

双金属MOF-74-CoMn催化剂的制备及其CO选择性催化还原技术应用
收稿日期: 2019-04-11
网络出版日期: 2019-07-08
基金资助
国家自然科学基金面上资助项目(No.21677022).
Synthesis of Bimetallic MOF-74-CoMn Catalyst and Its Application in Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with CO
Received date: 2019-04-11
Online published: 2019-07-08
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21677022).
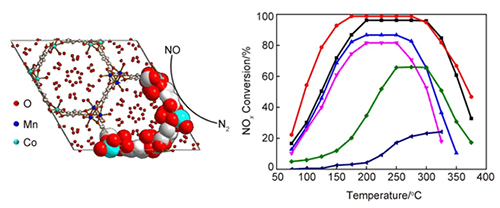
采用水热法成功地合成了不同比例的双金属MOF-74-CoMn催化剂,并成功用于以CO为还原剂的选择性催化还原脱硝(CO-SCR)反应.实验结果表明,双金属MOF-74-CoMn催化剂的NOx转化率普遍高于单金属MOF-74-Co催化剂,且反应温度窗口更宽,其中,MOF-74-Co1Mn2的NOx转化率最高,在175~275 ℃的温度范围内接近100%.进而,通过X射线粉末衍射(XRD),热重分析(TGA),扫描电镜(SEM),N2吸附/脱附,X-射线光电子光谱(XPS),氢气程序升温还原性能测试(H2-TPR)和原位红外光谱(FTIR)技术对双金属MOF-74-CoMn催化剂进行了表征和分析,发现金属Co、Mn的协同作用可以促进不饱和金属位点和氧空位的形成,从而提高CO选择性催化还原反应(CO-SCR)的效率.
武卓敏 , 石勇 , 李春艳 , 牛丹阳 , 楚奇 , 熊巍 , 李新勇 . 双金属MOF-74-CoMn催化剂的制备及其CO选择性催化还原技术应用[J]. 化学学报, 2019 , 77(8) : 758 -764 . DOI: 10.6023/A19040129
A series of bimetallic MOF-74-CoMn catalysts with different metal ratios have been successfully synthesized by hydrothermal method and applied in selective catalytic reduction of NO with CO (CO-SCR). The experimental procedure for the preparation of MOF-74-CoMn catalyst is as follows:The reaction solution was a 3.28 mmol mixture of Co(NO3)2·6H2O and Mn(NO3)2·6H2O, 1.09 mmol 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (H4DOBDC) and 90 mL ethanol-DMF-water. The molar ratio of mixture (Co/Mn) was 1:0, 1:1, 1:2, 1:4, 1:6, respectively. The reactant solution was ultrasonically stired for 30 min until homogeneous. Then, the mixture was transferred into a 100 mL Teflon autoclave then kept in an oven at 100℃ for 24 h. Finally, after purified with DMF and methanol, the products were dried in a vacuum oven at 80℃ for 24 h to obtain a purple MOF-74-CoMn catalyst, which were stored in vacuum or an inert atmosphere. The prepared sample is referred to as MOF-74-Co1Mnx, where x represents a molar ratio of Co to Mn is 1:x (x=0, 1, 2, 4, 6). The SCR catalytic activities were carried out in a fixed-bed flow reactor in gas stream. The experimental results show that the NOx conversion rate of bimetallic MOF-74-CoMn catalyst is generally higher than that of single metal MOF-74-Co catalyst, and their reaction temperature window is wider. Especially, MOF-74-Co1Mn2 exhibited the highest selective catalytic reduction of NO with CO (CO-SCR) performance which is close to 100% with a temperature range from 175 to 275℃. Further, the bimetallic MOFs catalysts were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), N2 adsorption/desorption, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Hydrogen-temperature programed reduction (H2-TPR) and Infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) techniques. The results showed that the synergistic effect between Co and Mn metals could obviously promote the formation of unsaturated metal sites and oxygen vacancies, thereby promoting their catalytic reduction efficiency of selective catalytic reduction of NO with CO (CO-SCR).

[1] Qu, Y.; An, J. L.; He, Y. J.; Zheng, J. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 44, 13.
[2] Saikawa, E.; Kim, H.; Zhong, M.; Avramov, A.; Zhao, Y.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Kurokawa, J.; Klimont, Z.; Wagner, F.; Naik, V.; Horowitz, L. W.; Zhang, Q. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6393.
[3] Hamada, H.; Hanedab, M. Appl. Catal. A 2012, 421, 1.
[4] Skalska, K.; Miller, J. S.; Ledakowicz, S. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3976.
[5] Liu, T. K.; Qian, J. N.; Yao, Y. Y.; Shi, Z. F.; Han, L. Y.; Liang, C. Y.; Li, B.; Dong, L. H.; Fan, M. G.; Zhang, L. L. J. Mol. Catal. A:Chem. 2017, 430, 43.
[6] Li, S. S; Wang, F. Z. R.; Liu, Y. M.; Cao, Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2017, 35, 591.
[7] Shin, H. U.; Lolla, D.; Nikolov, Z.; Chase, G. G. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 91.
[8] Liu, J.; Li, X. Y.; Zhao, Q. D.; Ke, J.; Xiao, H. N.; Lv, X. J.; Liu, S. M.; Tadéc, M.; Wang, S. B. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 200, 297.
[9] Lee, Y. R.; Kim, J.; Ahn, W. S. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 1667.
[10] Wang, J. H.; Zhao, H. W.; Haller, G.; Li, Y. D. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 202, 346.
[11] Cai, S. X.; Liu, J.; Zha, K. W.; Li, H. R.; Shi, L. Y.; Zhang, D. S. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 5648.
[12] Shi, Y.; Tang, X. L.; Yi, H. L.; Gao, F. Y.; Zhao, S. Z.; Wang, J. G.; Yang, K.; Zhang, R. C. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 3606.
[13] Shen, Q.; Zhang, L. Y.; Sun, N. N.; Wang, H.; Zhong, L. S.; He, C.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. H. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 46.
[14] Cheng, X. X.; Bi, X. T. Particuology 2014, 16, 1.
[15] Dai, X. X.; Jiang, W. Y.; Wang, W. L.; Weng, X, L.; Shang, Y.; Xue, Y. H.; Wu, Z. B. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 728.
[16] Zhang, L.; Shi L. Y.; Huang L.; Zhang, J. P.; Gao, R. H.; Zhang, D. S. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1753.
[17] Liu, Z. Z.; Shi, Y.; Li, C. Y.; Zhao, Q. D.; Li, X. Y. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2015, 31, 9. (刘震震, 石勇, 李春艳, 肇启东, 李新勇, 物理化学学报, 2015, 31, 9.)
[18] Huang, G.; Chen, Y. Z.; Jiang, H. L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 113. (黄刚, 陈玉贞, 江海龙, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 113.)
[19] Xiao, J. D.; Jiang, H. L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 356.
[20] Jiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H. L.; Xu, Q. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703663.
[21] Adhikari, A. K.; Lin, K. S. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1348.
[22] Yan, L. T.; Dai, P. C.; Wang, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, L. J.; Cao, L.; Zhao, X. B. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11642.
[23] Sun, D. R.; Ye, L.; Sun, F. X.; García, H.; Li, Z. H. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 5203.
[24] Pliekhov, O.; Pliekhova, O.; Lavrencic štangar, U.; Logar, N. Z. Catal. Commun. 2018, 110, 88.
[25] Jiang, H. X.; Niu, Y.; Wang, Q. Y.; Chen, Y. F.; Zhang, M. H. Catal. Commun. 2018, 113, 46.
[26] Chen, S.; Xue, M.; Li, Y. Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, L. K.; Qiu, S. L. J. Mater. Chem. 2015, 3, 20145.
[27] Liu, T. K.; Yao, Y. Y.; Wei, L. Q.; Shi, Z. F.; Han, L. Y.; Yuan, H. X.; Li, B.; Dong, L. H.; Wang, F.; Sun, C. Z. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 12757.
[28] Kim, S. H.; Lee, Y. J.; Kim, D. H.; Lee, Y. J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 660.
[29] Nguyen, H. T. T.; Doan, D. N. A.; Truong, T. J. Mol. Catal. A:Chem. 2017, 426, 141.
[30] Liu, K. J.; Yu, Q. B.; Liu, J. L.; Wang, K.; Han, Z. C.; Xuan, Y. N.; Qin, Q. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 13993.
[31] Hu, H.; Cai, S. X.; Li, H. R.; Huang, L.; Shi, L. Y.; Zhang, D. S. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6069.
[32] Qin, Y. L.; Huang, L.; Zheng, J. X.; Ren, Q. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2016, 72, 78.
[33] Gao, F. Y.; Tang, X. L.; Yi, H. H.; Li, J. Y.; Zhao, S. Z.; Wang, J. G.; Chu, C.; Li, C. L. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 20.
[34] Dietzel, P. D. C.; Morita, Y.; Blom, R.; Fjellvag, H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6354.
[35] Yan, L. T.; Cao, L.; Dai, P. C.; Gu, X.; Liu, D. D.; Li, L. J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. B. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1703455.
[36] Jiang, H. X.; Wang, Q. Y.; Wang, H. Q.; Chen, Y. F.; Zhang, M. H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26817.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |