

基于热电材料的新型传感器研究进展
收稿日期: 2017-06-09
网络出版日期: 2017-09-04
基金资助
项目受青年千人计划、国家自然科学基金(Nos.21422507,21635002,21321003)和中国科学院资助.
Research Progress in Thermoelectric Materials for Sensor Application
Received date: 2017-06-09
Online published: 2017-09-04
Supported by
Project supported by the 1000 Young Talents Program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21422507, 21635002, 21321003) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
柳冈 , 王铁 . 基于热电材料的新型传感器研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2017 , 75(11) : 1029 -1035 . DOI: 10.6023/A17060259
Sensors are core components for modern intelligent industry. Thermoelectric materials, which have significant influence on the design and functions for a variety types of sensors, attracted more and more attentions recently. In this paper, different categories of thermoelectric materials, such as silicon, carbon, lead, tellurium, precious metal, organic and catalysis based thermoelectric materials, are discussed in detail on their high sensitivity, fast response, and stability as potential candidates for specific sensors. The silicon-based thermoelectric materials are of particular efficiency in sensor data process and transmission due to their high purity. Carbon-based thermoelectric materials, including graphene and carbon nanotubes, advantage in their excellent conductivity, flexible structure, and manufactural controllability. Lead-based thermoelectric materials are mainly used as infrared sensors because of their natural sensitivity to infrared specially. Telluride-based thermoelectric materials, especially Bismuth Telluride and Antimony Telluride, can form PN junction and be applied as soft sensors. Products based on these materials have already been developed for detecting pulses. The precious metals-based thermoelectric materials, e.g. gold or silver, are commonly used as dopant in the organic thermoelectric materials to adjust their sensitivity. Organic thermoelectric materials benefit from their good stability and variability, while copper-bismuth alloy based thermoelectric materials are widely investigated to make gas sensors. In general, the inorganic thermoelectric materials normally feature high electrical conductivity, which enhances the sensitivity of sensors, whereas the organic thermoelectric materials have high stability to maintain the stability of sensors. At present, the miniaturization of sensors is the mainstream for both material study and device fabrication. Low dimensional thermoelectric materials, especially nano-scaled materials such as quantum dots, nanowires, etc., will for sure promote the progressing of sensor development. For example, carbon nanotube can be knit into specific sheets as we designed with tunable conductivity, which makes them of remarkable industrial potentials as soft sensors. Designing and fabricating multi-functional and space-saving thermoelectric materials with well aligned and effectively assembled nanomaterials would be a feasible and practicable approach for future sensors.
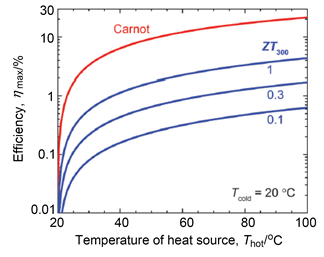
Key words: sensor; thermoelectric materials; silicon nanowire; graphene
[1] Chowdhury, I.; Prasher, R.; Lofgreen, K.; Chrysler, G.; Nara-simhan, S.; Mahajan, R.; Koester, D.; Alley, R.; Venkatasubramanian, R. Nature Nanotech. 2009, 4, 235.
[2] Li, J. F.; Liu, W.; Zhao, L. D.; Zhou, M. NPG Asia Mater. 2010, 2, 152.
[3] Rama, V.; Siivola, E.; Thomas, C.; O'Quinn, B. Nature 2001, 413, 597.
[4] Delaire, O.; Ma, J.; Marty, K.; May, A. F.; McGuire, M. A.; Du, M. H.; Singh, D. J.; Podlesnyak, A.; Ehlers, G.; Lumsden, M. D.; Sales, B. C. Nature Mater. 2011, 10, 614.
[5] Coucheron, D. A.; Fokine, M.; Patil, N.; Breiby, D. W.; Buset, O. T.; Healy, N.; Peacock, A. C.; Hawkins, T.; Jones, M.; Ballato, J.; Gibson, U. J. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13265.
[6] (a) Xie, P.; Xiong, Q.; Fang, Y.; Qing, Q.; Lieber, C. M. Nature Nanotech. 2011, 7, 119;
(b) Boukai, A. I.; Bunimovich, Y.; Ta-hir-Kheli, J.; Yu, J. K.; Goddard, W. A., 3rd; Heath, J. R. Nature 2008, 451, 168;
(c) Hochbaum, A. I.; Chen, R.; Delgado, R. D.; Liang, W.; Garnett, E. C.; Najarian, M.; Majumdar, A.; Yang, P. Nature 2008, 451, 163.
[7] Mao, J.; Liu, Z.; Ren, Z. npj Quantum Materials 2016, 1, 16028.
[8] McGrail, B. T.; Sehirlioglu, A.; Pentzer, E. Angew. Chem. 2015, 54, 1710.
[9] Kroon, R.; Mengistie, D. A.; Kiefer, D.; Hynynen, J.; Ryan, J. D.; Yu, L.; Muller, C. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6147.
[10] Wang, Z.; Leonov, V.; Fiorini, P.; Van Hoof, C. Sens. Actuators, A:Physical 2009, 156, 95.
[11] Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Feng, X.; Fan, Q.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 664. (刘兴奋, 王亚鹏, 黄艳琴, 冯晓苗, 范曲立, 黄维, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 664.)
[12] He, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Ji, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, X. Appl. Energy 2015, 143, 1.
[13] Marichy, C.; Bechelany, M.; Pinna, N. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1017.
[14] Pu, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Sun, J.; Du, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z. L. Science Advances 2017, 3, e1700015.
[15] Zhang, C.; Meng, Y.; Kuang, J.; Xu, L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 409. (张崇洋, 孟玉珠, 匡金志, 徐岚, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 409.)
[16] Qian, X.; Su, M.; Li, F.; Song, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 565. (钱鑫, 苏萌, 李风煜, 宋延林, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 565.)
[17] Zhu, W.; Deng, Y.; Cao, L. Nano Energy 2017, 34, 463.
[18] Zhang, F.; Zang, Y.; Huang, D.; Di, C. A.; Zhu, D. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8356.
[19] Wang, H.; He, Y. Sensors 2017, 17, 268.
[20] Rao, S.; Pangallo, G.; Della Corte, F. G. Sensors 2016, 16, 67.
[21] Li, W.; Feng, Z.; Dai, E.; Xu, J.; Bai, G. Sensors 2016, 16, 1880.
[22] Zhan, B.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Jenkins, G.; Huang, W.; Dong, X. Small 2014, 10, 4042.
[23] Singh, S.; Lee, S.; Kang, H.; Lee, J.; Baik, S. Energy Storage Materials 2016, 3, 55.
[24] Quan, Z.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Fang, J. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3729.
[25] Hong, M.; Chen, Z. G.; Yang, L.; Zou, J. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8681.
[26] Snyder, G. J.; Lim, J. R.; Huang, C. K.; Fleurial, J. P. Nature Mater. 2003, 2, 528.
[27] Galli, G.; Donadio, D. Nature Nanotech. 2010, 5, 701.
[28] Zhou, H.; Kropelnicki, P.; Lee, C. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 532.
[29] Jung, S. W.; Shin, J. Y.; Pi, K.; Goo, Y. S.; Cho, D. D. Sensors 2016, 16, 2035.
[30] Weiss, N. O.; Zhou, H.; Liao, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5782.
[31] Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, G. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7901.
[32] Wu, G.; Zhang, Z. G.; Li, Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, G. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5746.
[33] Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Gui, X.; Lin, Z.; Ke, X.; Hao, F.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, L. Carbon 2017, 114, 1.
[34] Ong, W.-L.; Rupich, S. M.; Talapin, D. V.; McGaughey, A. J. H.; Malen, J. A. Nature Mater. 2013, 12, 410.
[35] Lu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Mao, C.; Li, C. M. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 57.
[36] Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; Xu, F.; Duan, Y.; Yin, Z. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9881.
[37] Cao, Z.; Koukharenko, E.; Tudor, M. J.; Torah, R. N.; Beeby, S. P. Sens. Actuators A:Physical 2016, 238, 196.
[38] Yadav, A.; Pipe, K. P.; Shtein, M. J. Power Sources 2008, 175, 909.
[39] Russ, B.; Glaudell, A.; Urban, J. J.; Chabinyc, M. L.; Segalman, R. A. Nature Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16050.
[40] Bubnova, O.; Khan, Z. U.; Malti, A.; Braun, S.; Fahlman, M.; Berggren, M.; Crispin, X. Nature Mater. 2011, 10, 429.
[41] Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhu, D. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6829.
[42] Ju, H.; Kim, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 297, 66.
[43] Song, H.; Cai, K. Energy 2017, 125, 519.
[44] Kim, G. H.; Shao, L.; Zhang, K.; Pipe, K. P. Nature Mater. 2013, 12, 719-23.
[45] Park, S. C.; Yoon, S. I.; Lee, C. I.; Kim, Y. J.; Song, S. Analyst 2009, 134, 236.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |