

芳香胺盐酸盐/硼烷体系催化的氢胺化/还原反应研究
收稿日期: 2017-04-06
网络出版日期: 2017-05-24
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(No.21542011)和乐山师范学院科研(Nos.Z1414,Z1308)资助项目.
Research of B(C6F5)3/Aromatic Ammonium Chloride Systems Catalyzed Hydroamination/Reduction Reaction
Received date: 2017-04-06
Online published: 2017-05-24
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21542011) and Scientific Research Fund of Leshan Normal University (Nos.Z1414,Z1308).
近年来有关受限路易斯酸碱对(FLPs)化学的研究受到了国内外的广泛关注,但有关芳香胺类FLPs的应用研究却极少涉及.本工作以硅烷作为还原剂,路易斯酸三(五氟苯基)硼(BCF)作为催化剂,用芳香胺盐酸盐代替苯胺,可一步反应实现炔烃与苯胺的催化氢胺化还原反应.研究发现,取代基较多的三乙基硅烷在反应中表现出较高的反应活性,吸电子取代基取代的端基芳炔的转化率也较给电子取代基取代的端基芳炔的转化率高.对催化反应的机理研究表明,胺盐与B(C6F5)3及硅烷反应所生成的硼氢化芳胺盐活性中间体"[Ar2NH2]+[H-B(C6F5)3]-"的产生和分解速度决定着中间产物亚胺的生成和还原.
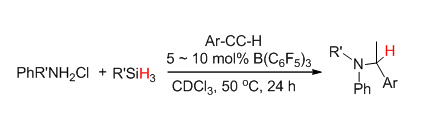
张露文 , 温志国 , Borzov Maxim , 聂万丽 . 芳香胺盐酸盐/硼烷体系催化的氢胺化/还原反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017 , 75(8) : 819 -823 . DOI: 10.6023/A17040142
Although in recent years the frustrated Lewis pairs (FLPs) reactivity towards small molecule activation has been widely concerned, the reports on the FLPs derived from aromatic amines are few. This paper describes a new method of an one-pot hydroamination/reduction reaction of terminal alkynes with aromatic amines catalyzed by the B(C6F5)3/aromatic ammonium chloride systems with a hydridosilane as a source of the hydride. We consider that the active intermediate[Ar2NH2]+[H-B(C6F5)3]- which formed by the aromatic ammonium chloride/B(C6F5)3 reaction with silanes plays a very important role on the formation and reduction of the mediate product imines. The hydroamination reaction is firstly induced by the trace amount amines produced by the dissociation of the borohydride aromatic amine salt, which then reacts with the alkynes and forms the imines. Then the borohydride intermediate[Ar2NH2]+[H-B(C6F5)3]- reduces the imines to amines. It has been proved that the borohydride intermediate[Ar2NH2]+[H-B(C6F5)3]- could successfully reduce the corresponding imines to amines in an in-situ reaction condition. However it has been found that the usually most active mono-substituted hydridosilane, such as PhSiH3 shows the poorest reactivity in this case. And the less active trisubstituted silanes such as Et3SiH or Ph3SiH exhibit the highest reactivity. To explain this abnormal phenomenon the different reaction speeds of the cascade hydroamination/reduction reaction and the dissociation of the borohydride aromatic amine salt should be concerned. Since the dissociation of[Ar2NH2]+[H-B(C6F5)3]- to H2 is comparably quicker than the hydroamination reaction. By reacting with the less active trisubstituted silanes could not only slow down the formation and dissociation of[Ar2NH2]+[H-B(C6F5)3]-, but could also let the hydroamination and reduction steps proceeded completely. Moreover by slowly adding the diluted hydrosilanes to the reaction systems could also improve the reaction. The reaction yield is affected by the substituent on the terminal alkynes, too. The alkynes with the electron withdrawn group show comparably higher reactivity than with the electron donating ones.
[1] Müller, T. E.; Hultzsch, K. C.; Yus, M.; Foubelo, F.; Tada, M. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3795.
[2] Severin, R.; Doye, S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1407.
[3] Nishina, N.; Yamamoto, Y. Top. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 43, 115.
[4] (a) Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.-R.; Yuan, D.; Yao,Y.-M.; Shen, Q. Organometallics 2014, 33, 994.
(b) Liang, S.-Z.; Hammond, L.; Xu, B.; Hammond, G. B. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358(20), 3313.
(c) Sakai, N.; Takahashi, N.; Ogiwara, Y. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 5078.
[5] Wang, J.; Cui, D.-M. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36(6), 1163(王剑, 崔冬梅, 有机化学, 2016, 36(6), 1163.)
[6] Bian, R.-J.; Bao, X.-G. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 37(1), 190(卞荣剑, 鲍晓光, 有机化学, 2017, 37(1), 190.)
[7] McCahill, J. S. J.; Welch, G. C.; Stephan, D. W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4968.
[8] Dureen, M. A.; Brown, C. C.; Stephan, D. W. Organometallics 2010, 29, 6594.
[9] Sajid, M.; Elmer, L.-M.; Rosorius, C.; Daniliuc, C. G.; Grimme, S.; Kehr, G.; Erker, G. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2243.
[10] Mçmming, C. M.; Otten, E.; Kehr, G.; Frçhlich, R.; Grimme, S.; Stephan, D. W.; Erker, G. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6643.
[11] Cardenas, A. J. P.; Culotta, B. J.; Warren, T. H.; Grimme, S.; Stute, A.; Froehlich, R.; Kehr, G.; Erker, G. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7567.
[12] Otten, E.; Neu, R. C.; Stephan, D. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9918.
[13] Sajid, M.; Klose, A.; Birkmann, B.; Liang, L.; Schirmer, B.; Wiegand, T.; Eckert, H.; Lough, A. J.; Froehlich, R.; Daniliuc, C. G.; Grimme, S.; Stephan, D. W.; Kehr, G.; Erker, G. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 213.
[14] Mahdi, T.; Stephan, D. W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12418.
[15] Mahdi, T.; Stephan, D. W. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 11134.
[16] Wen, Z.-G.; Tian, C.; Borzov, M.; Nie, W.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 498. (温志国, 田冲, Borzov Maxim, 聂万丽, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 498.)
[17] Hu, X.; Tian, C.; Borzov, M.; Nie, W.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 1025. (胡茜, 田冲, Borzov Maxim, 聂万丽, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 1025.)
[18] Nie, W.-L.; Sun, G.-F.; Tian, C.; Borzov, M. V. Z. Naturforsch. 2016, 71(10)b, 1029.
[19] Tian, C.; Jiang, Y.; Borzov, M.; Nie, W.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 1203. (田冲, 姜亚, Borzov Maxim, 聂万丽, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 1203.)
[20] Li, L.; Huang, G.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 28, 5564.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |