

纳米零价铁与重金属的反应:“核-壳”结构在重金属去除中的作用
收稿日期: 2017-02-13
网络出版日期: 2017-04-12
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(Nos.21677107,51578398)资助.
Heavy Metal-nZVI Reactions: the Core-shell Structure and Applications for Heavy Metal Treatment
Received date: 2017-02-13
Online published: 2017-04-12
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21677107, 51578398).
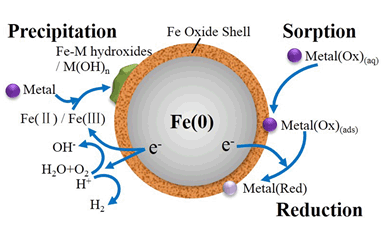
重金属是一类毒性较高、处理难度较大的环境污染物.纳米零价铁因为具有高效分离、固定重金属的潜能而受到广泛关注.其独特的纳米级核壳结构和表面性质使纳米零价铁能够通过吸附、还原和沉淀等多种作用高效去除重金属.现代仪器分析手段的进步,特别是高分辨电子显微成像技术的发展,为深入研究纳米零价铁的微观结构以及纳米零价铁与重金属的作用机理开辟了新的视角.本文重点讨论了纳米零价铁的结构、性质及其在重金属去除中的作用.研究借助高分辨率的球差校正扫描透射电镜(Cs-STEM)成像,配合高灵敏度的X射线能谱仪(XEDS)进行化学分析,旨在更好地了解纳米零价铁的精细结构及其与重金属的界面反应过程和机理.在深入理论研究的同时,通过"小试-中试-工程"逐级放大的方法,系统论证了纳米零价铁处理重金属废水的可行性.结果表明,纳米零价铁可有效、同步去除实际废水中铜、砷、铅、锌等多种重金属,并具有较高的去除负荷.
黄潇月 , 王伟 , 凌岚 , 张伟贤 . 纳米零价铁与重金属的反应:“核-壳”结构在重金属去除中的作用[J]. 化学学报, 2017 , 75(6) : 529 -537 . DOI: 10.6023/A17020051
Heavy metals are nonbiodegradable and bioaccumulative contaminants with high toxicity, thus heavy metal contamination and treatment have been hot research topics in recent years. Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) has received considerable attentions for its potential as a remedial agent for heavy metal sequestration and immobilization. In this paper, an overview is provided highlighting recent research progress on heavy metal-nZVI reactions, both laboratory studies and engineering applications are discussed. The core-shell structure with the core being metallic and the shell being iron oxides and the surface chemistry properties endow nZVI with unique and multifaceted functions for heavy metal removal including sorption, reduction and precipitation. Particle size of nZVI is in the range of nanoscale that imparts it with large specific surface area, high surface activity, and high density of reactive surface sites. A hybrid of effects, including instant separation, isolation, immobilization, and toxicity reduction can be achieved at the same time, making nZVI an effective remedial reagent for various heavy metals. Recent progress in instrumental analysis, especially the development of high-resolution electron microscopy, offers much-enhanced capability and new insights into the core-shell nature of nZVI and mechanisms of the heavy metal-nZVI reactions on a single nanoparticle. Research results obtained from a spherical aberration corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy (Cs-STEM) integrated with high sensitive X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) provide detailed information on the fine structural features of nZVI and the intraparticle reactions with individual nanoparticles. Technical feasibility and operational advantages of using nZVI for the treatment of industrial wastewater are assessed through systematic laboratory and pilot scale studies. Based on the encouraging results of bench-scale experiments, we have successfully applied nZVI for large scale applications of nZVI for treatment of industrial wastewater containing heavy metals such as Cu, As, Pb and Zn. The long-term operation results show tremendous potentials of nZVI-based process as an efficient method for heavy metal treatment.

[1] Agarwal, S. K. Heavy Metal Pollution, APH publishing, New Delhi, 2009.
[2] Asrari, E. Heavy Metal Contamination of Water and Soil:Analysis, Assessment, and Remediation Strategies, CRC Press, 2014.
[3] Fu, J. J.; Wang, Y. W.; Zhou, L. J.; Zhang, A. Q.; Jiang, G. B. Prog. Chem. 2011, 23, 1756(in Chinese). (傅建捷, 王亚韡, 周麟佳, 张爱茜, 江桂斌, 化学进展, 2011, 23, 1756.)
[4] Rodríguez-Lado, L.; Sun, G.; Berg, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, H.; Zheng, Q.; Johnson, C. A. Science 2013, 341, 866.
[5] Cullen, W. R.; Reimer, K. J. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 713.
[6] Kotas, J.; Stasicka, Z. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 107, 263.
[7] Järup, L. Brit. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167.
[8] Goyer, R.; Golub, M.; Choudhury, H.; Hughes, M.; Kenyon, E.; Stifelman, M. In US Environmental Protection Agency, Risk Assessment Forum, Vol. 1200, Washington, DC, 2004.
[9] El Samrani, A. G.; Lartiges, B. S.; Villiéras, F. Water Res. 2008, 42, 951.
[10] Matlock, M. M.; Howerton, B. S.; Atwood, D. A. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4757.
[11] Fu, F.; Wang, Q. J. Environ. Manage. 2011, 92, 407.
[12] Liu, Y.; Liang, P.; Guo, L.; Lu, H. B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2005, 63, 312(in Chinese). (刘艳, 梁沛, 郭丽, 卢汉兵, 化学学报, 2005, 63, 312.)
[13] Wan, Q. F.; Ren, Y. M.; Wang, L.; Jiang, H. Z.; Deng, D. C.; Bai, Y.; Xia, C. Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 1780(in Chinese). (万芹方, 任亚敏, 王亮, 姜海洲, 邓大超, 柏云, 夏传琴, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 1780.)
[14] Li, X. Q.; Zhang, W. X. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 6939.
[15] Yan, W. L.; Herzing, A. A.; Kiely, C. J.; Zhang, W. X. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2010, 118, 96.
[16] Li, S. L.; Wang, W.; Liang, F. P.; Zhang, W. X. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 163.
[17] Hua, M.; Zhang, S. J.; Pan, B. C.; Zhang, W. M.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Q. -X. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211, 317.
[18] Choi, C. J.; Dong, X. L.; Kim, B. K. Mater. Trans. 2001, 42, 2046.
[19] Crane, R.; Dickinson, M.; Popescu, I.; Scott, T. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2931.
[20] Glavee, G. N.; Klabunde, K. J.; Sorensen, C. M.; Hadjipanayis, G. C. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 28.
[21] Karlsson, M.; Deppert, K.; Wacaser, B.; Karlsson, L.; Malm, J. O. Appl. Phys. A 2005, 80, 1579.
[22] Kuhn, L. T.; Bojesen, A.; immermann, L.; Nielsen, M. M. J. Phys.:Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 13551.
[23] Carpenter, E.; Calvin, S.; Stroud, R.; Harris, V. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3245.
[24] Nurmi, J. T.; Tratnyek, P. G.; Sarathy, V.; Baer, D. R.; Amonette, J. E.; Pecher, K.; Wang, C.; Linehan, J. C.; Matson, D. W.; Penn, R. L. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1221.
[25] Wang, C.; Baer, D. R.; Amonette, J. E.; Engelhard, M. H.; Antony, J.; Qiang, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8824.
[26] Zhdanov, V. P.; Kasemo, B. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 452, 285.
[27] Wang, C. M.; Baer, D. R.; Thomas, L. E.; Amonette, J. E.; Antony, J.; Qiang, Y.; Duscher, G. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 094308.
[28] Wang, Q.; Kanel, S. R.; Park, H.; Ryu, A.; Choi, H. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 749.
[29] Ling, L.; Pan, B. C.; Zhang, W. X. Water Res. 2015, 71, 274.
[30] Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 209.
[31] Ling, L.; Zhang, W. X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2788.
[32] Chen, G. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 38, 11.
[33] Grosvenor, A.; Kobe, B.; McIntyre, N. Surf. Sci. 2004, 572, 217.
[34] Liu, A.; Zhang, W. X. Analyst 2014, 139, 4512.
[35] Scherer, M. M.; Balko, B. A.; Tratnyek, P. G. The Role of Oxides in Reduction Reactions at the Metal-Water Interface, ACS Symposium Series, American Chemical Society, 1998.
[36] Loyaux-Lawniczak, S.; Refait, P.; Ehrhardt, J. J.; Lecomte, P.; Génin, J. M. R. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 438.
[37] Melitas, N.; Chuffe-Moscoso, O.; Farrell, J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3948.
[38] Li, X. Q.; Zhang, W. X. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4638.
[39] Fan, H. J.; Gösele, U.; Zacharias, M. Small 2007, 3, 1660.
[40] Yin, Y.; Rioux, R. M.; Erdonmez, C. K.; Hughes, S.; Somorjai, G. A.; Alivisatos, A. P. Science 2004, 304, 711.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |