

手性膦烯配体在铑催化的芳基硼酸对β-芳基-α,β-不饱和磺酸酯不对称共轭加成反应中的应用
收稿日期: 2014-06-04
网络出版日期: 2014-06-26
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(No.21325209)、上海市科委(No.14XD1404400)资助.
Chiral Phosphite-Olefin Ligands:Application in Rh-Catalyzed Asymmetric 1,4-Addition of Arylboronic Acids to β-Aryl-α,β-unsaturated Sulfonates
Received date: 2014-06-04
Online published: 2014-06-26
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21325209), the Shanghai Municipal Committee of Science and Technology (No. 14XD1404400).
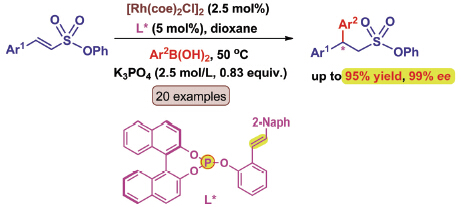
报道了手性膦烯配体在金属铑催化的芳基硼酸对β-芳基-α,β-不饱和磺酸酯不对称共轭加成中的应用. 经过系统的反应条件筛选和配体结构优化,发现含手性1,1'-联-2-萘酚骨架的膦烯配体L7与Rh(I)形成的催化剂可以高对映选择性地实现β-芳基-α,β-不饱和磺酸酯化合物的不对称1,4-加成反应. 此反应体系条件温和,底物普适性广,并取得了较高的收率(up to 95%)和优秀的对映选择性(up to 99% ee),为合成手性偕二芳基取代的磺酸酯类化合物提供了一种新方法.
关键词: 不对称催化; 膦烯配体; α,β-不饱和磺酸酯; 1,4-加成; 手性偕二芳基化合物
于月娜 , 徐明华 . 手性膦烯配体在铑催化的芳基硼酸对β-芳基-α,β-不饱和磺酸酯不对称共轭加成反应中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2014 , 72(7) : 815 -819 . DOI: 10.6023/A14060436
Chiral sulfonyl compounds have great versatility in organic synthesis, and they are also important as biologically active substances in medicinal chemistry. Among various methods developed for their synthesis, rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric 1,4-addition of arylboronic acids to α,β-unsaturated sulfonyl compounds represents one of the most practical methods due to the stability and availability of the boronic acid used as a nucleophile. Although several Rh(I) complexes of bidentate ligands have been discovered for asymmetric conjugation addition of α,β-unsaturated sulfonyl compounds, some challenging issues still remain in terms of efficiency, enantioselectivity and substrate scope. Therefore, the development of an efficient catalytic system for the synthesis of chiral sulfonyl compounds is an important goal in extending the current methodology. Here, a general and mild method for the rhodium-catalyzed enantioselective catalytic conjugate addition of arylboronic acids to β-aryl-α,β-unsaturated sulfonate is described. The success of the process relies on the use of extraordinary simple chiral phosphite-olefin ligands as bidentate ligands which offer notable synthetic and economic advantages. Optimum reaction condition was determined to run the reaction at 50 ℃ using dioxane as the solvent, in the presence of 2.5 mol% of [Rh(coe)2Cl]2 and 5 mol% of chiral P/olefin ligand L7. This Rh(I) catalyst containing chiral P/olefin ligand has a broad substrate scope, a wide range of arylboronic acids with varying electronic and steric demands were successfully examined with α,β-unsaturated sulfonate (1). Notably, all transformations proceed efficiently to give the desired products in good yields (84%~95%) and excellent selectivities (92%~99% ee). The electronic properties of the arylboronic acids did not appear to affect the reactivity of the reaction. Besides, α,β-unsaturated sulfonate 1 with either an electron-donating or electron-withdrawing group on any aromatic carbon readily underwent the asymmetric arylation with arylboronic acids, affording chiral sulfonates in high yields and enantioselectivities. The current reaction provides a practical approach to the synthesis of diverse highly enantioenriched gem-diaryl substituted sulfonates.

[1] (a) Perlmutter, P. Conjugate Addition Reactions in Organic Synthesis;Tetrahedron Organic Chemistry Series 9, Pergamon Press, Oxford, U. K., 1992.
(b) Rossiter, B. E.; Swingle, N. M. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 771.
(c) Zhang, Z.; Xie, F.; Yang, B.; Yu, H.; Zhang, W. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 31, 429. (张振锋, 谢芳, 杨波, 余焓, 张万斌, 有机化学, 2011, 31, 429.)
(d) Ying, A.; Wu, C.; Fu, Y.; Ren, S.; Liang, H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 32, 1587. (应安国, 武承林, 付永前, 任世斌, 梁华定, 有机化学, 2012, 32, 1587.)
[2] For reviews, see: (a) Tomioka, K.; Nagaoka, Y. Comprehensive Asymmetric Catalysis, Eds.: Jacobsen, E. N.; Pfaltz, A.; Yamamoto, H., Springer, New York, 1999, p. 1105
(b) Feringa, B. L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 346.
(c) Krause, N.; Hoffmann-Röder, A. Synthesis 2001, 2, 171.
(d) Feringa, B. L.; Naasz, R.; Imbos, R.; Arnold, L. A. In Modern Organocopper Chemistry, Ed.: Krause, N., VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2002, p. 224.
(e) Alexakis, A.; Benhaim, C. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 3221.
(f) Hayashi, T.; Yamasaki, K. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2829.
(g) Woodward, S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5560.
(h) López, F.; Minnaard, A. J.; Feringa, B. L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 179.
(i) López, F.; Minnaard, A. J.; Feringa, B. L. In The Chemistry of Organomagnesium Compounds, Eds.: Rappoport, Z.; Marek, I., Wiley, Chichester, U. K., 2008; Part 2, Chapter 17.
(j) Harutyunyan, S. R.; den Hartog, T.; Geurts, K.; Minaard, A. J.; Feringa, B. L. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2824.
[3] For reviews, see: (a) Tian, P.; Dong, H.-Q.; Lin, G.-Q. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 95.
(b) Partyka, D. V. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1529.
(c) Berthon, G.; Hayashi, T. In Catalytic Asymmetric Conjugate Reactions, Ed.: Córdova, A., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2010, Chapter 1, p. 1.
(d) Edwards, H. J.; Hargrave, J. D.; Penrose, S. D.; Frost, C. G. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2093.
(e) Johnson, J. B.; Rovis, T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 840.
(f) Darses, S.; Genet, J.-P. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 4313.
(g) Hayashi, T.; Yamasaki, K. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2829.
(h) Fagnou, K.; Lautens, M. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 169.
(i) Bolm, C.; Hildebrand, J. P.; Muñiz, K.; Hermanns, N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 3284.
(j) Christoffers, J.; Koripelly, G.; Rosiak, A.; Rössle, M. Synthesis 2007, 1279.
(k) Enders, D.; Lüttgen, K.; Narine, A. A. Synthesis 2007, 959.
(l) Hayashi, T. Synlett 2001, 879.
(m) Hayashi, T.; Yamasaki, K. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2829.
(n) Shintani, R.; Tokunaga, N.; Doi, H.; Hayashi, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 6240.
[4] Takaya, Y.; Ogasawara, M.; Hayashi, T.; Sakai, M.; Miyaura, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 5579.
[5] Early studies of α,β-unsaturated ketones, see: (a) Reetz, M. T.; Moulin, D.; Gosberb, A. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 4083.
(b) Kuriyama, M.; Nagai, K.; Yamada, K.-i.; Miwa, Y.; Taga, T.; Tomioka, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8932.
(c) Boiteau, J. G.; Imbos, R.; Minnaard, A. J.; Feringa, B. L. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 681.
(d) Iguchi, Y.; Itooka, R.; Miyaura, N. Synlett 2003, 1040.
(e) Defieber, C.; Paquin, J.-F.; Serna, S.; Carreira, E. M. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 3873.
[6] α,β-Unsaturated Esters, Amides, and Aldehydes: (a) Takaya, Y.; Senda, T.; Kurushima, H.; Ogasawara, M.; Hayashi, T. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1999, 10, 4047.
(b) Sakuma, S.; Sakai, M.; Itooka, R.; Miyaura, N. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 5951.
(c) Senda, T.; Ogasawara, M.; Hayashi, T. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 6852.
(d) Sakuma, S.; Miyaura, N. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 8944.
(e) Paquin, J.-F.; Defieber, C.; Stephenson, C. R. J.; Carreira, E. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10850.
[7] Alkenylphosphonates: Hayashi, T.; Senda, T.; Takaya, Y.; Ogasawara, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 11591.
[8] Nitroalkenes: Hayashi, T.; Senda, T.; Ogasawara, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10716.
[9] Alkenylheteroarenes and alkenylarenes: (a) Pattison, G.; Piraux, G.; Lam, H. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14373.
(b) Saxena, A.; Lam, H. W. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 2326.
[10] For reviews, see: (a) Simpkins, N. S. Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 6951.
(b) Rayner, C. M. Contemp. Org. Synth. 1996, 3, 499.
(c) Nájera, C.; Yus, M. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 10547.
(d) Nájera, C.; Yus, M. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 10547.
(e) Bäckvall, J.-E.; Chinchilla, R.; Nájera, C.; Yus, M. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2291.
(f) Meadows, D. C.; Gervay-Hague, J. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 26, 793.
(j) Tozer, M. J.; Harper, E. A.; Kalindjian, S. B.; Pether, M. J.; Shankley, N. P.; Watt, G. F. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1825.
(h) Tamamura, H.; Koh, Y.; Ueda, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Yamasaki, T.; Aoki, M.; Maeda, K.; Watai, Y.; Arikuni, H.; Otaka, A.; Mitsuya, H.; Fujii, N. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 1764.
(i) Hanessian, S.; Sailes, H.; Therrien, E. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 7047.
(j) Zajac, M.; Peters, R. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 8204.
[11] For recent examples, see: (a) Enders, D.; Müller, S. F.; Raabe, G. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 195.
(b) Grimaud, L.; Rotulo, D.; Ros-Perez, R.; Guitry-Azam, L.; Prunet, J. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 7477.
(c) Luis, L. A.; Krische, M. J. Synthesis 2004, 2579.
(d) Tsui, G. C.; Lautens, M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8938.
(e) García Ruano, J. L.; Schöpping, C.; Alvarado, C.; Alemán, J. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 8968.
(f) So, C. M.; Kume, S.; Hayashi, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10990.
(g) Lu, J.; Ye, J.; Duan, W. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 698.
[12] For examples of copper-catalyzed asymmetric transformations, see: (a) Llamas, T.; Arrayás, R. G.; Carretero, J. C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 3329.
(b) Desrosiers, J.-N.; Charette, A. B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5955.
(c) Bechara, W. S.; Charette, A. B. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2315.
(d) Bos, P. H.; Minnaard, A. J.; Feringa, B. L. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4219.
(e) Bos, P. H.; Maciá, B.; Fernández-Ibáñez, M.Á.; Minnaard, A. J.; Feringa, B. L. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 47.
[13] For a review of organocatalytic asymmetric addition to alkenyl sulfones, see: Nielsen, M.; Jacobsen, C. B.; Holub, N.; Paixão, M. W.; Jørgensen, K. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2668.
[14] (a) Mauleón, P.; Carretero, J. C. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 3195.
(b) Mauleón, P.; Carretero, J. C. Chem. Commun. 2005, 41, 4961.
(c) Mauleón, P.; Alonso, I.; Rivero, M. R.; Carretero, J. C. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 9924.
[15] Nishimura, T.; Takiguchi, Y.; Hayashi, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9086.
[16] (a) Jin, S.-S.; Wang, H.; Xu, M.-H. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7230.
(b) Qi, W.-Y.; Zhu, T.-S.; Xu, M.-H. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 3410.
(c) Jin, S.-S.; Wang, H.; Zhu, T.-S.; Xu, M.-H. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 1764.
(d) Zhu, T.-S.; Jin, S.-S.; Xu, M.-H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 780.
(e) Wang, H.; Zhu, T.-S.; Xu, M.-H. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 9158.
(f) Zhu, T.-S.; Chen, J.-P.; Xu, M.-H. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 865.
(g) Wang, H.; Jiang, T.; Xu, M.-H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 971.
(h) Wang, H.; Xu, M.-H. Synthesis 2013, 45, 2125.
(i) Li, Y.; Zhu, D.-X.; Xu, M.-H. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11659.
(j) Li, Y.; Xu, M.-H. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3771.
[17] Yu, Y.-N.; Xu, M.-H. Org. Chem. Front. 2014, DOI: 10. 1039/c4qo00135d.
[18] Selected early examples of the use of chiral phosphorus-based olefin ligands: (a) Maire, P.; Deblon, S.; Breher, F.; Geier, J.; Böhler, C.; Rügger, H.; Schönberg, H.; Grtrümacher, H. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 4198.
(b) Shintani, R.; Duan, W.-L.; Nagano, T.; Okada, A.; Grützmacher, T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4611.
(c) Defieber, C.; Ariger, M. A.; Moriel, P.; Carreira, E. M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 3139.
(d) Mariz, R.; Briceño, A.; Dorta, R.; Dorta, R. Organometallics 2008, 27, 6605.
(e) Liu, Z.; Du, H. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 3054.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |