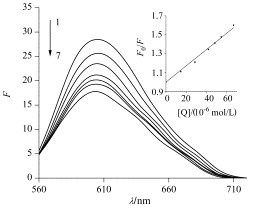
The interaction between luteolin-7-O-glucoside and duplex DNA was investigated by ESI-MS, ultraviolet and fluorescence spectroscopy in conjunction with fluorescent probe ethidium bromide (EB). We synthetized a critical sequence of GC-rich human survivin promoter DNA for ESI-MS investigation. The stock solutions of DNA and the drug for MS analysis were diluted with methanol/20 mmol/L ammonium acetate (20:80, V/V) solvent, giving a final concentration of DNA of 5 and 20 μmol/L for luteolin-7-O-glucoside. In negative ion mode, we found the duplex DNA/drug complex as well as complex of single-strand oligodeoxynucleotide/luteolin-7-O-glucoside in ESI-MS spectrum. At the same time, it can be seen that the flavonoid shows 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3 binding stoichiometries. In positive ion mode, only 1:1 complex was observed from the spectrum. This suggests that the complex between the drug and the duplex has hydrogen bond interaction. The spectra of tandem mass spectrometry reveal that the 5- charged 1:1 complex underwent the predominant loss G base and a little of losing a neutral drug. Moreover, for 6- charged 1:1 complex of duplex and luteolin-7-O-glucoside, its fragmentation pathway is loss of a 1-charged drug yielding a 5- charged DNA ion. The results of MS/MS data demonstrate that luteolin-7-O-glucoside is an intercalator. UV data were measured by addition of ct-DNA (80 μmol/L) to Lug (20 μmol/L)-20 mmol/L ammonium acetate solution. The result shows obvious hypochromic and red shift effect, indicating that the compound may be inserted between the pairs of the DNA helix bases. The fluorescence experiments were obtained by the drug (final concentrations: 0—66.66 μmol/L) titrating certain EB-DNA system (c(EB)=3 μmol/L, c(ct-DNA)=9.78 μmol/L) in 20 mmol/L ammonium acetate solvent. The emission spectra were recorded at an excitation wavelength of 520 nm. The results show that luteolin-7-O-glucoside can quench the fluorescence of EB-DNA system, and the wavelength of EB-DNA hypsochromic shift. The quenching of luteolin-7-O-glucoside on the fluorescence of EB-DNA is a static quenching process, quenching constant Kq=8.61×1011 L·mol-1·s-1. This reveals that luteolin-7-O-glucoside has only one mode to interact with duplex DNA. Based on the above mentioned experimental results, we can conclude that luteolin-7-O-glucoside is an intercalator. These results are expected to provide a basis to understand the DNA-binding properties of flavonoids and useful information for development of new efficient duplex DNA ligands.
[1] Kelly, E. H.; Anthony, R. T.; Dennis, J. B. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 572.
[2] Vitorino, J.; Sottomayor, M. J. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 975, 292.
[3] Hu, C.; Kitts, D. D. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 52, 301.
[4] Hu, C.; Kitts, D. D. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 265, 107.
[5] Spencer, J. P. E.; Chowrimootoo, G.; Choudhury, R.; Debnam, E. S.; Srai, S. K.; Rice-Evans, C. FEBS Lett. 1999, 485, 224.
[6] Baskar, A. A.; Ignacimuthu, S.; Michael, G. P.; AlNumair, K. S. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 130.
[7] Zhang, Q.; Feng, W.-J.; Li, X.-D. J. Pharmaceut. Univ. 2010, 41, 555. (张强, 冯文军, 李晓冬, 中国医科大学学报, 2010, 41, 555.)
[8] Mello, L. D.; Pereira, R. M. S.; Sawaya, A. C. H. F.; Eberlin, M. N.; Kubota, L. T. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 706.
[9] Wang, L.-F.; Song, Y.-M.; Feng, Y.-F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2004, 62, 2277. (王流芳, 宋玉民, 冯亚非, 张歧, 王印月, 化学学报, 2004, 62, 2277.)
[10] Wang, Z. F.; Cui, M.; Song, F. R.; Lu, L.; Liu, Z. Q.; Liu, S. Y. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 19, 914.
[11] Nafisi, S.; Hashemi, M.; Rajabi, M.; Tajmir-Riahi, H. A. DNA Cell Biol. 2008, 27, 433.
[12] Qu, L.-B.; Zhao, J.-H.; Li, J.-J.; Yang, R. J. Instrument. Anal. 2008, 27, 79. (屈凌波, 赵俊宏, 李建军, 杨冉, 分析测试学报, 2008, 27, 79.)
[13] Wan, C. H.; Cui, M.; Song, F. R.; Liu, Z. Q.; Liu, S. Y. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 283, 48.
[14] Li, H.-H.; Han, D.-W.; Yuan, G. Acta Chim. Sinica 2007, 65, 1543. (李卉卉, 韩德伟, 袁谷, 化学学报, 2007, 65, 1543.)
[15] Zhao, L.; Wu, B.-Y.; Gao, L.-H.; Wang, K.-Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2006, 64, 1402. (赵琳, 吴宝燕, 高丽华, 王科志, 化学学报, 2006, 64, 1402.)
[16] Wang, Z. F.; Guo, X. H.; Liu, Z. Q.; Cui, M.; Song, F. R.; Liu, S. Y. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 327.
[17] Keller, K. M.; Zhang, J. M.; Oehlers, L.; Brodbelt, J. S. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 40, 1362.
[18] Long, E. C.; Barton, J. K. Acc. Chem. Res. 1990, 23, 271.
[19] Animesh, P.; Sandipan, S.; Titas, M.; Ennio, Z.; Pabitra, C. Polyhedron 2011, 30, 2783.



