化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (11): 1349-1355.DOI: 10.6023/A25060237 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
洪朝国a,†, 肖顺丽b,†, 杨凯a, 夏家涛a, 刘兴旺a, 单申a, 吴高荣a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-07-31
基金资助:
Hong Zhaoguoa, Xiao Shunlib, Yang Kaia, Xia Jiataoa, Liu Xingwanga, Shan Shena, Wu Gaoronga,*( )
)
Received:2025-06-25
Published:2025-07-31
Contact:
*E-mail: gaorongwu09@163.com
About author:Supported by:文章分享
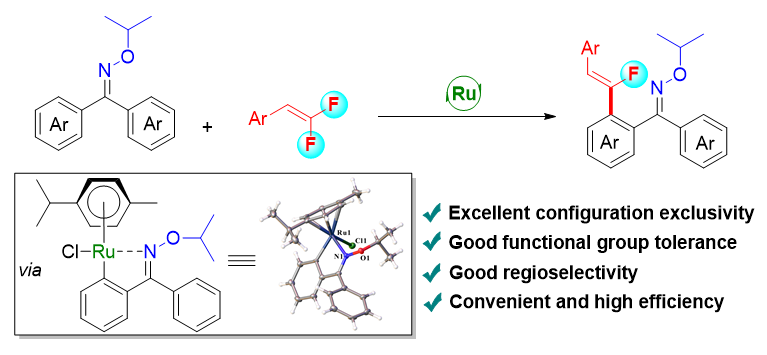
在元素周期表的众多成员中, 氟元素因其极小的体积和强电负性所赋予的独特理化性质, 成为了现代医药化工中不可或缺的“魔法元素”, 向有机小分子中引入单氟烯烃可为含氟先导化合物的开发奠定基础. 目前, 通过定位基导向过渡金属催化的C—H键活化已成为引入单氟烯烃的高效策略, 然而, 作为结构简单且易于安装的强效导向基团, 肟醚导向的C—H键单氟烯基化研究却较为罕见. 基于上述背景, 本工作报道了一种钌(II)催化二苯甲酮肟醚类化合物的Z-选择性C—H键单氟烯基化新方法. 该方法展现出优异的官能团兼容性、立体构型选择性、区域选择性, 在简便的条件下以中等至优异的产率获得目标产物. 此外, 该方法可实现克级规模合成. 进一步地, 本工作成功合成了关键五元钌环中间体, 并分别通过X-单晶衍射分析和相关验证实验明确了其结构及作用, 阐明了反应机理.
洪朝国, 肖顺丽, 杨凯, 夏家涛, 刘兴旺, 单申, 吴高荣. 钌(II)催化二苯甲酮肟醚的Z-选择性C−H键单氟烯基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(11): 1349-1355.
Hong Zhaoguo, Xiao Shunli, Yang Kai, Xia Jiatao, Liu Xingwang, Shan Shen, Wu Gaorong. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed Z-Selective C−H Monofluoroalkenylation of Benzophenone Oximes[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(11): 1349-1355.
| Entry | Catalyst | Base | Solvent | Yieldb/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Ca(OH)2 | HFIP | 81 |
| 2 | [Cp*RhCl2]2 | Ca(OH)2 | HFIP | 0 |
| 3 | Pd(OAc)2 | Ca(OH)2 | HFIP | 0 |
| 4 | Cu(OAc)2 | Ca(OH)2 | HFIP | 0 |
| 5 | — | Ca(OH)2 | HFIP | 0 |
| 6 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | CsOAc | HFIP | 29 |
| 7 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 90 |
| 8 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | DBU | HFIP | 0 |
| 9 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | pyridine | HFIP | 0 |
| 10 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | — | HFIP | 0 |
| 11 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | TFE | 34 |
| 12 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | MeOH | 0 |
| 13 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | THF | 0 |
| 14c | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 16 |
| 15d | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 77 |
| 16e | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 84 |
| 17f | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 79 |
| 18g | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 89 |
| 19h | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 46 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Base | Solvent | Yieldb/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Ca(OH)2 | HFIP | 81 |
| 2 | [Cp*RhCl2]2 | Ca(OH)2 | HFIP | 0 |
| 3 | Pd(OAc)2 | Ca(OH)2 | HFIP | 0 |
| 4 | Cu(OAc)2 | Ca(OH)2 | HFIP | 0 |
| 5 | — | Ca(OH)2 | HFIP | 0 |
| 6 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | CsOAc | HFIP | 29 |
| 7 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 90 |
| 8 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | DBU | HFIP | 0 |
| 9 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | pyridine | HFIP | 0 |
| 10 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | — | HFIP | 0 |
| 11 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | TFE | 34 |
| 12 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | MeOH | 0 |
| 13 | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | THF | 0 |
| 14c | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 16 |
| 15d | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 77 |
| 16e | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 84 |
| 17f | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 79 |
| 18g | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 89 |
| 19h | [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | Cs2CO3 | HFIP | 46 |
| [1] |
(a)
doi: 10.1126/science.1131943 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/jm800219f |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1039/B610213C |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.6023/A2024E001 |
|
|
(胡金波, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 103).
doi: 10.6023/A2024E001 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.6023/A23080373 |
|
|
(王成强, 冯超, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 160);
doi: 10.6023/A23080373 |
|
|
(f)
doi: 10.6023/A23080387 |
|
|
(易敬霖, 陈茂, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 126).
doi: 10.6023/A23080387 |
|
|
(g)
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v42.18 |
|
| [2] |
(a)
doi: 10.1039/c0cs00201a pmid: 23403084 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1002/anie.200802223 pmid: 23403084 |
|
|
(c)
pmid: 23403084 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1021/jm0495982 pmid: 23403084 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.01.057 pmid: 23403084 |
|
| [3] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00032 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202108006 |
|
|
(常哲, 王佳鑫, 陆熹, 傅尧, 有机化学, 2022, 42, 147).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202108006 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202200015 |
|
|
(叶诚, 龚和贵, 有机化学, 2022, 42, 915).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202200015 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202200017 |
|
|
(陈健强, 吴劼, 有机化学, 2022, 42, 921).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202200017 |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1038/ncomms8472 |
| [5] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03203 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1002/chem.v23.50 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b01208 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1039/C7CC04131D |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1039/C8QO00297E |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b00118 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1039/C8QO00947C |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1039/C7CC06048C |
| [9] |
(a)
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2025.134634 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/ja062856v |
|
|
(c)
|
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c03387 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b01524 |
|
|
(f)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01901 |
|
|
(g)
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.41 |
|
|
(h)
doi: 10.1126/science.abb2559 |
|
|
(i)
doi: 10.1038/s41557-022-00971-8 |
|
|
(j)
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c07506 |
|
|
(k)
doi: 10.15227/orgsyn.102.0236 |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c01842 pmid: 32885652 |
| [11] |
(a)
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.03.040 pmid: 27027818 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b03129 pmid: 27027818 |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.3c04123 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1002/adsc.v360.5 |
| [1] | 蔡海婷, 李丹丹, 刘姿, 王官武. 钯催化下肟醚导向的sp2 C—H键邻位酰氧化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(05): 717-721. |
| [2] | 陈亮,姚建华,袁莉萍,曹瑾,黄迎,谢微倪长春,沈宙,栗秀丽,张一宾. 苯乙酮肟醚类化合物的合成及基于定量构效关系研究的分子设计[J]. 化学学报, 2007, 65(22): 2583-2591. |
| [3] | 牟其明,赵志明,陈淑华. 芳杂环类多重氢键分子钳人工受体对中性分子的识别性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2002, 60(10): 1841-1845. |
| [4] | 孙守恒,孟庆金,朱丹红,姚亦明,朱慧珍,游效曾. ArCCo~3(CO)~9~-~nL~n的化学ETC合成及其电化学研究[J]. 化学学报, 1992, 50(5): 444-448. |
| [5] | 郑国康,周效贤,王立峰,蔡晔,刘平. 气液色谱法研究醇类在芳烃中的缔合溶液热力学[J]. 化学学报, 1992, 50(1): 5-10. |
| [6] | 方培基,王尔鉴. 二苯酮在功能胶束中的光还原反应的研究[J]. 化学学报, 1991, 49(3): 303-307. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||