

分子印迹电化学传感器选择性识别及电催化检测多巴胺
收稿日期: 2012-12-28
网络出版日期: 2013-03-26
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(No. 21165007)和广西自然科学基金(No. 2012GXNSFAA053032)资助.
A Molecular Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor For Selectively and Electro-catalytically Voltammetric Determination of Dopamine
Received date: 2012-12-28
Online published: 2013-03-26
Supported by
Project supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21165007) and Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2012GXNSFAA053032).
魏小平 , 常川 , 李建平 . 分子印迹电化学传感器选择性识别及电催化检测多巴胺[J]. 化学学报, 2013 , 71(06) : 951 -956 . DOI: 10.6023/A12121087
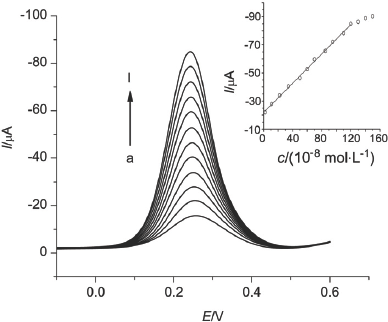
A novel strategy for improving the sensitivity of molecular imprinted electrochemical sensor was proposed and dopamine (DA) was selected as the template molecular in this assay. The electroactive membrane of poly-bromophenol blue (BB) which was polymerized on the electrode surface acted as molecular imprinted membrane of DA. To prepare poly-BB-DA molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP), CV scans were performed for 30 cycles in the potential range between -1.0 and 1.8 V at 50 mV/s in an acetate buffer solution (pH=4.0) containing 1.0×10-3 mol/L DA and 3.0×10-3 mol/L BB at 25 ℃. The MIP electrode was washed by methanol (50% in volume) for 12 min to remove template molecules. Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) was performed after the rebinding reaction of the DA and the MIP membrane in DA sample solutions for 6 min. With the increasing of the DA concentration, the binding sites in the membrane taken by DA molecules also increased, so was the peak current in the DPV analysis. The sensitivity was improved significantly due to the signal amplifying effect produced by the catalytic effect of electro oxidation of dopamine on BB membrane. The experimental conditions were also optimized. Electrochemical measurements for the MIP membrane characterization were carried out in the supporting electrolyte of 0.01 mol/L K3[Fe(CN)6] solution containing 0.5 mol/L KCl. CV was performed from -0.2 to 0.6 V at a scan rate of 100 mV/s. DPV was performed in the supporting electrolyte of 0.1 mol/L PBS (pH 7.4) over a potential range of -0.1 to 0.6 V, with the pulse amplitude of 50 mV and the scan rate of 50 mV/s. All measurements were carried out at room temperature (25 ℃). DA was determined by DPV, and there was a linear relationship between oxidation currents and DA concentrations in the range of 0~1.2×10-6 mol/L with a detection limit of 1.62×10-10 mol/L. This is one of the most sensitive sensors for DA determination due to the catalytic oxidation of DA on electroactive MIP.
Key words: molecular imprint; electro-catalysis; dopamine; sensor; poly-bromophenol blue
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |