

固态纳米孔对蛋白质易位的实验研究
收稿日期: 2017-06-16
网络出版日期: 2017-09-04
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(Nos.51375092,51435003,51675101)和中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(No.2242015R30002)资助.
Experimental Research of Protein Translocation Using Solid-state Nanopore
Received date: 2017-06-16
Online published: 2017-09-04
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51375092, 51435003 and 51675101) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2242015R30002).
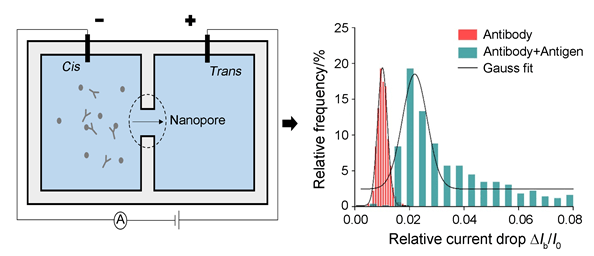
蛋白质因其多样性和功能性,是生物体内一类非常重要的分子.通常蛋白质的表征需要借助荧光或者酶的标记.而纳米孔技术,得益于免标记、单分子检测等优势,为蛋白质的表征提供了新方向.我们使用固态纳米孔完成了单个蛋白质分子及蛋白质-蛋白质结合物的检测.可以发现,外部电压和电解质溶液的酸碱度会直接影响蛋白质分子表面带电量,从而加快或延迟其在孔内的易位时间.抗原、抗体本质上都是蛋白质,两者之间具有高度特异性.通过比较抗体溶液在添加特异性抗原前后的易位事件,实现了单个蛋白质分子和蛋白质-蛋白质结合物的区分.未来,纳米孔技术有望应用于多蛋白质分子的辨识、蛋白质分子相互作用机制等方面的研究.
关键词: 牛血清蛋白(BSA); 抗原; 抗体; 固态纳米孔; 单分子检测
沙菁? , 徐冰 , 陈云飞 , 杨颜菁 . 固态纳米孔对蛋白质易位的实验研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017 , 75(11) : 1121 -1125 . DOI: 10.6023/A17060271
For proteins' diverse range of structural and functional features, they are important populations of biomolecules within organisms. Common methods to detect proteins are with the help of fluorescence or enzyme. Due to the advantages like lable-free and single-molecule detection, nanopore technology provides a novel platform for proteins' characterization. In this experiment, the patch clamp amplifier is used to apply the voltage and acquire the tiny current blockage. The Si3N4 membrane drilled with a nanopore separated the buffer solution into two sides:cis and trans. When the voltage applied into the buffer solution, charged proteins would been driven through the pore from one side to the other. Then, a series of current blockages could be obtained. By analysing these data, the size and conformation of the biomolecules could be acquired. In this paper, we using solid-state nanopore detected single protein and protein-protein complexes. The nanopore was characterized firstly. Then, both the applied voltage and the pH of the electrolyte solution were regulated. Under the low voltage, the sample proteins could be regarded as a rigid spheroid, and the dwell time is decreased with the voltage increasing. It was found that, the charges carried by proteins could be improved by higher pH of buffer solution, so that the dwell time would been shortened. Furthermore, based on the high specific between the antigen and antibody which are proteins, the translocation events before and after the addition of specific antigen into the solution with antibody were compared. Results showed that the relative current drop of the complex is larger than the pure antibody, implying that the antigen has been bound into the antibody. Due to the difference of excluded volume, the antibody and antigen-antibody complexes could be distinguished by the solid-state nanopore. In the future, the nanopore technology is promising to be applied into the recognition of multiply proteins and protein-protein interaction.

[1] Wang, J.-Y. Biochemistry 1, Higher Education Press, Beijing, 2002, pp. 123~124. (王镜岩, 生物化学, 上册, 高等教育出版社, 北京, 2002, pp. 123~124.)
[2] Li, C.-Y. Basic Immunology, Science Press, Beijing, 2012, pp. 35~39(in Chinese). (李春艳, 免疫学基础, 科学出版社, 北京, 2012, pp. 35~39.)
[3] Waduge, P.; Hu, R.; Bandarkar, P.; Yamazaki, H.; Cressiot, B.; Zhao, Q.; Whitford, P. C.; Wanunu, M. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5706.
[4] Zhang, J.-Y.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Zhou, M.; Jia, H.-X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 513(in Chinese). (张佳玉, 周晓毓, 周曼, 贾红霞, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 513.)
[5] Deamer, D.; Akeson, M.; Branton, D. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 518.
[6] Dekker, C. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 209.
[7] Howorka, S.; Cheley, S.; Bayley, H. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 636.
[8] Meller, A.; Nivon, L.; Branton, D. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 3435.
[9] Nakane, J. J.; Akeson, M.; Marziali, A. J. Phys.-Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 1365.
[10] Storm, A. J.; Storm, C.; Chen, J. H.; Zandbergen, H.; Joanny, J. F.; Dekker, C. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1193.
[11] Ying, Y. L.; Cao, C.; Long, Y. T. Analyst 2014, 139, 3826.
[12] Oukhaled, A.; Bacri, L.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.; Betton, J. M.; Pelta, J. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1935.
[13] Kasianowicz, J. J.; Brandin, E.; Branton, D.; Deamer, D. W. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1996, 93, 13770.
[14] Wendell, D.; Jing, P.; Geng, J.; Subramaniam, V.; Lee, T. J.; Montemagno, C.; Guo, P. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 765.
[15] Cao, C.; Liao, D.-F.; Ying, Y.-L.; Long, Y.-T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 734(in Chinese). (曹婵, 廖冬芳, 应佚伦, 龙亿涛, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 734.)
[16] Ma, J.; Qiu, Y. H.; Yuan, Z. S.; Zhang, Y.; Sha, J. J.; Liu, L.; Sun, L. T.; Ni, Z. H.; Yi, H.; Li, D. Y.; Chen, Y. F. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 022719.
[17] Wang, Y.; Yu, X.-F.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Xie, X.; Cheng, X.-L.; Huang, S.-M.; Wang, Z.-M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 378(in Chinese). (王跃, 余旭丰, 刘芸芸, 谢骁, 程秀兰, 黄少铭, 王志民, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 378.)
[18] Jiang, Y.-N.; Guo, W. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 491.
[19] Guo, W.; Jiang, L. Sci. China Matter 2014, 57, 2.
[20] Su, B.; Guo, W.; Jiang L. Small 2015, 11, 1072.
[21] Wu, L.-Z.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Liu, W.; Chen, D.; Chen, H. Acta Biophys. Sinica 2014, 5, 360(in Chinese). (武灵芝, 刘玉棋, 刘伟, 陈栋, 陈豪, 生物物理学报, 2014, 5, 360.)
[22] Farimani, A. B.; Heiranian, M.; Min, K.; Aluru, N. R. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 1670.
[23] Freedman, K. J.; Jurgens, M.; Prabhu, A.; Ahn, C. W.; Jemth, P.; Edel, J. B.; Kim, M. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5137.
[24] Niedzwiecki, D. J.; Grazul, J.; Movileanu, L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10816.
[25] Ying, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xue, M.-Z.; Li, H.-L.; Long, Y.-T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 44(in Chinese). (应佚伦, 张星, 刘钰, 薛梦竹, 李洪林, 龙亿涛, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 44.)
[26] Ying, Y.-L.; Long, Y.-T. Sci. Chi. Chem. 2017, 60, doi:10.1007/s11426-017-9082-5.
[27] Reiner, J. E.; Balijepalli, A.; Robertson, J. W. F.; Campbell, J.; Suehle, J.; Kasianowicz, J. J. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6431.
[28] Saleh, O. A.; Sohn, L. L. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 820.
[29] Takakura, T.; Yanagi, I.; Goto, Y.; Ishige, Y.; Kohara, Y. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 123701.
[30] Alzghoul, S.; Hailat, M.; Zivanovic, S.; Que, L.; Shah, G. V. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 491.
[31] Kwak, D. K.; Chae, H.; Lee, M. K.; Ha, J. H.; Goyal, G.; Kim, M. J.; Kim, K. B.; Chi, S. W. Angew Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5713.
[32] Wang, S.; Haque, F.; Rychahou, P. G.; Evers, B. M.; Guo, P. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9814.
[33] Han, A.; Creus, M.; Schurmann, G.; Linder, V.; Ward, T. R.; de Rooij, N. F.; Staufer, U. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 4651.
[34] Freedman, K. J.; Bastian, A. R.; Chaiken, I.; Kim, M. J. Small 2013, 9, 750.
[35] Peters, T. Adv. Protein. Chem. 1985, 37, 161.
[36] Li, J. L.; Talaga, D. S. J. Phys.-Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 454.
[37] Ling, D. Y.; Ling, X. S. J. Phys.-Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 375102.
[38] Li, J. L.; Fologea, D.; Rollings, R.; Ledden, B. Protein and Peptide Letters. 2014, 21, 256.
[39] Deblois, R. W.; Bean, C. P. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1970, 41, 909.
[40] Han, A. P.; Schurmann, G.; Mondin, G.; Bitterli, R. A.; Hegelbach, N. G.; de Rooij, N. F.; Staufer, U. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 093901.
[41] Larkin, J.; Henley, R. Y.; Muthukumar, M.; Rosenstein, J. K.; Wanunu, M. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 696.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |