

白光发射超分子水凝胶的构筑和发光性能研究
收稿日期: 2018-04-25
网络出版日期: 2018-06-21
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(Nos.21432004,21672113,21772099,21861132001 and 91527301)资助.
Construction and Luminescent Behavior of Supramolecular Hydrogel with White-Light Emission
Received date: 2018-04-25
Online published: 2018-06-21
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21432004, 21672113, 21772099, 21861132001 and 91527301).
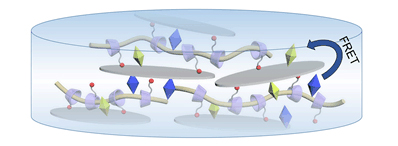
具有白光发射性质且发光可调的超分子水凝胶在发光材料和荧光检测领域具有广泛的应用前景.采用双(2-氨基丙基醚)聚丙二醇(PPG-NH2)链穿线带有正电荷的6-乙二胺修饰β-环糊精构成准轮烷,进而与锂皂石作用构筑了超分子水凝胶,并通过流变、zeta电势和扫描电镜等手段对凝胶性质进行了表征.当将扭曲分子内电荷转移(TICT)型的有机染料分子硫黄素T(ThT)和碘化4-[4-(二甲基氨基)苯乙烯基]-1-甲基吡啶鎓(DASPI)引入到水凝胶中,这两种有机染料能够在凝胶相中发生荧光共振能量转移(FRET),从而产生包括白光在内的不同颜色的荧光发射.本研究为水基超分子发光软材料提供了一种新的构筑方法.
张依 , 陈湧 , 李晶晶 , 梁璐 , 刘育 . 白光发射超分子水凝胶的构筑和发光性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018 , 76(8) : 622 -626 . DOI: 10.6023/A18040171
Color-tunable luminescent supramolecular hydrogel with white-light emission is widely applied in the fields of light-emitting materials and fluorescence sensors due to their good physicochemical and biochemical properties. Using β-cyclodextrin, a class of cyclic oligosaccharide with seven D-glucose units linked by α-1,4-glucose bonds, and laponite as staring materials, we herein developed a photo-luminescent supramolecular hydrogel from laponite and pseudorotaxane that was constructed by the threading of ethylenediamine-modified β-cyclodextrins onto the poly(propylene glycol) bis(2-amiono-propylether) (PPG-NH2) chain. The supramolecular hydrogel properties thus obtained were characterized by rheological experiments, zeta potential measurements and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results showed that the supramolecular hydrogel possessed satisfactory mechanical properties, negative charges and porous three-dimensional structure. Then, thioflavin T (ThT) and 4-(4-dimethylaminostyryl)-1-methylpyridinium (DASPI), two typical distorted intramolecular charge transfer (TICT) molecules with dramatically increased fluorescence when the molecules are in confined region, were selected as model substrates. Generally, ThT and DASPI had almost no fluorescent emission at an excitation wavelength of 412 nm. By comparing the normalized fluorescence emission spectrum of ThT and the UV-visible absorption spectrum of DASPI, we found that the UV-Vis absorption band of DASPI showed a good overlap with the fluorescence emission band of ThT. Therefore, the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) process would occur between ThT and DASPI in the laponite/pseudorotaxane supermolecular hydrogel phase, where ThT acted as an energy donor and DASPI acted as an energy receptor. Then the fluorescence behavior of ThT/DASPI pairs in the supramolecular hydrogel phase was investigated. The results showed, after two TICT dyes, ThT and DASPI, were introduced in the hydrogel, the efficient FRET between ThT and DASPI led to the different emission colors including white light through adjusting the ratios of dyes. The convenient preparation and tunable luminescent behaviors of this supramolecular hydrogel will open a new practical path for water-based functional soft materials.

[1] Rao, K. V.; Datta, K. K. R.; Eswaramoorthy, M.; George, S. J. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1713.
[2] Vijayakumar, C.; Praveen, V. K.; Ajayaghosh, A. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2059.
[3] Zhao, Z. J.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Z. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 4564.
[4] Abbel, R.; van der Weegen, R.; Pisula, W.; Surin, M.; Leclere, P. Lazzaroni, R.; Meijer, E. W.; Schenning, A. P. H. J. Chem.-Eur. J. 2009, 15, 9737.
[5] Chen, Z.-L.; Li, H.-L.; Wei, J.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, H.-B. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 35, 789. (陈忠林, 李红玲, 韦驾, 肖义, 于海波, 有机化学, 2015, 35, 789.)
[6] Ikeda, M.; Yoshii, T.; Matsui, T.; Tanida, T.; Komatsu, H.; Hamachi, I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1670.
[7] Cai, Z. Y.; Kwak, D. H.; Punihaole, D.; Hong, Z. M.; Velankar, S. S.; Liu, X. Y.; Asher, S. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13036.
[8] Ji, X. F.; Yao, Y.; Li, J. Y.; Yan, X. Z.; Huang, F. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 74.
[9] Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, S. H.; Liu, Y. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 200.
[10] Zhao, T.; Ding, H.-L.; Shi, G.-Y.; Jin, L.-T. Acta Chim. Sinica 2008, 66, 1209. (赵婷, 丁洪流, 施国跃, 金利通, 化学学报, 2008, 66, 1209.)
[11] Yu, G. C.; Yan, X. Z.; Han, C. Y.; Huang, F. H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6697.
[12] Tang, L.; Liu, W. G.; Liu, G. P. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2652.
[13] Cordier, P.; Tournilhac, F.; Soulie-Ziakovic, C.; Leibler, L. Nature 2008, 451, 977.
[14] Dai, X. Y.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Gao, L. N.; Bai, T.; Wang, W.; Cui, Y. L.; Liu, W. G. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3566.
[15] Wang, H. Y.; Heilshorn, S. C. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3717.
[16] Nakahata, M.; Mori, S.; Takashima, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Harada, A. Chem 2016, 1, 766.
[17] Ji, X. F.; Shi, B. B.; Wang, H.; Xia, D. Y.; Jie, K. C.; Wu, Z. L.; Huang, F. H. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 8062.
[18] Sutar, P.; Suresh, V. M.; Maji, T. K. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9876.
[19] Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 84.
[20] Praveen, V. K.; Ranjith, C.; Armaroli, N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 365.
[21] Yang, H.-W.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Li, Y.-J.; Wang, J.-X.; Li, X.-M.; Song, J.; Zhang, B.; Feng, Y.-Q. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 37, 1991. (杨贺玮, 张宇哲, 李艳杰, 王京翔, 李小萌, 宋健, 张宝, 冯亚青, 有机化学, 2017, 37, 1991.)
[22] Labanda, J.; Sabate, J.; Llorens, J. Colloids Surf., A 2007, 301, 8.
[23] Wang, Q. G.; Mynar, J. L.; Yoshida, M.; Lee, E.; Lee, M.; Okuro, K.; Kinbara, K. I.; Aida, T. Nature 2010, 463, 339.
[24] Li, Z. Q.; Zhang, Y. M.; Wang, H. Y.; Li, H. R.; Liu, Y. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 1141.
[25] Zhang, Y. M.; Zhang, X. J.; Xu, X. F.; Fu, X. N.; Hou, H. B.; Liu, Y. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 3932.
[26] Khan, A. R.; Forgo, P.; Stine, K. J.; D'Souza, V. T. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1977.
[27] Liu, G. X.; Zhang, Y. M.; Xu, X. F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1700149.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |