甲基环己烷(MCH)的选择性达到94.2%. Ni2P-Nx/SiO2催化剂上间甲酚HDO主要以加氢-脱氧(HYD)路径为主.
王帅, 宋华. 氮修饰Ni2P-Nx/SiO2催化剂设计合成及间甲酚加氢脱氧性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 979-986.
Shuai Wang, Hua Song. Preparation of N Modified Ni2P-Nx/SiO2 Catalysts and Hydrodeoxygenation Performance of m-Cresol[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(9): 979-986.
| Sample | SBET/(m2•g−1) | Pore volume/(cm3•g−1) | Pore size/nm | Ni loadinga/% | Surface N contentb | Surface P contentc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2P/SiO2 | 381.2 | 0.776 | 7.9 | 8.79 | — | 2.68 |
| Ni2P-N0.25/SiO2 | 321.5 | 0.636 | 7.7 | — | — | — |
| Ni2P-N0.5/SiO2 | 331.2 | 0.653 | 7.5 | — | — | — |
| Ni2P-N1.0/SiO2 | 359.5 | 0.665 | 7.4 | 8.63 | 1.34 | 2.54 |
| Ni2P-N1.5/SiO2 | 354.4 | 0.650 | 7.7 | — | — | — |
| Ni2P-N2.0/SiO2 | 350.5 | 0.637 | 7.3 | — | — | — |
| Sample | SBET/(m2•g−1) | Pore volume/(cm3•g−1) | Pore size/nm | Ni loadinga/% | Surface N contentb | Surface P contentc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2P/SiO2 | 381.2 | 0.776 | 7.9 | 8.79 | — | 2.68 |
| Ni2P-N0.25/SiO2 | 321.5 | 0.636 | 7.7 | — | — | — |
| Ni2P-N0.5/SiO2 | 331.2 | 0.653 | 7.5 | — | — | — |
| Ni2P-N1.0/SiO2 | 359.5 | 0.665 | 7.4 | 8.63 | 1.34 | 2.54 |
| Ni2P-N1.5/SiO2 | 354.4 | 0.650 | 7.7 | — | — | — |
| Ni2P-N2.0/SiO2 | 350.5 | 0.637 | 7.3 | — | — | — |
| Sample | Total acid/ (μmol•g−1) | Acid sites distributiona/(μmol•g−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brönsted acid | Lewis acid | B/L | ||
| Ni2P/SiO2 | 373.6 | 48.8 | 324.8 | 0.15 |
| Ni2P-N0.5/SiO2 | 271.4 | 31.3 | 240.0 | 0.14 |
| Ni2P-N1.0/SiO2 | 298.3 | 32.2 | 266.1 | 0.12 |
| Ni2P-N1.5/SiO2 | 230.2 | 22.9 | 207.3 | 0.11 |
| Sample | Total acid/ (μmol•g−1) | Acid sites distributiona/(μmol•g−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brönsted acid | Lewis acid | B/L | ||
| Ni2P/SiO2 | 373.6 | 48.8 | 324.8 | 0.15 |
| Ni2P-N0.5/SiO2 | 271.4 | 31.3 | 240.0 | 0.14 |
| Ni2P-N1.0/SiO2 | 298.3 | 32.2 | 266.1 | 0.12 |
| Ni2P-N1.5/SiO2 | 230.2 | 22.9 | 207.3 | 0.11 |
| Catalyst | t/h | T/℃ | p/MPa | Con./% | O-free product sel/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2P-N1.0/SiO2 | 1 | 250 | 3 | 93.2 | 94.2 | This work |
| MoS2 | 5 | 250 | 4 | 48.9 | 96.2 | [ |
| FeS2 | 5 | 250 | 4 | 1.1 | 90.6 | [ |
| FeS-MoS2-0.3 | 5 | 250 | 4 | 98.3 | 98.4 | [ |
| Mo-S | 5 | 275 | 4 | 33.3 | 85.9 | [ |
| Co-Mo-S | 5 | 275 | 4 | 76.4 | 98.3 | [ |
| Co-MoS2 | 4 | 300 | 4 | 33.1 | 95.6 | [ |
| Catalyst | t/h | T/℃ | p/MPa | Con./% | O-free product sel/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2P-N1.0/SiO2 | 1 | 250 | 3 | 93.2 | 94.2 | This work |
| MoS2 | 5 | 250 | 4 | 48.9 | 96.2 | [ |
| FeS2 | 5 | 250 | 4 | 1.1 | 90.6 | [ |
| FeS-MoS2-0.3 | 5 | 250 | 4 | 98.3 | 98.4 | [ |
| Mo-S | 5 | 275 | 4 | 33.3 | 85.9 | [ |
| Co-Mo-S | 5 | 275 | 4 | 76.4 | 98.3 | [ |
| Co-MoS2 | 4 | 300 | 4 | 33.1 | 95.6 | [ |
| 底物 | 目标产物 | 转化率/% | 选择性/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 苯酚 | 环己烷 | 97.8 | 96.4 |
| 对甲酚 | 甲基环己烷 | 93.5 | 95.3 |
| 邻甲酚 | 甲基环己烷 | 91.9 | 93.4 |
| 愈创木酚 | 环己烷 | 87.6 | 92.9 |
| 底物 | 目标产物 | 转化率/% | 选择性/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 苯酚 | 环己烷 | 97.8 | 96.4 |
| 对甲酚 | 甲基环己烷 | 93.5 | 95.3 |
| 邻甲酚 | 甲基环己烷 | 91.9 | 93.4 |
| 愈创木酚 | 环己烷 | 87.6 | 92.9 |
| [1] |
Chen S.; Miao C.; Xie H.; Jiao Z.; Zhang X.; Zhou G. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 180, 107002.
|
| [2] |
Wang S.; Jiang N.; Zhu T.; Zhang Q.; Zhang C.; Wang H.; Chen Y.; Li F.; Song H. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 1586.
|
| [3] |
Zhang Q.; Wang S.; Jiang, N ; Jiang, B.; Liu Y.; Chen Y.; Li F.; Song H. J. Catal. 2024, 432, 115338.
|
| [4] |
Liu L.; Zhang J.; Wang L.; Xiao F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 533 (in Chinese).
|
|
(刘露杰, 张建, 王亮, 肖丰收, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 533.)
doi: 10.6023/A23020042 |
|
| [5] |
Li Z.; Ren X.; Wang Y.; Li Z.; Ma S.; Qiu Z. Journal of Molecular Catalysis 2022, 36, 42 (in Chinese).
|
|
(李志勤, 任枭雄, 王元哲, 李宗轩, 马少博, 邱泽刚, 分子催化, 2022, 36, 42.)
|
|
| [6] |
Ochoa E.; Torres D.; Pinilla J. L.; Suelves I. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105146.
|
| [7] |
LiBretto N.; Tacey S.; Zubair M.; Bui T.; Unocic K.; Baddour F.; Griffin M.; Schaidle J.; Farberow C.; Ruddy D.; Bedford N.; Habas S. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 16788.
|
| [8] |
Pitakjakpipop P.; Song C. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 8311.
|
| [9] |
Jiang B.; Zhang Y. ; Wang H.; Liu K.; Jiang N.; Li J.; Song H. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153118.
|
| [10] |
Gou X.; Jiang B.; Zhu T.; Zhang Q.; Wang S.; Li F.; Wang H.; Song H. Fuel 2024, 375, 32580.
|
| [11] |
Zhu T.; Liu K.; Wang H.; Wang J.; Li F.; Wang C.; Song H. Fuel 2023, 331, 125663.
|
| [12] |
Xu B.; Wei X.; Sun J.; Liu J.; Ma L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 239 (in Chinese).
|
|
(徐斌, 韦秀芝, 孙江敏, 刘建国, 马隆龙, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 239.)
doi: 10.6023/A22120481 |
|
| [13] |
Wang S.; Li F.; Liu Y.; Zhang Q.; Song H. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 16941.
|
| [14] |
Ning X.; Sun Y.; Fu H.; Qu X.; Xu Z.; Zheng S. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 124978.
|
| [15] |
Zhang Z.; Tang M.; Chen J. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 353.
|
| [16] |
Zhao H.; Liu C.; Zheng Y.; Li S.; Gao Y.; Ma Q.; Wang F.; Dong Z. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 8619.
|
| [17] |
Feitosa L. F.; Berhault G.; Laurenti D.; Teixeira da Silva V. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 16164.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b00491 |
| [18] |
Zhou M.; Ye J.; Liu P.; Xu J.; Jiang J. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 8824.
|
| [19] |
Zhang Q.; Wang H.; Wang S.; Wang Y.; Zhang M.; Song H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2024, 82, 287 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张强, 王欢, 王帅, 王园园, 张梅, 宋华, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 287.)
doi: 10.6023/A23120546 |
|
| [20] |
Wang W.; Wang X.; Wang Y.; Jiang B.; Song H. React. Chem. Eng. 2022, 7, 978.
|
| [21] |
Wu C.; Kopold P.; Aken P. A.; Maier J.; Yu Y. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604015.
|
| [22] |
Wang M.; Lin M.; Li J.; Huang L.; Zhuang Z.; Lin C.; Zhou L.; Mai L. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8372.
|
| [23] |
Jampa S.; Puente-Urbina A.; Ma Z. Q.; Wongkasemjit S.; Luterbacher J. S.; van Bokhoven J. A. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 4058.
|
| [24] |
Antar M.; Lyu D. M.; Nazari M.; Shah A.; Zhou X. M.; Smith D. L. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110691.
|
| [25] |
Kabir G.; Hameed B. H. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 945.
|
| [1] | 张强, 王欢, 王帅, 王园园, 张梅, 宋华. NiCe(x)/FLRC-TiO2催化剂的制备及其加氢脱氧性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 287-294. |
| [2] | 刘露杰, 张建, 王亮, 肖丰收. 生物质基多元醇的多相催化选择性氢解★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 533-547. |
| [3] | 田钊炜, 达伟民, 王雷, 杨宇森, 卫敏. 第二代生物柴油制备的多相催化剂的结构设计及研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1322-1337. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
