

网络出版日期: 2018-06-06
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(Nos.51671006和61575010),北京自然科学基金(No.4162016)和北京市科学技术委员会(No.Z151100003315018)资助.
Preparation and Characterization of Black Phosphorus
Online published: 2018-06-06
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51671006 and 61575010), the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (No. 4162016), and the Science and Technology Commission of Beijing Municipality (No. Z151100003315018).
黑磷是一种具有高的载流子迁移率、高的通断比,带隙为0.3~2 eV的二维材料,对中红外、近红外新型光电器件的开发具有十分重要的意义.本文利用高能球磨法和化学气相转移法成功将红磷转化为黑磷,并进行液相剥离,得到了一层或两层的磷烯.利用X射线衍射仪、透射电子显微镜、差示扫描量热仪对其微观结构和稳定性进行了研究,并表征了化学气相转移法制备黑磷的电学性能.结果表明:高能球磨法制备的黑磷尺寸小、结晶度低,样品中有红磷存在,稳定性差.化学气相转移法制备的黑磷尺寸大、结晶度好、纯度高,且较为稳定.此方法制备的黑磷可成为剥离磷烯的优异原料,进而应用于先进微电子器件.
张丹丹 , 袁振洲 , 张国庆 , 田楠 , 刘丹敏 , 张永哲 . 黑磷的制备及表征研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018 , 76(7) : 537 -542 . DOI: 10.6023/A18040175
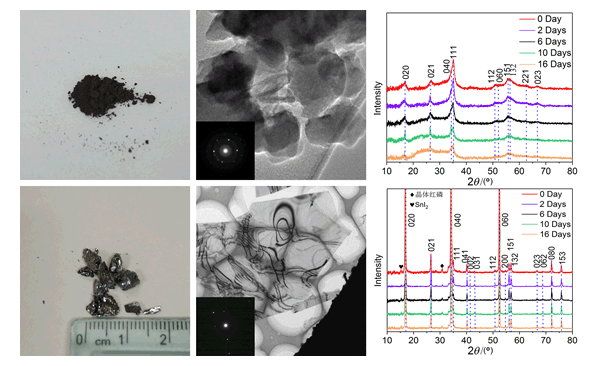
Black phosphorus has attracted broad interest because of their low-dimensional effect, and has become a new kind of two-dimensional (2D) materials. Phosphorus has several allotropes. Black phosphorus is the most thermodynamic stable in them. As a kind of two-dimensional materials, black phosphorus has high carrier mobility and on/off ratio. The band gap of black phosphorus can be adjusted by its number of layers from 0.3 to 2 eV. It is of great significance to the development of new infrared and near-infrared optoelectronic devices. Currently, the main methods for preparing black phosphorus are chemical vapor transfer and high energy ball milling methods. In this paper, black phosphorus was successfully synthesized from red phosphorus via chemical vapor transfer and high energy ball milling methods. Then black phosphorus was put in ethanol for 10 min to liquid exfoliation, in which the ultrasonic power was 400 W. The microstructures and stability of black phosphorus synthesized by two methods were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and differential scanning calorimeter (DSC). In situ electrical measurements of black phosphorus prepared by chemical vapor transfer were performed using a commercial scanning tunnelling microscope-transmission electron microscope probing system (STM-TEM, Nanofactory Instruments) inserted into a JEOL-2010F TEM. The microstructural characterization results show that there is some red phosphorus and amorphous phases in black phosphorus prepared by high energy ball milling method. On the contrary, the black phosphorus prepared by chemical vapor transfer method has no amorphous phases. The XRD results show that black phosphorus synthesized by chemical vapor transfer method did not change significantly after keeping in the air for 16 days. The DSC results show that the volatile points of the black phosphorus prepared by high energy ball milling and chemical vapor transfer methods are respectively 394.5 and 432.2℃, which means the latter has better thermal stability. The TEM results show that a layer or two layers of phosphorene via liquid exfoliation had been obtained, which is large in size and clean in surface. After being irradiated in TEM with a dose of 0.8 eV/(Å2·s) at 200 kV for 60 min, few new diffraction spots appeared in black phosphorus synthesized by chemical vapor transfer method, which indicates it is relatively stable under electron radiation in vacuum. In a word, the black phosphorus prepared by chemical vapor transfer method has large size, good crystallinity, high purity, and high stability. It can be used to prepare two-dimensional black phosphorus by mechanical exfoliation and liquid exfoliation, and then be applied to advanced microelectronic devices.

[1] Novoselov, K. S.; Geim, A. K.; Morozov, S. V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S. V.; Grigorieva, I. V.; Firsov, A. A. Science 2004, 306, 666.
[2] Susarla, S.; Manimunda, P.; Morais Jaques, Y.; Hachtel, J.; Idrobo, J. C.; Syed Amanulla, S. A.; Galvao, D. S.; Tiwary, C. S.; Ajayan, P. M. ACS Nano 2018, DOI:10. 1021/acsnano. 8b01786.
[3] Lin, X.; Wang, J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 979. (in Chinese). (林潇雨, 王璟, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 979.)
[4] Yang, L.; Fu, Q.; Wang, W.; Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, B. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10490.
[5] Tan, C.; Yu, P.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, B.; Lu, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10430.
[6] Liang, Y.; Feng, R.; Yang, S.; Ma, H.; Liang, J.; Chen, J. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 640.
[7] Yoo, J. J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Huang, J.; Meunier, V.; Sumpter, B. G.; Srivastava, A.; Conway, M.; Reddy, A. L.; Yu, J.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P. M. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 1423.
[8] Wang, X.; Zhi, L.; Müllen, K. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 323.
[9] Balandin, A. A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C. N. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902.
[10] Nair, R. R.; Blake, P.; Grigorenko, A. N.; Novoselov, K. S.; Booth, T. J.; Stauber, T.; Peres, N. M. R.; Geim, A. K. Science 2008, 320, 1308.
[11] Novoselov, K. S.; Geim, A. K.; Morozov, S. V.; Jiang, D.; Katsnelson, M. I.; Grigorieva, I. V.; Dubonos, S. V.; Firsov, A. A. Nature 2005, 438, 197.
[12] Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J. W.; Hone, J. Science 2008, 321, 385.
[13] Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y. W.; Stormer, H. L.; Kim, P. Nature 2005, 438, 201.
[14] Hu, P.; Wang, L.; Yoon, M.; Zhang, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, X.; Wen, Z.; Idrobo, J. C.; Miyamoto, Y.; Geohegan, D. B.; Xiao, K. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1649.
[15] He, X.; Liu, F.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 924(in Chinese). (何学侠, 刘富才, 曾庆圣, 刘政, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 924.)
[16] Radisavljevic, B.; Radenovic, A.; Brivio, J.; Giacometti, V.; Kis, A. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 147.
[17] Liu, S.; Huo, N.; Gan, S.; Li, Y.; Wei, Z.; Huang, B.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, H. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10974.
[18] Xia, F.; Wang, H.; Jia, Y. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4458.
[19] Li, L.; Yu, Y.; Ye, G. J.; Ge, Q.; Ou, X.; Wu, H.; Feng, D.; Chen, X. H.; Zhang, Y. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 372.
[20] Liu, H.; Neal, A. T.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Tománek, D.; Ye, P. D. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4033.
[21] Koenig, S. P.; Doganov, R. A.; Schmidt, H.; Castro Neto, A. H.; Ozyilmaz, B. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 10451.
[22] Yuan, Z.; Liu, D.; Tian, N.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 488(in Chinese). (袁振洲, 刘丹敏, 田楠, 张国庆, 张永哲, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 488.)
[23] Li, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Lu, J.; Goh, W. P.; Fang, H.; Qiu, Z.; Tian, B.; Chen, Z.; Yao, C.; Liu, W.; Yan, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Lin, M.; Su, C.; Lu, J. Chem. Mater. 2018, DOI:10. 1021/acs. chemmater. 8b00521.
[24] Zhang, Z.; Xin, X.; Yan, Q.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.-L. Sci. China Mater. 2016, 59, 122.
[25] Qiao, J.; Kong, X.; Hu, Z. X.; Yang, F.; Ji, W. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4475.
[26] Buscema, M.; Groenendijk, D. J.; Blanter, S. I.; Steele, G. A.; Zant, H. S. J.; Castellanos-Gomez, A. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3347.
[27] Bridgeman, P. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1914, 36, 1344.
[28] Krebs, H.; Weitz, H.; Worms, K. H. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1955, 280, 119.
[29] Brown, A.; Rundqvist, S. Acta Crystallogr. 1965, 19, 684.
[30] Mamoru, B.; Fukunori, I.; Yuji, T.; Akira, M. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1989, 28, 1019.
[31] Maruyama, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Tanuma, S. Physica B+C 1981, 105, 99.
[32] Park, C. M.; Sohn, H. J. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2465.
[33] Nilges, T.; Kersting, M.; Pfeifer, T. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 17071.
[34] Köpf, M.; Eckstein, N.; Pfister, D.; Grotz, C.; Krüger, I.; Greiwe, M.; Hansen, T.; Kohlmann, H.; Nilges, T. J. Cryst. Growth 2014, 405, 6.
[35] Lange, S.; Schmidt, P.; Nilges, T. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 4028.
[36] Zhao, M.; Niu, X.; Guan, L.; Qian, H.; Wang, W.; Sha, J.; Wang, Y. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 7737.
[37] Zhang, Z.; Xing, D.-H.; Li, J.; Yan, Q. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 905.
[38] Hanlon, D.; Backes, C.; Doherty, E.; Cucinotta, C. S.; Berner, N. C.; Boland, C.; Lee, K.; Harvey, A.; Lynch, P.; Gholamvand, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K.; Moynihan, G.; Pokle, A.; Ramasse, Q. M.; McEvoy, N.; Blau, W. J.; Wang, J.; Abellan, G.; Hauke, F.; Hirsch, A.; Sanvito, S.; O'Regan, D. D.; Duesberg, G. S.; Nicolosi, V.; Coleman, J. N. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8563.
[39] Yasaei, P.; Kumar, B.; Foroozan, T.; Wang, C.; Asadi, M.; Tuschel, D.; Indacochea, J. E.; Klie, R. F.; Salehi-Khojin, A. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1887.
[40] Guo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, S.; Wang, Z.; Tang, S.; Shao, J.; Sun, Z.; Xie, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, X.-F.; Chu, P. K. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 6996.
[41] Yang, Z.; Hao, J.; Yuan, S.; Lin, S.; Yau, H. M.; Dai, J.; Lau, S. P. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3748.
[42] Smith, J. B.; Hagaman, D.; Ji, H. F. J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 27, 215602.
[43] Shao, R.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Han, X. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 1409.
[44] Tian, T.; Liu, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Shao, R.; Zheng, K.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y. Mater. Lett. 2016, 183, 432.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |