

不同寡聚度磺酸盐表面活性剂与支化羧酸盐混合体系的聚集行为
网络出版日期: 2018-04-03
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(No.21633002)资助.
Aggregation in the Mixture of Branched Carboxylate Salts and Sulfonate Surfactants with Different Oligomeric Degrees
Online published: 2018-04-03
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21633002).
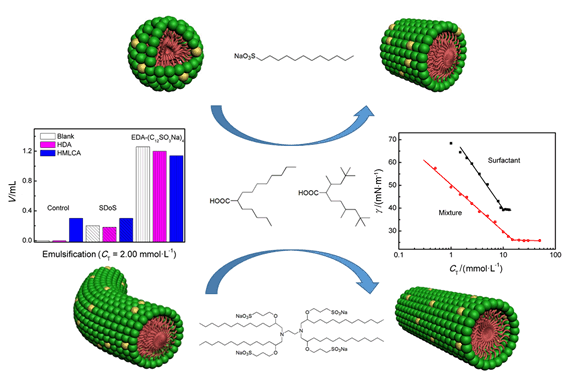
采用表面张力、Zeta电位和小角中子散射技术,研究了pH 11条件下2-己基癸酸、异硬脂酸对具有单头单链十二烷基磺酸钠(SDoS)和星状四聚磺酸盐表面活性剂EDA-(C12SO3Na)4的气液界面性质、胶束化行为和乳化性能的影响.结果表明,在气液界面和胶束中支化羧酸盐分子与磺酸盐表面活性剂间有不同程度的相互吸引作用,而且在降低表面张力效率方面具有协同作用,但胶束中分子间相互吸引作用更强的四聚磺酸盐表面活性剂混合体系在聚集体形成方面却未表现出协同作用.同时,随着羧酸盐的加入,SDoS和EDA-(C12SO3Na)4呈现出不同的聚集体转变规律,羧酸盐与SDoS的混合聚集体随着浓度增大逐渐由球形胶束转变为棒状胶束,而羧酸盐与EDA-(C12SO3Na)4的棒状胶束随着羧酸盐摩尔分数的增大而增长,随着总浓度的增大而减小.此外,在同等乳化烷烃的效果下,支化羧酸盐分子的加入可以大幅减少寡聚磺酸盐表面活性剂的使用量.
李浩飞 , 乔富林 , 范雅珣 , 王毅琳 . 不同寡聚度磺酸盐表面活性剂与支化羧酸盐混合体系的聚集行为[J]. 化学学报, 2018 , 76(7) : 564 -574 . DOI: 10.6023/A18030086
Understanding the effects of molecules with branched structures on surface activities and micellization of star-shaped oligomeric surfactants will promote the applications of oligomeric surfactants. The present work has studied the interactions and aggregation of branched carboxylate 2-hexyldecanoic acid (HDA) and 2,2,4,8,10,10-hexamethylundecane-5-carboxylic acid (HMLCA) with single chain sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDoS) and star-shaped tetrameric sulfonate surfactant (EDA-(C12SO3Na)4) in aqueous solution of pH 11 by surface tension, ζ-Potential and small angle neutron scattering (SANS). Surface tension measurements have shown that the addition of HDA or HMLCA can significantly reduce the surface tension at critical micellar concentration (CMC), meanwhile, the CMC values increase slightly as the mole fraction of HDA or HMLCA increases. The interaction parameter (β), calculated according to the non-ideal mixed solution model, indicate that different interaction degrees exist between branched carboxylate and sulfonate surfactant on surface activities and micellization. The four mixtures all exhibit synergism in surface tension reduction efficiency. The mixtures of single chain sulfonate surfactant and branched carboxylate also exhibit synergism in micelle formation, whereas the mixtures of tetrameric sulfonate surfactant and branched carboxylate do not, although the attractive interaction of HDA/EDA-(C12SO3Na)4 and HMLCA/EDA-(C12SO3Na)4 is stronger than that of HDA/SDoS and HMLCA/SDoS in mixed micelles. Taking HDA as a representative, SANS and ζ-Potential results reveal that the addition of HDA into these two sulfonate surfactants leads to different aggregate transitions in the solution. For HDA/SDoS, when the molar fraction of HDA (XHDA) is constant and the total surfactant concentration increases, spherical micelles transfer into rod-like micelles. For the HDA/EDA-(C12SO3Na)4 mixture, the rod-like micelles become shorter as XHDA increases at a fixed total surfactant concentration, while the rod-like micelles are growing longer with increasing XHDA at a fixed total surfactant concentration. This observation suggests that the branched structure of carboxylates can improve the aggregation ability of the mixed system. In addition these mixtures show excellent performance at emulsifying dodecane, and HDA or HMLCA can greatly reduce the dosage of sulfonate surfactants.

Key words: star-shaped oligomeric surfactant; SANS; surface tension; interaction; aggregate
[1] Zana, R. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 97, 205.
[2] Han, Y. C.; Fan, Y. X.; Wu, C. X.; Hou, Y. B.; Wang, Y. L. Sci. Sin. Chem. 2015, 45, 327(in Chinese). (韩玉淳, 范雅珣, 武春娴, 侯研博, 王毅琳, 中国科学:化学, 2015, 45, 327.)
[3] Yoshimura, T.; Ohno, A.; Esumi, K. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 272, 191.
[4] Yoshimura, T.; Yoshida, H.; Ohno, A.; Esumi, K. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 267, 167.
[5] In, M.; Bec, V.; Aguerre-Chariol, O.; Zana, R. Langmuir 2000, 16, 141.
[6] In, M.; Aguerre-Chariol, O.; Zana, R. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 7747.
[7] Danino, D.; Talmon, Y.; Levy, H.; Zana, R. Science 1995, 269, 1420.
[8] Esumi, K.; Taguma, K.; Koide, Y. Langmuir 1996, 12, 4039.
[9] Kastner, U.; Zana, R. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 218, 468.
[10] Zana, R.; Levy, H.; Papoutsi, D.; Beinert, G. Langmuir 1995, 11, 3694.
[11] Menger, F. M.; Migulin, V. A. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 8916.
[12] Menger, F. M.; Keiper, J. S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 1906.
[13] Laschewsky, A.; Wattebled, L.; Arotcarena, M.; Habib-Jiwan, J.; Rakotoaly, R. H. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7170.
[14] Wattebled, L.; Laschewsky, A.; Moussa, A.; Habib-Jiwan, J. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2551.
[15] Yoshimura, T.; Esumi, K. Langmuir 2003, 19, 3535.
[16] Sumida, Y.; Oki, T.; Masuyama, A.; Maekawa, H.; Nishiura, M.; Kida, T.; Nakatsuji, Y.; Ikeda, I.; Nojima, M. Langmuir 1998, 14, 7450.
[17] Hou, Y. B.; Han, Y. C.; Deng, M. L.; Xiang, J. F.; Wang, Y. L. Langmuir 2010, 26, 28.
[18] Wu, C. X.; Hou, Y. B.; Deng, M. L.; Huang, X.; Xiang, J. F.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. B.; Wang, Y. L. Langmuir 2010, 26, 7922.
[19] Fan, Y. X.; Hou, Y. B.; Xiang, J. F.; Yu, D. F.; Wu, C. X.; Tian, M. Z.; Wang, Y. L. Langmuir 2011, 27, 10570.
[20] Murguia, M. C.; Cabrera, M. I.; Guastavino, J. E.; Grau, R. J. Colloids Surf., A 2005, 262, 1.
[21] Zhou, C. C.; Wang, F. Y.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Qiao, F. L.; Liu, Z.; Hou, Y. B.; Wu, C. X.; Fan, Y. X.; Liu, L. B.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. L. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4242.
[22] Zhou, C. C.; Wang, D.; Cao, M. W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, C. X.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. L. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016, 8, 30811.
[23] Jurasin, D.; Habus, I.; Filipovic-Vincekovic, N. Colloids Surf., A 2010, 368, 119.
[24] Qiao, F. L.; Wang, M. N.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y. X.; Wang, Y. L. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 2763.
[25] Tian, M. Z.; Fan, Y. X.; Ji, G.; Wang, Y. L. Langmuir 2012, 28, 12005.
[26] Wang, T. F.; Shang, Y. Z.; Peng, C. J.; Liu, H. L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2009, 67, 1159(in Chinese). (王腾芳, 尚亚卓, 彭昌军, 刘洪来, 化学学报, 2009, 67, 1159.)
[27] Sadeghi, R.; Shahabi, S. J. Chem. Thermodynamics 2011, 43, 1361.
[28] Xu, G. Y.; Gu, Y. H.; Zeng, L. R.; Zhu, H. P.; Mao, H. Z. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 1992, 8, 352(in Chinese). (徐桂英, 顾影慧, 曾利容, 竺和平, 毛宏志, 物理化学学报, 1992, 8, 352.)
[29] Zhu, B. Y.; Zhao, G. X. Fine Chemicals 1985, 2, 1(in Chinese). (朱(王步)瑶, 赵国玺, 精细化工, 1985, 2, 1.)
[30] Vora, S.; George, A.; Desai, H.; Bahadur, P. J. Surfactants Deterg. 1999, 2, 213.
[31] Singh, O. G.; Ismail, K. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2008, 11, 89.
[32] Azum, N.; Naqvi, A. Z.; Akram, M.; Kabir-ud-Din J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 429.
[33] Xue, J. Y.; Liu, T. S.; Liu, Y. C. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 2012, 33, 599.
[34] Hayter, J. B.; Penfold, J. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1983, 261, 1022.
[35] Tanford, C. J. Phys. Chem. 1972, 76, 3020.
[36] Chen, Z. D.; Penfold, J.; Li, P. X.; Doutch, J.; Fan, Y. X.; Wang, Y. L. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 8980.
[37] Holland, P. M.; Rubingh, D. N. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 1984.
[38] Rosen, M. J.; Gao, T.; Nakatsuji, Y.; Masuyama, A. Colloids Surf., A 1994, 88, 1.
[39] Liu, L.; Rosen, M. J. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 179, 454.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |