

微纳结构超疏水表面的浸润性分析及设计
收稿日期: 2018-10-16
网络出版日期: 2018-12-03
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(Nos.11672024,11372026)和国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(No.2015CB755803)资助.
Wettability Analysis and Design of Micro-nanostructured Superhydrophobic Surface
Received date: 2018-10-16
Online published: 2018-12-03
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11672024, 11372026) and National Basic Research Program of China (Grants No. 2015CB755803).
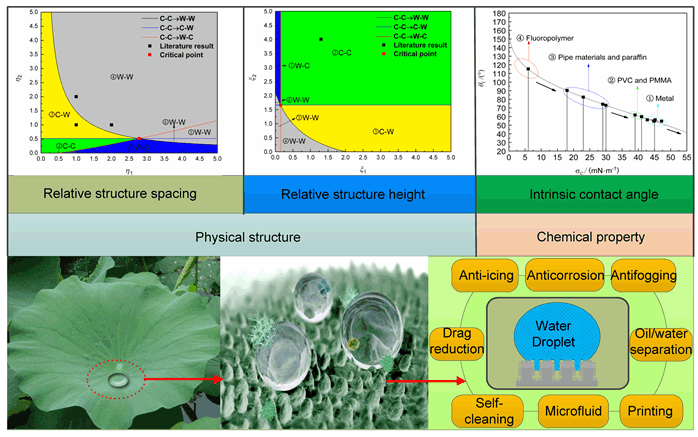
微纳复合结构超疏水表面在防污、流动减阻、防冰等领域具有广阔的应用前景,超疏水表面主要通过设计表面化学性质和微观几何结构来获得.合理设计保持表面润湿态的稳定性是其性能发挥的关键.以"液滴-超疏水表面"系统为研究对象,基于最小能原理分析了四种稳定润湿形态,指出影响润湿状态的本征接触角和微观结构参数(相对柱距、相对柱高).推导了本征接触角的计算公式并对常见材料的本征接触角进行了讨论.结合四种润湿态方程,绘制了随着相对柱距和相对柱高的润湿云图,并将润湿云图归纳为"一点三线六区四状态".分析了相对柱距和相对柱高对浸润状态的影响,结果表明较大的本征接触角、较小的相对柱距和较大的相对柱高能够减小浸润状态发生转变的临界参数,从而拓展超疏水表面的区域范围,有利于超疏水表面的稳定性.利用文献数据验证了上述润湿云图能够准确反映出润湿形态.在上述工作基础之上总结提炼了超疏水表面设计的一般思路.研究结果可为超疏水表面的设计提供理论依据和技术基础.
马国佳 , 郑海坤 , 常士楠 , 王硕硕 . 微纳结构超疏水表面的浸润性分析及设计[J]. 化学学报, 2019 , 77(3) : 269 -277 . DOI: 10.6023/A18100430
The special wettability of superhydrophobic surface usually has high contact angles (CA>150°) and low contact angle hysteresis (CAH<5°), which has been exploited for many potential applications. It is well known that wettability is mainly determined by micro/nano structure and surface composition, and various types of natural superhydrophobic surface could exhibit different wetting states, showing different wetting properties, such as low adhesive lotus leaf; the anisotropic superhydrophobic rice leaf; high adhesive rose petal. Therefore, the relationship between the wetting state and the surface structure should have a deeper understanding, especially in the design preliminary stage. The "droplet-superhydrophobic surface" system is taken as the research objects, four stable wetting state expressions are analyzed based on the principle of minimum energy. Wetting state transitions are studied on superhydrophobic surface coverd with micro/nano structured pillars of different distributions. The calculation formula of intrinsic contact angle is derived and the intrinsic contact angle of common materials is investigated. Based on the four wetting state of apparent contact angle equations, wetting diagrams were drew for investigating the wetting behavior, which include "one point, three lines, six areas, four state". The influence of the relative structure spacing and relative structure height on the wetting state is analyzed. It is found that the larger relative structure height, the smaller relative structure spacing, which can reduce the critical parameters of the transition state of the infiltration state, thereby expanding the range of the superhydrophobic surface, the more design options are available. It is also beneficial to the stability of the superhydrophobic surface, but should be controlled within certain scales because of mechanical stability. The simulation results accurately reflect the wetting state with the changes of the relative structure spacing and relative structure height. Finally, the general design of the superhydrophobic surface is refined. The results can provide theoretical guidance and technical fundament for the design of superhydrophobic surfaces.

[1] Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Planta 1997, 202, 1.
[2] Marmur, A. Langmuir 2003, 19, 5956.
[3] Zheng, H. K.; Chang, S. N.; Zhao, Y. Y. Prog. Chem. 2017, 29, 102. (郑海坤, 常士楠, 赵媛媛, 化学进展, 2017, 29, 102.)
[4] Kreder, M. J.; Alvarenga, J.; Kim, P.; Aizenberg, J. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 15003.
[5] Liang, W. X.; Zhang, Y. B.; Wang, B.; Guo, Z. G.; Liu, W. M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 2393(梁伟欣, 张亚斌, 王奔, 郭志光, 刘维民, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 2393.)
[6] Zhang, J. N.; Yu, J. H. Chin. J. Chem. 2018, 36, 51.
[7] Cui, L. Y.; Fan, S. S.; Yu, C. L.; Kuang, M. X.; Wang, J. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 967. (崔丽影, 范莎莎, 于存龙, 邝旻翾, 王京霞, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 967.)
[8] Wenzel, R. N. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988.
[9] Cassie, A. B. D.; Baxter, S. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546.
[10] Bico, J.; Tiele, U.; Quere, D. Colloid Surface A 2002, 206, 41.
[11] Bhushan, B.; Nosonovsky, M. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 4713.
[12] Suzuki, S.; Ueno, K. Langmuir 2017, 33, 138.
[13] Hejazi, V.; Nosonovsky, M. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 329.
[14] Tuvshindorj, U.; Yildirim, A.; Ozturk, F. E.; Bayindir, M. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 9680.
[15] Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3423.
[16] Rahmawan, Y.; Moon, M. W.; Kim, K. S. Langmuir 2009, 26, 484.
[17] Wu, B. B.; Wu, H. P.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, C. C.; Chai, G. Z. Acta Phys. Sin. 2015, 64, 176801. (吴兵兵, 吴化平, 张征, 董晨晨, 柴国钟, 物理学报, 2015, 64, 176801.)
[18] Lv, P. Y.; Xue, Y. H.; Duan, H. L. Adv. Mech. 2016, 46, 179. (吕鹏宇, 薛亚辉, 段慧玲, 力学进展, 2016, 46, 179.)
[19] Moosmann, M.; Schimmel, T.; Barthlott, W.; Mail, M. Beilstein J. Nanotech. 2017, 8, 1671.
[20] Seo, J.; García-Mayoral, R.; Mani, A. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 8, 35.
[21] Lafuma, A.; Queré, D. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 457.
[22] Ye, X. M.; Zhang, X. S.; Li, M. L.; Li, C. X. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 67, 114702. (叶学民, 张湘珊, 李明兰, 李春曦, 物理学报, 2018, 67, 114702.)
[23] Kwon, H. M.; Paxson, A. T.; Varanasi, K. K.; Patankar, N. A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 036102.
[24] Bartolo, D.; Bouamrirene, F.; Verneuil, É.; Buguin, A.; Silberzan, P.; Moulinet, S. EPL 2006, 74, 299.
[25] Bormashenko, E.; Pogreb, R.; Whyman, G.; Erlich, G. Langmuir 2007, 23, 12217.
[26] Girifalco, L. A.; Good, R. J. J. Phys. Chem. 1957, 61, 904.
[27] Zisman, W. A. Adv. Chem. 1964, 43, 1.
[28] Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C.; Cutler, D.; Ditsch, F.; Meusel, I.; Theisen, I. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1998, 126, 237.
[29] Nishino, T.; Meguro, M.; Nakamae, K. Langmuir 1999, 15, 4321.
[30] Han, J. T.; Sun, Y. K.; Woo, J. S.; Lee, G. W. Adv. Mater. 2010, 20, 3724.
[31] Raza, M. A.; Kooij, E. S.; Silfhout, A. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12962.
[32] Liu, X.; Dai, B.; Zhou, L.; Sun, J. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 497.
[33] Dong, J.; Jin, Y.; Dong, H.; Sun, L. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1041.
[34] Guan, Z. S.; Zhang, Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2005, 63, 880. (管自生, 张强, 化学学报, 2005, 63, 880.)
[35] Kulinich, S. A.; Farhadi, S.; Nose, K. Langmuir 2011, 27, 25.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |