

基于硅量子点电子转移荧光淬灭的2,4,6-三硝基甲苯/2,4,6-三硝基苯酚检测新方法
收稿日期: 2014-03-20
网络出版日期: 2014-04-25
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(Nos. 21025521,21221003)和中央高校基本科研业务费(No. 531107040687)资助.
A Novel Approach to Detect 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene/2,4,6-trinitrophenol Based on Fluorescence Quenching via Charge Transfer of Silicon Quantum Dots
Received date: 2014-03-20
Online published: 2014-04-25
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21025521, 21221003) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central University (No. 531107040687).
李西平 , 刘斯佳 , 吴战 , 蒋健晖 . 基于硅量子点电子转移荧光淬灭的2,4,6-三硝基甲苯/2,4,6-三硝基苯酚检测新方法[J]. 化学学报, 2014 , 72(5) : 563 -568 . DOI: 10.6023/A14030201
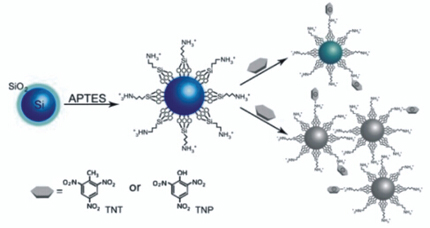
Due to the significant detrimental effects of nitroaromatic explosive on the environment and human health, sensitive, rapid, on-site and simple detection methods for explosives are in high demand. A novel label-free silicon quantum dots (SiQDs)-based sensor is designed for ultrasensitive detection of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) and 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP). In this work, amino-functionalized SiQDs are obtained through treating the SiQDs with (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES). The amine-coated SiQDs are not only water-stable but also highly luminescent. Based on the dramatic and selective fluorescence quenching of the amine-coated SiQDs due to charge transfer that resulting from the formation of stable Meisenheimer complexes between electron-deficient TNT/TNP and electron-rich primary amine on the surface of SiQDs, an instant and sensitive sensor is developed for the detection of TNT/TNP which is able to not only directly suppress the fluorescent emission intensity of SiQDs but also induce SiQDs aggregation to result in self-quenching of SiQDs. The results reveal that the developed sensor has high sensitivity for the detection of TNT/TNP. As indicated in experimental results, the fluorescence intensity is proportional to the concentration of TNT/TNP. Meanwhile, linear correlations are obtained respectively for the fluorescence signals to the logarithmic TNT and TNP concentration with 6 and 7 order of range and the detection limit of TNT and TNP is 50 pg/mL for TNT and 5 pg/mL for TNP. Further experiments demonstrate that this analytical method is not susceptible to pH and prevent interference from other nitroaromatics or cationic ions. This simple and cost-effective sensor can be used to detect ultra-trace TNT/TNP in groundwater or seawater. Additionally, this sensor strategy may provide a convenient, rapid, highly sensitive and selective assay platform for nitroaromatic explosive.
[1] Shriver-Lake, L. C.; Donner, B. L.; Ligler, F. S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31(3), 837.
[2] Kim, T. H.; Lee, B. Y.; Jaworski, J.; Yokoyama, K.; Chung, W. -J.; Wang, E.; Hong, S.; Majumdar, A.; Lee, S.-W. ACS Nano 2011, 5(4), 2824.
[3] Toxicological Profile for 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene, U. S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, 1995.
[4] Charles, P. T.; Adams, A. A.; Howell, P. B. Jr.; Trammell, S. A.; Deschamps, J. R.; Kusterbeck, A. W. Sensors 2010, 10(1), 876.
[5] Du, H. Y.; Ding, L. P.; Fang, Y. Chem. Online 2011, 74, 881. (杜海英, 丁立平, 房喻, 化学通报, 2011, 74, 881.)
[6] Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.; Zahedi, M. M.; Pourmortazavi, S. M.; Heydari, R.; Rai, H.; Jazayeri, J.; Javidan, A. Microchim. Acta 2012, 177(1~2), 145.
[7] Berg, M.; Bolotin, J.; Hofstetter, T. B. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79(6), 2386.
[8] Dasary, S. S. R.; Singh, A. K.; Senapati, D.; Yu, H. T.; Ray, P. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131(38), 13806.
[9] Zhang, C. L.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z. L.; Han, D. J. Spectroscopy Spect. Anal. 2012, 32(3), 686. (张春玲, 李喆, 吴正龙, 韩德俊, 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32, 686.)
[10] Guerra-Diaz, P.; Gura, S.; Almirall, J. R. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82(7), 2826.
[11] Jiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, N. N.; Lin, Y. Q.; Yu, P.; Mao, L. Q. Angew. Chem. 2008, 120(45), 8729.
[12] Ma, Y. X.; Li, H.; Peng, S.; Wang, L. Y. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84(19), 8415.
[13] Kartha, K. K.; Babu, S. S.; Srinivasan, S.; Ajayaghosh, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134(10), 4834.
[14] Zhang, K.; Zhou, H. B.; Mei, Q. S.; Guan, G. J.; Liu, R. Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133(22), 8424.
[15] Goldman, E. R.; Medintz, I. L.; Whitley, J. L.; Hayhurst, A.; Clapp, A. R.; Uyeda, H. T.; Deschamps, J. R.; Lassman, M. E.; Mattoussi, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127(18), 6744.
[16] Erogbogbo, F.; Yong, K.-T.; Roy, I.; Hu, R.; Law, W.-C.; Zhao, W. W.; Ding, H.; Wu, F.; Kumar, R.; Swihart, M. T.; Prasad, P. N. ACS Nano 2011, 5(1), 413.
[17] He, Y.; Fan, C. H.; Lee, S.-T. Nano Today 2010, 5(4), 282.
[18] Jurbergs, D.; Rogojina, E.; Mangolini, L.; Kortshagen, U. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 233116.
[19] Warner, J. H.; Hoshino, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Tilley, R. D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44(29), 4550.
[20] He, Y.; Kang, Z. H.; Li, Q. S.; Tsang, C. H. A.; Fan, C. H.; Lee, S. T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48(1), 128.
[21] Xie, C. G.; Liu, B. H.; Wang, Z. Y.; Gao, D. M.; Guan, G. J.; Zhang, Z. P. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80(2), 437.
[22] Gao, D. M.; Zhang, Z. P.; Wu, M. H.; Xie, C. G.; Guan, G. J.; Wang, D. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129(25), 7859.
[23] Gao, D. M.; Wang, Z. Y.; Liu, B. H.; Ni, L.; Wu, M. H.; Zhang, Z. P. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80(22), 8545.
[24] Xu, S. F.; Lu, H. Z.; Li, J. H.; Song, X. L.; Wang, A. X.; Chen, L. X.; Han, S. B. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5(16), 8146.
[25] Kang, Z. H.; Liu, Y.; Tsang, C. H. A.; Ma, D. D. D.; Fan, X.; Wong, N. B.; Lee, S. T. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21(6), 661.
[26] Aptekar, J. W.; Cassidy, M. C.; Johnson, A. C.; Barton, R. A.; Lee, M. Y.; Ogier, A. C.; Vo, C.; Anahtar, M. N.; Ren, Y.; Bhatia, S. N.; Ramanathan, C.; Cory, D. G.; Hill, A. L.; Mair, R. W.; Rosen, M. S.; Walsworth, R. L.; Marcus1, C. M. ACS Nano 2009, 3(12), 4003.
[27] Cullis, A. G.; Canham, L. T. Nature 1991, 353, 335.
Sohn, H.; Calhoun, R. M.; Sailor, M. J.; Trogler, W. C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001, 40(11), 2104.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |