

铑和手性螺环磷酸协同催化α-芳基重氮酮对醇的O—H键的不对称插入反应
收稿日期: 2018-06-15
网络出版日期: 2018-08-14
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(Nos.21625204,21532003,21421062)、教育部“111”创新引智计划(No.B06005)、国家万人计划和中央高校基本科研业务费资助.
Enantioselective O-H Bond Insertion of α-Diazoketones with Alcohols Cooperatively Catalyzed by Achiral Dirhodium Complexes and Chiral Spiro Phosphoric Acids
Received date: 2018-06-15
Online published: 2018-08-14
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21625204, 21532003, 21421062), the "111" Project of the Ministry of Education of China (No. B06005), the National Program for Special Support of Eminent Professionals and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
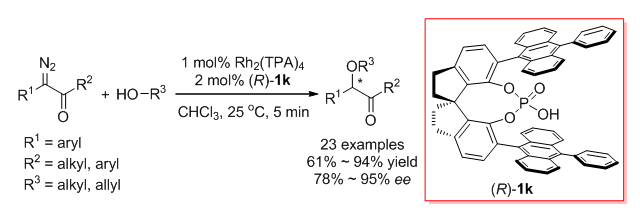
过渡金属催化卡宾对O-H键的不对称插入反应是合成手性醇及其衍生物的直接方法.近年来,人们发展了多种手性催化剂实现了重氮酯衍生的金属卡宾对醇、酚、羧酸甚至水的O-H键的高对映选择性插入反应,但是重氮酮作为卡宾前体的不对称O-H键插入反应鲜有成功的例子.以非手性双铑络合物和手性螺环磷酸组成的协同催化体系,首次实现了α-重氮酮对醇的O-H键的不对称插入反应,获得了较高的收率和高达95%ee的对映选择性.反应为手性α-烷氧基酮这类重要手性化合物提供了高效的合成方法.还通过密度泛函理论计算,对反应机理进行了初步研究,发现水很可能参与了手性磷酸促进的烯醇中间体质子转移过程.
李茂霖 , 陈梦青 , 徐彬 , 朱守非 , 周其林 . 铑和手性螺环磷酸协同催化α-芳基重氮酮对醇的O—H键的不对称插入反应[J]. 化学学报, 2018 , 76(11) : 883 -889 . DOI: 10.6023/A18060234
Transition-metal-catalyzed asymmetric insertion of carbene into O-H bonds is a straightforward method for the synthesis of chiral alcohols and their derivatives. In recent years, a variety of chiral catalysts have been developed to achieve high enantioselective insertions of metal carbenes derived from α-diazoesters into O-H bonds of alcohols, phenols, carboxylic acids, and even water. However, there are few successful examples of the asymmetric O-H bond insertion using α-diazoketones as carbene precursors. In this paper, we report the first asymmetric O-H insertion of α-diazoketones with alcohols co-catalyzed by achiral dirhodium complexes and chiral spiro phosphoric acids. The reaction has high yields and high enantioselectivity (up to 95% ee). The present O-H bond insertion reaction provides an efficient method for the synthesis of very useful chiral α-alkoxy ketones, which are easily transformed to corresponding 1,2-diol derivatives with excellent diastereoselectivity. The density functional theory (DFT) calculation was performed to study the mechanism of the reaction. It is found that the chiral spiro phosphoric acid can promote the proton transfer process of enol intermediates generated from rhodium carbene and alcohol like chiral proton-transfer shuttle and realize enantioselectivity control accordingly. Water are likely to participate in this proton transfer step and has a remarkable effect on the enantiocontrol of the reaction. A typical procedure for the enantioselective O-H bond insertion of α-diazoketones is as follows. Powered Rh2(TPA)4 (2.9 mg, 0.002 mmol, 1 mol%) and chiral spiro phosphoric acid (R)-1k (3.3 mg, 0.004 mmol, 2 mol%) were introduced into an oven-dried Schlenk tube in an argon-filled glovebox. After CHCl3 (2 mL) was injected into the Schlenk tube, the solution was stirred at 25℃ under the argon atmosphere. A solution of benzyl alcohol (21.6 mg, 0.2 mmol) and 1-diazo-1-phenylpropan-2-one (2a, 33.8 mg, 0.21 mmol) in 1 mL of CHCl3 were then introduced into the Schlenk tube containing catalysts. The resulting mixture was stirred at 25℃ until the diazo compound 2a disappeared. After concentration in vacuo, the residue was purified by flash chromatography on silica gel (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate, V:V=15:1) to give (-)-1-(benzyloxy)-1-phenyl-propan-2-one (4a, 43.2 mg, 0.18 mmol, 90% yield) as a colorless oil.

[1] (a) Boger, D. L. Modern Organic Synthesis:Lecture Notes, TSRI Press, La Jolla, CA, 1999.
(b) Paquette, L. A. Chiral Reagents for Asymmetric Synthesis, Wiley, Columbus, OH, USA, 2003.
(b) Wang, Z.-H.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Liu, Y.-G.; Zhang, W.-B. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 447. (王志惠, 张振锋, 刘燕刚, 张万斌, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 447.)
(c) Zhang, Z.-J.; Tao, Z.-L.; Arafate, A.; Gong, L.-Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 1196. (张子競, 陶忠林, 阿拉法特·阿地力, 龚流柱, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 1196.)
[2] For selected reviews, see:(a) Ye, T.; Mckervey, M. A. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 1091.
(b) Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, J.-B. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 6577.
(c) Zhu, S.-F.; Zhou, Q.-L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1365.
(d) Fei, N.; Gillingham, D. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4918.
(e) Zhu, S.-F.; Zhou, Q.-L. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 580.
(f) Maguire, A. R.; McKervey, M. A. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9981.
[3] For selected examples, see:(a) Maier, T. C.; Fu, G. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 4594.
(b) Chen, C.; Zhu, S.-F.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.-X.; Zhou, Q.-L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12616.
(c) Zhu, S.-F.; Chen, C.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, Q.-L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 932.
(d) Zhu, S.-F.; Song, X.-G.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, Q.-L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 16374.
(e) Zhu, S.-F.; Cai, Y.; Mao, H.-X.; Xie, J.-H.; Zhou, Q.-L. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 546.
(f) Osako, T.; Panichakul, D.; Uozumi, Y. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 194.
(g) Song, X.-G.; Zhu, S.-F.; Xie, X.-L.; Zhou, Q.-L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2555.
(h) Xie, X.-L.; Zhu, S.-F.; Guo, J.-X.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, Q.-L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2978.
(i) Tan, F.; Liu, X.-H.; Hao, X.-Y.; Tang, Y.; Lin, L.-L.; Feng, X.-M. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 6930.
(j) Zhang, Y.-L.; Yao, Y.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2017, 359, 2754.
(k) Huang, D.-R.; Xu, G.-Y.; Peng, S.-Y.; Sun, J.-T. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3197.
[4] For preparation and applications of α-diazoketones in catalytic asymmetric reactions, see:(a) Doyle, M. P.; McKervey, M. A.; Ye, T. Modern Catalytic Methods for Organic Synthesis with Diazo Compounds, Wiley, New York, 1998.
(b) Doyle, M. P.; Eismont, M. Y.; Zhou, Q.-L. Russ. Chem. Bull. 1997, 46, 955.
(c) Kitagaki, S.; Anada, M.; Kataoka, O.; Matsuno, K.; Umeda, C.; Watanabe, N.; Hashimoto, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 1417.
(d) Barberis, M.; Pérez-Prieto, J.; Stiriba, S.-E.; Lahuerta, P. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3317.
(e) Hwang, C. H.; Chong, Y. H.; Song, S. Y.; Kwak, H. S.; Lee, E. Chem. Commun. 2004, 816.
(f) Suga, H.; Ishimoto, D.; Higuchi, S.; Ohtsuka, M.; Arikawa, T.; Tsuchida, T.; Kakehi, A.; Baba, T. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 4359.
(g) Taber, D. F.; Tian, W. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 7560.
(h) Denton, J. R.; Davies, H. M. L. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 787.
(i) Xu, X.; Qian, Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, W. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 797.
(j) Qian, Y.; Jing, C.; Liu, S.; Hu, W. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2700.
(k) Taber, D. F.; Paquette, C. M.; Gu, P.; Tian, W. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 9772.
[5] For non-enantioselective O-H insertion using α-diazoketones as carbene precursors, see:(a) Yates, P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 5376.
(b) Shinada, T.; Kawakami, T.; Sakai, H.; Takada, I.; Ohfune, Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 3757.
(c) Nelson, T. D.; Song, Z. J.; Thompson, A. S.; Zhao, M.; DeMarco, A.; Reamer, R. A.; Huntington, M. F.; Grabowsk, E. J.; Reider, P. J. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 1877.
(d) Muthusamy, S.; Babu, S. A.; Gunanathan, C. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 3133.
(e) Ronan, B.; Bacqué, E.; Barrière, J. C. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 3819.
(f) Muthusamy, S.; Gnanaprakasam, B.; Suresh, E. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 4577.
(g) Jung, J. C.; Avery, M. A. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 7969.
[6] For a review, see:(a) Ren, Y.-Y.; Zhu, S.-F.; Zhou, Q.-L. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 3087. For selected examples, see:
(b) Xu, B.; Zhu, S.-F.; Xie, X.-L.; Shen, J.-J.; Zhou, Q.-L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11483.
(c) Xu, B.; Zhu, S.-F.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Yu, Z.-X.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Q.-L. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1442.
(d) Xu, B.; Zhu, S.-F.; Zuo, X.-D.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Zhou, Q.-L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3913.
(e) Xu, B.; Li, M.-L.; Zuo, X.-D.; Zhu, S.-F.; Zhou, Q.-L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8700.
(f) Guo, J.-X.; Zhou, T.; Xu, B.; Zhu, S.-F.; Zhou, Q.-L. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1104. For selected reviews on cooperative catalysis, see:
(g) Zhou, J. Chem.-Asian J. 2010, 5, 422.
(h) Zhong, C.; Shi, X.-D. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2999.
(i) Allen, A. E.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 633.
(j) Du, Z.; Shao, Z. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1337.
(k) Wu, X.; Li, M.-L.; Gong, L.-Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 1091. (吴祥, 李明丽, 龚流柱, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 1091.)
(l) Chen, D.-F.; Han, Z.-Y.; Zhou, X.-L.; Gong, L.-Z. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2365.
[7] For highly enantioselective insertion reactions of α-diazoketones with other heteroatom-hydrogen bonds, see:(a) Ge, M.; Corey, E. J. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 2319.
(b) Cheng, Q.-Q.; Xu, H.; Zhu, S.-F.; Zhou, Q.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 326. (程清卿, 许唤, 朱守非, 周其林, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 326.)
(c) Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Qi, W.-Y.; Xu, B.; Xu, M.-H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5268.
[8] Franklin, A. D.; Haque, M. S.; Robert, M. P. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 2021.
[9] Yin, J.-J.; Mark, A. H.; Karen, M. C.; Joseph, D. A. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 840.
[10] For details of DFT calculation, see supporting information and relevant literature ref. 6c.
[11] Liang, Y.; Zhou, H.-L.; Yu, Z.-X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17783.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |